Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge
| Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Revolutionary War | |||||||
 Reconstructed earthworks at Moores Creek National Battlefield | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 1,050 militia[1] |
Start of march: 1,400–1,600[2][3] Battle: 900–1,000[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1 killed 1 wounded[1] |
50 killed or wounded 850 captured[1] | ||||||
Location in North Carolina | |||||||
The Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge was a minor conflict of the American Revolutionary War fought near Wilmington (present-day Pender County), North Carolina, on February 27, 1776. The victory of the North Carolina Provincial Congress' militia force over British governor Josiah Martin's and Tristan Worsley's reinforcements at Moore's was a turning point in the war; American independence was declared less than five months later.
Loyalist recruitment efforts in the interior of North Carolina began in earnest with news of the Battles of Lexington and Concord, and patriots in the province also began organizing for the Continental Army and militia. When word arrived in January 1776 of a planned British Army expedition to the area, Martin ordered his militia to muster in anticipation of their arrival. Revolutionary militia and Continental units mobilized to prevent the junction, blockading several routes until the poorly armed loyalists were forced to confront them at Moore's Creek Bridge, about 18 miles (29 km) north of Wilmington.
In a brief early-morning engagement, a charge across the bridge by sword-wielding loyalists was met by a barrage of musket and artillery fire. Two loyalist leaders were killed, another captured, and the whole force was scattered. In the following days, many loyalists were arrested, damaging further recruiting efforts. North Carolina was not militarily threatened again until 1780, and memories of the battle and its aftermath negated efforts by Charles Cornwallis to recruit loyalists in the area in 1781.
Background
[edit]British recruiting
[edit]In early 1775, with political and military tensions rising in the Thirteen Colonies, North Carolina's royal governor, Josiah Martin, hoped to combine the recruiting of Scots Gaels in the North Carolina interior with that of sympathetic former Regulators (a group originally opposed to corrupt colonial administration) and disaffected loyalists in the coastal areas to build a large loyalist force to counteract patriot sympathies in the province.[4] His petition to London to recruit an army of 1,000 men had been rejected, but he continued efforts to rally loyalist support.[5]
At about the same time, Scotsman Allan Maclean successfully lobbied King George III for permission to recruit Loyalist Scots throughout North America. In April, he received royal permission to raise a regiment known as the Royal Highland Emigrants by recruiting retired Scottish soldiers living in North America.[6] One battalion was to be recruited in the northern provinces, including New York, Quebec and Nova Scotia, while a second battalion was to be raised in North Carolina and other southern provinces, where a large number of these soldiers had been given land. After receiving his commissions from General Thomas Gage in June, Maclean sent Donald MacLeod and Donald MacDonald, two veterans of the June 17 Battle of Bunker Hill, south to lead the recruitment drive there. These recruiters were also aware that Allan MacDonald, husband of the famous Jacobite heroine Flora MacDonald was already actively recruiting in North Carolina.[7] Their arrival at New Bern was cause for suspicion by members of North Carolina's Committee of Safety, but they were not arrested.[8]
On January 3, 1776, Martin learned that an expedition of more than 2,000 troops under the command of General Henry Clinton was planned for the southern colonies and that their arrival was expected in mid-February.[9] He sent word to the recruiters that he expected them to deliver recruits to the coast by February 15 and dispatched Alexander Mclean to Cross Creek (present-day Fayetteville) to coordinate activities in that area. Mclean optimistically reported to Martin that he would raise and equip 5,000 Regulators and 1,000 Scots.[4][10]
In a meeting of Scots and Regulator leaders at Cross Creek on February 5, there was disagreement on how to proceed. The Scots wanted to wait until the British troops had arrived before mustering, while the Regulators wanted to move immediately. The views of the latter prevailed since they claimed to be able to raise 5,000 men, while the Scots believed they would only raise 700 to 800.[4] When the forces mustered on February 15, there were about 3,500 men, but the number rapidly dwindled over the next few days. Many men had expected to be met and escorted by British troops and did not relish the possibility of fighting to the coast. When they marched three days later, Brigadier General Donald MacDonald led between 1,400 and 1,600 men, predominantly Scots.[2][3] This number was further reduced over the coming days as more men deserted the column.[11]
Revolutionary reaction
[edit]
A: Moore moves from Wilmington to Rockfish Creek
B: MacDonald moves to Corbett's Ferry
C: Caswell moves from New Bern to Corbett's Ferry
Meanwhile, word of the Cross Creek muster reached the Patriots of the North Carolina Provincial Congress just a few days after it happened. The colonies were broadly prosperous on the eve of the American Revolution. Under resolutions of the Second Continental Congress, the provincial congress had raised the 1st North Carolina Regiment of the Continental Army in fall 1775 and given the command to Colonel James Moore. Local committees of safety in Wilmington and New Bern also had active militia units led by Alexander Lillington and Richard Caswell, respectively. On February 15, the Provincial Congress' militia force began to mobilize.[3]
Moore led 650 Patriot militiamen out of Wilmington, intending to prevent the loyalists from reaching the coast. They camped on the southern shore of Rockfish Creek on February 15, about 7 miles (11 km) from the loyalist camp. General MacDonald learned of their arrival and sent Colonel Moore a copy of a proclamation issued by Governor Martin and a letter calling on all Patriots to lay down their arms. Colonel Moore responded with a call that the loyalists lay down their arms and support the cause of Congress.[3] In the meantime, Caswell led 800 New Bern District Brigade militiamen toward the area.[12]
Loyalist march
[edit]MacDonald, his preferred road blocked by Moore, chose an alternate route that would eventually bring his force to the Widow Moore's Creek Bridge, about 18 miles (29 km) from Wilmington. On February 20, he crossed the Cape Fear River at Cross Creek; he destroyed the boats to deny Moore their use.[12] His forces then crossed the South River, heading for Corbett's Ferry, a crossing of the Black River. On orders from Moore, Caswell reached the ferry first and set up a blockade there.[13] Moore, as a precaution against Caswell being defeated or circumvented, detached Lillington with 150 Wilmington militia and 100 men under Colonel John Ashe from the New Hanover Volunteer Company of Rangers to take up a position at the Widow Moore's Creek Bridge. These men, moving by forced marches, traveled down the southern bank of the Cape Fear River to Elizabethtown, where they crossed to the north bank. From there, they marched down to the confluence of the Black River and Moore's Creek and began entrenching on the creek's east bank. Moore detached other militia companies to occupy Cross Creek and followed Lillington and Ashe with the slower Continentals. They followed the same route but did not arrive until after the battle.[12]
When MacDonald and his force reached Corbett's Ferry, they found the crossing blocked by Caswell and his men.[13] MacDonald prepared for battle but was informed by a local enslaved person that there was a second crossing a few miles up the Black River that they could use. On February 26, he ordered his rearguard to make a demonstration as if they were planning to cross while he led his main body up to this second crossing and headed for the bridge at Moore's Creek.[12] Caswell, once he realized that MacDonald had given him the slip, hurried his men the 10 miles (16 km) to Moore's Creek, and beat MacDonald there by only a few hours.[14] MacDonald sent one of his men into the patriot camp under a flag of truce to demand their surrender and to examine the defenses. Caswell refused, and the envoy returned with a detailed plan of the patriot fortifications.[15]
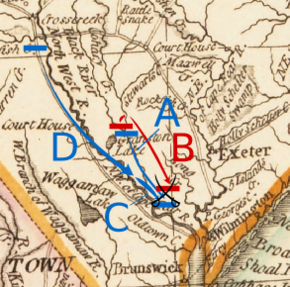
A: Caswell's movement
B: MacDonald's movement
C: Lillington and Ashe's movement
D: Moore's movement
Caswell had thrown up some entrenchments on the west side of the bridge, but these were not located to patriot advantage. Their position required the patriots to defend a position whose only line of retreat was across the narrow bridge, a distinct disadvantage MacDonald recognized when he saw the plans.[14] In a council held that night, the loyalists decided to attack since the alternative of finding another crossing might give Moore time to reach the area. During the night, Caswell decided to abandon that position and instead take up a position on the far side of the creek. To further complicate the loyalists' use of the bridge, the militia took up its planking and greased the support rails.[11]
Battle
[edit]By their arrival at Moore's Creek, the loyalist contingent had shrunk to 700–800 men. About 600 were Highland Scots, and the remainder were Regulators.[16] Furthermore, the marching had taken its toll on the elderly Brigadier General MacDonald; he fell ill and turned over command to Lieutenant Colonel Donald MacLeod. The loyalists broke camp at 1 am on February 27 and marched a few miles from their camp to the bridge.[15]
Arriving shortly before dawn, the Loyalists found the defenses on the west side of the bridge unoccupied. MacLeod ordered his men to adopt a defensive line behind nearby trees, but then a Patriot sentry across the river fired his musket to warn Caswell of the loyalist arrival. Hearing this, Lt.-Col. MacLeod immediately ordered his men to attack.[11]
In the pre-dawn mist, a company of Loyalist Gaels approached the bridge. In response to a Patriot call for identification shouted from across the creek, Captain Alexander Mclean identified himself as a friend of the King. He responded with his own challenge in Scottish Gaelic. Hearing no reply, he ordered his company to open fire, beginning an exchange of gunfire with the Patriot sentries. Lieutenant-Colonel MacLeod and Captain John Campbell then led a hand-picked company of swordsmen on a charge across the bridge.[15]
When the Loyalists were within 30 paces of the earthworks, the Patriot militia opened fire, to devastating effect. MacLeod and Campbell both went down in a hail of gunfire; 20 musket balls had struck MacLeod.[15] Armed only with swords and faced with the overwhelming firepower of Patriot muskets and artillery, the Highland Scots retreated. The surviving elements of Campbell's company got back over the bridge, and the governor's force dissolved and retreated.[17]
Capitalizing on the success, the Revolutionary forces quickly replaced the bridge planking and gave chase. One enterprising company led by one of Caswell's lieutenants forded the creek above the bridge, flanking the retreating loyalists. Colonel Moore arrived on the scene a few hours after the battle. He stated in his report that 30 loyalists were killed or wounded, "but as numbers of them must have fallen into the creek, besides more that were carried off, I suppose their loss may be estimated at fifty."[16] The Revolutionary leaders reported one killed and one wounded.[16]
Aftermath
[edit]Over the next several days, the North Carolina Provincial Congress' militia force mopped up the fleeing loyalists. In all, about 850 men were captured. Most of these were released on parole, but the ringleaders were sent to Philadelphia as prisoners.[16] Despite very hard feelings on both sides, the Loyalist prisoners were treated with respect. This helped convince many not to take up arms again.[18]
Among those who survived to be taken prisoner was the Loyalist war poet Iain mac Mhurchaidh (John Macrae), a member of Clan Macrae, a recent immigrant from Kintail, and important figure in Scottish Gaelic literature. The poet's son, Murdo Macrae, also fought on the Loyalist side during the battle and was mortally wounded.[19][20]
Combined with the capture of the loyalist camp at Cross Creek, the patriots confiscated 1,500 muskets, 300 rifles, and $15,000 (as valued at the time) of Spanish gold.[21] Many weapons were probably hunting equipment and may have been taken from people not directly involved in the loyalist uprising.[22] The action galvanized patriot recruiting, and the arrests of many loyalist leaders throughout North Carolina cemented patriot control of the state. A pro-patriot newspaper reported after the battle, "This, we think, will effectually put a stop to loyalists in North Carolina".[18]
The battle had significant effects on the Scottish Gaels of North Carolina, where loyalist sympathizers refused to take up arms whenever recruitment efforts were made later in the war, and those who did were routed out of their homes by the pillaging activities of their patriot neighbors.[21]
Following the end of the war, many regions of North Carolina, which had been mainly settled by Scottish Gaels, were almost depopulated, as Gaelic-speaking Loyalists fled northward towards what remained of British North America.[23]
According to Marcus Tanner, despite the post-Revolutionary War flight of many local United Empire Loyalists and the subsequent redirection of Scottish Highland emigration to Canada, a large Gàidhealtachd community continued to exist in North Carolina, "until it was well and truly disrupted", by the American Civil War.[24]
The Moore's Creek Bridge battlefield site was preserved in the late 19th century through private efforts that eventually received state financial support. The Federal government took over the battle site as a National Military Park operated by the War Department in 1926. The War Department operated the park until 1933, when the National Park Service took over the site as the Moores Creek National Battlefield.[25] It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1966.[26] The battle is commemorated every year during the last full weekend of February.[27]
Order of battle
[edit]Early accounts of the battle often misstated the size of both forces involved, typically reporting that 1,600 loyalists faced 1,000 patriots. The National Park Service still uses these numbers.[28]
North Carolina
[edit]The patriot forces were also underreported since Caswell casually grouped the ranger forces of John Ashe as part of Lillington's company in his report.[16]
The Provincial Congress' militia forces order of battle included a mix of North Carolina Minutemen and Militia units. Because of the performance of the local militia and the higher costs of Minutemen, the North Carolina General Assembly abandoned the use of Minutemen on April 10, 1776, in favor of local militia brigades and regiments. The following units participated in this battle:[29]
- New Bern District Minutemen Battalion, 13 companies
- Wilmington District Minutemen Battalion, 4 companies
- Halifax District Minutemen Battalion, 5 companies
- Hillsborough District Minutemen Battalion, 7 companies
- 1st Salisbury District Minutemen Battalion, 1 company
- 2nd Salisbury District Minutemen Battalion, 11 companies
- 1st North Carolina Regiment, 7 companies
- Halifax District Brigade
- Halifax County Regiment, 1 company
- Northampton County Regiment, 1 company
- Hillsborough District Brigade
- Chatham County Regiment, 4 companies
- Granville County Regiment, 1 company
- Orange County Regiment, 1 company
- Wake County Regiment, 4 companies
- New Bern District Brigade
- Craven County Regiment, 4 companies
- Dobbs County Regiment, 8 companies
- Johnston County Regiment, 5 companies
- Pitt County Regiment, 4 companies
- Salisbury District Brigade
- Anson County Regiment, 2 companies
- Guilford County Regiment, 12 companies
- Surry County Regiment, 3 companies
- Tryon County Regiment, 8 companies
- Wilmington District Brigade
- Bladen County Regiment, 8 companies
- Brunswick County Regiment, 1 company
- Cumberland County Regiment, 2 companies
- Duplin County Regiment, 10 companies
- Onslow County Regiment, 3 companies
- New Hannover County Regiment, 2 companies of volunteer independent rangers
Great Britain
[edit]Historian David Wilson, however, points out that the large loyalist size is attributed to reports by General MacDonald and Colonel Caswell. MacDonald gave that figure to Caswell, representing a reasonable estimate of the number of men starting the march at Cross Creek. Alexander Mclean, who was present at both Cross Creek and the battle, reported that only 800 loyalists were present at the battle, as did Governor Martin.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Wilson, p. 34
- ^ a b Wilson, p. 35
- ^ a b c d Russell, p. 80
- ^ a b c Russell, p. 79
- ^ Meyer, p. 140
- ^ Fryer, p. 118
- ^ Fryer, pp. 121–122
- ^ Demond, p. 91
- ^ Meyer, p. 142
- ^ Wilson, p. 23
- ^ a b c Wilson, p. 28
- ^ a b c d Russell, p. 81
- ^ a b Wilson, p. 26
- ^ a b Wilson, p. 27
- ^ a b c d Russell, p. 82
- ^ a b c d e Wilson, p. 30
- ^ Wilson, p. 29
- ^ a b Wilson, p. 33
- ^ Michael Newton (2001), We're Indians Sure Enough: The Legacy of the Scottish Highlanders in the United States, Saorsa Media, p. 141.
- ^ "MacRae, John | NCpedia". www.ncpedia.org.
- ^ a b Russell, p. 83
- ^ Wilson, p. 31
- ^ Michael Newton (2001), We're Indians Sure Enough: The Legacy of the Scottish Highlanders in the United States, Saorsa Media. p. 143.
- ^ Marcus Tanner (2004), The Last of the Celts, p. 289.
- ^ Capps and Davis
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ^ "Moores Creek National Battlefield – Things to do". National Park Service. Archived from the original on May 28, 2010. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- ^ "Moores Creek National Battlefield website". National Park Service. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved April 22, 2010.
- ^ Lewis
Sources
[edit]- Capps, Michael A.; Davis, Stephen A (1999). "Moores Creek National Battlefield – Administrative History". National Park Service. Retrieved June 1, 2010.[permanent dead link]
- Demond, Robert O (1979) [1940]. The Loyalists in North Carolina During the Revolution. Baltimore, MD: Genealogical Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8063-0839-5. OCLC 229188174.
- Fryer, Mary Beacock (1987). Allan Maclean, Jacobite General: the Life of an Eighteenth Century Career Soldier. Toronto: Dundurn Press. ISBN 978-1-55002-011-3. OCLC 16042453.
- Greene, Jack P. (February 2000). "The American Revolution". American Historical Review. 1. 105 (1): 91–102. doi:10.2307/2652437. JSTOR 2652437.
- Lewis, J.D. "Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge". The American Revolution in North Carolina. Retrieved April 14, 2019.
- Meyer, Duane (1987) [1961]. The Highland Scots of North Carolina, 1732–1776. Chapel Hill, NC: UNC Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-4199-0. OCLC 316095450.
- Murray, Aaron (2004). The American Revolution Battles and Leaders. New York: DK Publishing. pp. 30–31.
- Purcell, L. Edward & Sarah J. (2000). Encyclopedia of Battles in North America 1517 to 1916. New York: Facts on File Inc. p. 187.
- Russell, David Lee (2000). The American Revolution in the Southern Colonies. Jefferson, NC: McFarland. ISBN 978-0-7864-0783-5. OCLC 44562323.
- Wilson, David K (2005). The Southern Strategy: Britain's Conquest of South Carolina and Georgia, 1775–1780. Columbia, SC: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 1-57003-573-3. OCLC 56951286.
Further reading
[edit]- "The Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge," Revolutionary North Carolina, a digital textbook the UNC School of Education produced.
- 1776 in North Carolina
- Battles in the Southern theater of the American Revolutionary War 1775–1779
- Battles involving Great Britain
- Battles involving the United States
- Battles of the American Revolutionary War in North Carolina
- Conflicts in 1776
- Last stands
- Pender County, North Carolina
- Scottish-American culture in North Carolina
- Scottish-American history