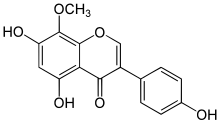
ψ-Tectorigenin
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4′,5,7-Trihydroxy-8-methoxyisoflavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-8-methoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Isotectorigenin
Pseudotectorigenin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 300.266 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
ψ-Tectorigenin is an O-methylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be isolated from Belamcanda chinensis, Dalbergia sissoo. It can also be isolated from the bacterium Nocardiopsis sp,[1] and from the mold Stemphilium sp. No. 644.[2]
See also
[edit]- Tectorigenin, a related favonoid
References
[edit]- ^ Imoto, M; Shimura, N; Umezawa, K (1991). "Inhibition of epidermal growth factor-induced activation of phospholipase C by psi-tectorigenin". The Journal of Antibiotics. 44 (8): 915–7. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.44.915. PMID 1917707.
- ^ Psi-tectorigenin on knapsack
