Wikipedia:Today's featured article/April 2022
| << | Today's featured articles for April 2022 | >> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa |
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
April 1
Coropuna is a dormant volcano with several perennially snowbound conical summits in the Andes mountains of southern Peru. The highest peak of the compound volcano reaches an altitude of 6,377 metres (20,922 feet) above sea level, making the Coropuna complex the third-highest in Peru. Its thick ice cap is the most extensive in Earth's tropical zone, with several outlet glaciers stretching out to lower altitudes. Below an elevation of 5,000 metres (16,000 feet), the vegetation belts include trees, peat bogs and grasses, as well as agricultural areas and pastures. The Coropuna complex consists of several stratovolcanos composed chiefly of ignimbrites and lava flows, on a basement formed by similar material from the Middle Miocene. The complex has been active for at least five million years. Current activity occurs exclusively in the form of hot springs. The Inca archaeological site of Mawk'allaqta is on the volcano's slopes. (Full article...)
April 2
The northern rosella (Platycercus venustus) is a species of parrot native to northern Australia, ranging from the Gulf of Carpentaria and Arnhem Land to the Kimberley. It was described by Heinrich Kuhl in 1820, and two subspecies are recognised. The species is unusually coloured for a rosella, with a dark head and neck with pale cheeks—predominantly white in the nominate subspecies from the Northern Territory and blue in the Western Australian subspecies. The northern rosella's mantle and scapulars are black with fine yellow scallops, while its back, rump and underparts are pale yellow with fine black scallops. The long tail is blue-green and the wings are black and blue-violet. Found in woodland and open savannah country, the northern rosella consumes seeds, particularly of grasses and eucalypts, as well as flowers and berries, but it may also eat insects. Nesting takes place in tree hollows. Although uncommon, the species is not threatened. (Full article...)
April 3
The 2009 Women's Cricket World Cup Final was a Women's One Day International cricket match between England (pictured) and New Zealand, played on 22 March at the North Sydney Oval in Australia. It was the second time that the two teams had met at this stage of a World Cup – England had won their previous final contest in 1993. This game was the culmination of the 2009 Women's Cricket World Cup, the ninth edition of the tournament. England, who were considered the favourites, built an opening partnership of 74 runs and continued to score steadily. Despite regularly losing wickets, they won by four wickets with 23 balls to spare. This World Cup title was their first in 16 years, their third overall, and their first outside England. Nicky Shaw, a bowler who replaced the injured Jenny Gunn in England's starting lineup minutes before the game started, took a career-best four wickets for 34 runs and was named the player of the match. (Full article...)
April 4
Martin Rundkvist (born 4 April 1972) is a Swedish archaeologist who focuses on the Bronze, Iron, and Middle Ages of Scandinavia. He has excavated various sites in Sweden. In a 2011 book, he identified nine possible regional power centres in Östergötland, and attempted to determine where the "Beowulfian mead halls" of the day once stood. Years later at one of these sites, Aska, he uncovered the foundations of a large mead hall, and 22 ornate gold figures that may have represented gods or royals. Rundkvist has also catalogued the finds from Barshalder, the largest prehistoric cemetery on Sweden's Gotland island; excavated the boat grave of a Viking; and analysed both the placement of deposited artefacts in the landscape and the lifestyles of élite Scandinavians during the Middle Ages. Rundkvist authors the blog Aardvarchaeology, which the James Randi Educational Foundation termed "the most-read archaeology blog on the Internet". He is an associate professor at the University of Łódź in Poland. (Full article...)
April 5
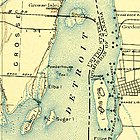
Powder House Island (also known as Dynamite Island) is an artificial island on the lower Detroit River in southeast Michigan, directly adjacent to the Canada–United States border. It was constructed in the late 1880s by the Dunbar & Sullivan Company to manufacture and store explosives during their dredging of the Livingstone Channel, in a successful attempt to circumvent an 1880 court order forbidding the company from storing explosives on nearby Fox Island. In 1906, twenty short tons (18,000 kg) of the island's dynamite exploded after two men "had been shooting with a revolver" near it. The explosion was clearly audible from 85 mi (137 km) away. By the 1980s, it was completely unused; by 2015, the island was owned by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources, managed by its Wildlife Division as part of the Pointe Mouillee State Game Area, and accessible to the public for hunting and camping. (Full article...)
April 6
The Treaty of Guînes was a draft agreement to end the Hundred Years' War, negotiated between England and France from 1353 to 1354. War had broken out in 1337 and was aggravated when the English king claimed the French throne. After a French defeat at the Battle of Crécy a truce was agreed in 1347, although it was not fully observed. In 1352 full-scale fighting broke out again, which went badly for the French. A faction in favour of peace gained influence in the French king's council, negotiations were reopened and a peace agreement that exchanged French land for the English claim to the French throne was agreed. A draft treaty was formally signed at Guînes on 6 April 1354. The detailed treaty was supposed to be publicly announced in October, but a new French council turned against it and the draft was repudiated. In 1360 the Treaty of Brétigny, which largely replicated the Treaty of Guînes, was agreed. War flared up again in 1369 and the Hundred Years' War finally ended in 1453, 99 years after the Treaty of Guînes was signed. (Full article...)
April 7
Pomona College is a private liberal arts college in Claremont, California. It was established in 1887 by a group of Congregationalists who wanted to recreate a "college of the New England type" in Southern California. In 1925 it became the founding member of the Claremont Colleges consortium of adjacent, affiliated institutions. A four-year undergraduate college, it enrolls about 1700 students and offers 48 majors in liberal arts disciplines. Pomona's student body is noted for its racial, geographic, and socioeconomic diversity. Among the college's traditions is a reverence for the number 47. Its athletics teams, the Sagehens, compete jointly with Pitzer College in the SCIAC, a Division III conference. Pomona has the lowest acceptance rate of any U.S. liberal arts college. It is considered the most prestigious liberal arts college in the American West and one of the most prestigious in the U.S. It is a top producer of fellowship recipients and has prominent alumni in various fields. (Full article...)
April 8
Sonic the Hedgehog is a 2006 platform game developed by Sonic Team and published by Sega. It was produced in commemoration of the 15th anniversary of the Sonic series, and intended as a reboot for the seventh-generation video game consoles. Players control Sonic, Shadow, and the new character Silver, who battle Solaris, an ancient evil pursued by Doctor Eggman. Development was rushed after Sonic co-creator Yuji Naka (pictured) resigned from the team to form his own company, and half of the team was diverted to work on the Wii game Sonic and the Secret Rings. Sonic the Hedgehog was released for the Xbox 360 in November and for the PlayStation 3 the following month; versions for Wii and Windows were canceled. Praised in prerelease showings, the game was a critical failure, described as one of the worst games in the series. Reviewers criticized its loading times, camera system, story, stability, and controls. In 2010, Sega delisted the game from retailers. (Full article...)
April 9
Viatkogorgon is a genus of gorgonopsian (a type of therapsid, a group that includes modern mammals) that lived during the Permian Period in what is now Russia. The first fossil was named as V. ivachnenkoi after the paleontologist M. F. Ivakhnenko. It was found at the Kotelnich near the river Vyatka in 1999. The holotype skeleton (pictured) is one of the most complete gorgonopsian specimens known and includes some rarely preserved elements, including gastralia and a sclerotic ring. A larger, less well preserved specimen has also been assigned to this species. The smaller specimen is about 80 cm (31 in) long, including the 14 cm (5.5 in) skull, and may have been a young animal. It was robust with a dog-like stance, high snout, and very large canine teeth. Gorgonopsians would have been relatively fast predators, which killed their prey by delivering slashing bites with their saber-teeth, and this genus may have been adapted for swimming. (Full article...)
April 10

Sir Robert de Umfraville (c. 1363 – 1437) was a late medieval English knight who took part in the later stages of the Hundred Years' War, particularly against Scotland. Much of his career was focused on defending the border with Scotland, which had seen near-constant warfare since the late 13th century. He both fought there and participated in embassies, negotiating treaties as a diplomat. Beginning his career under Richard II, he probably fought at the 1388 Battle of Otterburn with Henry "Hotspur" Percy. In 1415, de Umfraville travelled with Henry V to France, where he may have taken part in the Battle of Agincourt. He was famed for his prowess in martial arts, and his successes in the north attracted praise and reward from the kings he served. On a campaign deep into Scottish territory, he destroyed Peebles and its market, bringing back so much booty that he was popularly nicknamed "Robin Mendmarket". He carried out his last mission to Scotland in March 1436 and died early the next year. (Full article...)
April 11
The Shadow was an American pulp magazine published by Street & Smith from 1931 to 1949. Each issue contained a novel about The Shadow, a mysterious crime-fighting figure who spoke the line "Who knows what evil lurks in the hearts of men? The Shadow knows" in radio broadcasts of stories from Street & Smith's Detective Story Magazine. For the first issue, dated April 1931, Walter Gibson wrote the lead novel, The Living Shadow. Sales were strong, and Street & Smith soon changed it from quarterly to monthly publication, and then to twice-monthly, with the lead novels written by Gibson. From 1946 to 1948, the novels were by Bruce Elliott, who made The Shadow mostly a background figure. Gibson returned to Street & Smith and resumed writing in 1948, but in 1949 the firm ended its remaining pulp titles, including The Shadow. The success of The Shadow made it very influential, and many other single-character pulps soon appeared, featuring a lead novel in every issue about the magazine's main character. (Full article...)
April 12
The Connecticut Tercentenary half dollar is a commemorative fifty-cent piece struck by the United States Bureau of the Mint in 1935. The commemorative coin was designed by Henry Kreis and depicts the Charter Oak, where according to legend Connecticut's charter was hidden to save it from confiscation. An eagle appears on the coin's reverse side. The Connecticut Tercentenary Commission wanted a half dollar issued, with proceeds from its sale to further its projects. A bill passed through Congress without dissent and became law on June 21, 1935, when President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed it, providing for 25,000 half dollars. Kreis's design was a Public Works Administration project and technically in violation of the new law, which said the federal government was not to pay for its design. Nevertheless, the design was approved and the commission, setting a price of $1 per coin, exhausted the entire issue. Kreis's design has generally been praised by numismatic writers. (Full article...)
April 13

Messiah (HWV 56) is an English-language sacred oratorio composed in 1741 by George Frideric Handel. Its text was compiled by Charles Jennens from the King James Bible and the Book of Common Prayer. It covers episodes related to the Messiah mostly in verses from the Old Testament and the Book of Revelation. Handel structured the work in three parts, each in scenes as in Baroque opera. Part I covers prophecies, the birth of Jesus and his work, Part II focuses on his Passion, while Part III deals with the resurrection of the dead. Messiah was first performed in Dublin on 13 April 1742, with a small orchestra of trumpets, oboes, strings and continuo. After an initially modest reception, the oratorio became one of the most frequently performed Western choral works, often adapted to large orchestras and choirs after Handel's death. Mozart modified the instrumentation in his arrangement Der Messias to a German text. The famous "Hallelujah" chorus, concluding Part II, is often performed individually. (Full article...)
April 14
The history of the Nashville Sounds, a Minor League Baseball team, began in Nashville, Tennessee, in 1978, after Larry Schmittou and a group of American investors purchased the rights to operate an expansion franchise of the Double-A level Southern League. Home games were played at Herschel Greer Stadium from its opening in 1978 until the end of 2014. In 2015, they moved to the new First Horizon Park (pictured) on the site of the former Sulphur Dell ballpark. They won the league's championship in 1979 as an affiliate of the Cincinnati Reds and in 1982 as an affiliate of the New York Yankees. Before the 1985 season, the owners bought the Evansville Triplets, a Triple-A team, and relocated them to Nashville as the Triple-A Sounds. They joined the Triple-A Pacific Coast League in 1998 and won its championship in 2005 as an affiliate of the Milwaukee Brewers. In 2021, they were placed in the Triple-A East, which became the International League in 2022. (This article is part of a featured topic: Nashville Sounds.)
April 15

The 4th Army was a Royal Yugoslav Army formation mobilised prior to the German-led invasion of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia during World War II. It initially consisted of three infantry divisions, one brigade-strength detachment, one horse cavalry regiment and one independent infantry regiment. It was responsible for defending a large section of the Yugoslav–Hungarian border, being deployed behind the Drava river between Varaždin and Slatina. Like all Yugoslav formations at the time, the 4th Army had serious deficiencies in both mobility and firepower, and it was only partially mobilised when the invasion began on 6 April 1941. The 4th Army put up scattered resistance, but began to withdraw southwards on 9 April, and on 10 April it ceased to exist as an operational formation. The remains of the 4th Army were ordered to stop fighting on 15 April, and the Yugoslav Supreme Command surrendered unconditionally, effective on 18 April. (This article is part of a featured topic: 1st Army Group (Kingdom of Yugoslavia).)
April 16
Apollo 16 (April 16–27, 1972) was the tenth crewed mission in the United States Apollo space program, administered by NASA, and the fifth and penultimate to land on the Moon. The mission was crewed by John Young, Commander; Charles Duke, Lunar Module Pilot; and Ken Mattingly, Command Module Pilot. Launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 16, 1972 (pictured), Apollo 16 experienced a number of minor glitches en route to the Moon. These culminated with a problem with the spaceship's main engine that resulted in a six-hour delay in the Moon landing. Young and Duke explored the Descartes Highlands, a site thought volcanic, although this proved to be not so. Mattingly orbited the Moon in the command and service module, taking photos and operating scientific instruments. During the return trip to Earth, Mattingly performed a one-hour spacewalk to retrieve several film cassettes from the exterior of the service module. Apollo 16 returned safely to Earth on April 27, 1972. (Full article...)
April 17
Seleucus VI Epiphanes (c. 115 – 94 BC) was a Seleucid monarch who reigned as King of Syria between 96 and 94 BC during the Hellenistic period. He was the son of Antiochus VIII and his Egyptian wife Tryphaena. A period of civil war between his father and his uncle Antiochus IX ended in 96 BC when his father was assassinated. Antiochus IX then occupied the capital Antioch while Seleucus VI established his power base in western Cilicia. After his uncle was killed, Seleucus VI became the master of the capital but shared Syria with his brother Demetrius III and his cousin Antiochus X. According to the ancient historian Appian, Seleucus VI was a violent ruler. He taxed his dominions extensively to support his wars, and resisted allowing the cities a measure of autonomy, as former kings allowed. His reign did not last long; in 94 BC, he was expelled from Antioch by Antiochus X, who followed him to the Cilician city of Mopsuestia, where his attempts to raise money led to riots that eventually claimed his life. (Full article...)
April 18

The Sei pezzi per pianoforte ('Six pieces for piano'), assigned catalogue number P 044, is a set of six solo piano pieces composed by the Italian composer Ottorino Respighi between 1903 and 1905. These predominantly salonesque pieces are eclectic, drawing influence from different musical styles and composers, particularly music of earlier periods. The pieces have various musical forms and were composed separately and later published together between 1905 and 1907 in a set under the same title for editorial reasons; Respighi had not composed them as a suite, and therefore did not intend to have uniformity among the pieces. Styles present in the set include Baroque, Impressionism, Classicism, and Romanticism. The set, under Bongiovanni, became his first published work. Five of the six pieces are derived from earlier works by Respighi, and only one of them, the "Canone", has an extant manuscript. (Full article...)
April 19
The Minute Man is an 1874 sculpture by Daniel Chester French located in Minute Man National Historical Park in Concord, Massachusetts. The statue depicts a minuteman stepping away from his plow to join the patriot forces at the Battle of Concord, with a musket in his hand. Cast from ten bronze cannons, it was unveiled on April 19, 1875, during the centennial celebration of the Battle of Concord. It received critical acclaim and continues to be praised by commentators. The pose resembles that of the Apollo Belvedere and it was assumed that the pose was transposed from this, but modern art historians have shown that the Apollo Belvedere was only one of several statues used in French's research. The statue has been a symbol for the suffragettes, the United States National Guard and the Air National Guard, and has been used on the Lexington–Concord Sesquicentennial half dollar and the Massachusetts state quarter coins. (Full article...)
April 20
Nicoll Highway MRT station is an underground Mass Rapid Transit station on the Circle Line in Singapore. Located underneath Republic Avenue near the Kallang River, the station serves commercial and residential developments along Nicoll Highway such as the Golden Mile Complex and The Concourse. During its construction, a section of the tunnels and the segment of the highway above caved in on 20 April 2004, killing four people. Following an investigation, which found human error and organisational failures as causes of the collapse, the station was relocated. Alongside the other stations on Stages 1 and 2 of the Circle Line, Nicoll Highway station opened on 17 April 2010. Designed by ONG & ONG, the station is 21.5 metres (71 ft) deep and has a black and grey scheme. Nicoll Highway station features the public artwork Re-claiming the Peripherals by Khiew Huey Chian, consisting of four reliefs depicting wild plants, displayed over the platform doors (example pictured). (Full article...)
April 21
John Watts Young (1930–2018) was an American astronaut, naval officer and aviator, test pilot, and aeronautical engineer. On April 21, 1972, he became the ninth person to walk on the Moon as commander of Apollo 16. He flew on four different classes of spacecraft: the Gemini capsule, the Apollo command and service module, the Apollo lunar module, and the Space Shuttle. Young served in the U.S. Navy as an aviator, and graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School. He set multiple world time-to-climb records, and was selected as a member of NASA Astronaut Group 2 in 1962. He flew on Gemini 3 in 1965, and commanded Gemini 10 in 1966. He flew as the command module pilot on Apollo 10 in 1969. After that, he commanded Apollo 16, and spent three days on the lunar surface exploring the Descartes Highlands with Charles Duke. Young also commanded STS-1, the Space Shuttle program's first launch, in 1981, and STS-9 in 1983. He retired from NASA in 2004. (This article is part of a featured topic: NASA Astronaut Group 2.)
April 22
Regine Velasquez (born April 22, 1970) is a Filipino singer and actress. Her career began with wins in the television talent show Ang Bagong Kampeon in 1984 and the Asia Pacific Singing Contest in 1989. Her 1987 debut album Regine was guided by Viva Records executive Vic del Rosario and producer Ronnie Henares. With PolyGram Records, she achieved commercial success in Asia with her albums Listen Without Prejudice (1994), My Love Emotion (1995), and Retro (1997). Velasquez played the female lead in the romantic comedies Kailangan Ko'y Ikaw (2000), Till I Met You (2006), and Paano Kita Iibigin (2007), and in the primetime television series Forever in My Heart (2004), Diva (2010), I Heart You, Pare! (2011), and Poor Señorita (2016). She won a Star Award for playing an intellectually disabled woman in the anthology series Maalaala Mo Kaya (2001) and a Golden Screen Award for playing a document forger in the comedy Of All the Things (2012). (This article is part of a featured topic: Overview of Regine Velasquez.)
April 23
The American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) is a smooth-skinned ray-finned freshwater fish that is the only living species of the paddlefish family. The fish is often considered a relict species as it retains some morphological traits of its early ancestors, including a mostly cartilaginous skeleton and a paddle-shaped rostrum extending from its cranium for roughly one-third its body length. It is also considered a highly derived fish due to its novel adaptations, such as filter feeding. The planktivorous fish averages 5 ft (1.5 m) in length, and has a heterocercal tail fin resembling that of sharks. It is native to the Mississippi River basin, with a range extending to the Great Lakes, but is now considered vulnerable due to overfishing, poaching, habitat destruction, and pollution, and its naturally occurring populations have died off in most of its peripheral range, including New York and Pennsylvania. (Full article...)
April 24
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. At the orders of Talaat Pasha, an estimated 800,000 to 1,200,000 Armenian women, children, and elderly or infirm people were sent on death marches to the Syrian Desert in 1915 and 1916. Driven forward by paramilitary escorts, the deportees were deprived of food and water and subjected to robberies, rapes, and massacres. In the desert, the survivors were dispersed into concentration camps. In 1916 another wave of massacres was ordered, leaving about 200,000 deportees alive by the end of 1916. Around 100,000 to 200,000 Armenian women and children were forcibly converted to Islam and integrated into Muslim households. The Turkish nationalist movement carried out massacres and ethnic cleansing of survivors during the Turkish War of Independence after World War I. The Armenian genocide destroyed more than two millennia of Armenian civilization in eastern Anatolia. (Full article...)
April 25
No. 79 Squadron is a Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) flight training squadron that has been formed on four occasions. Established in April 1943 as a fighter unit equipped with Supermarine Spitfires, it saw combat in the South West Pacific theatre of World War II. The squadron disbanded in November 1945 but re-formed in 1962 to operate CAC Sabres (pictured) to help defend Thailand against a feared attack from neighbouring states. No. 79 Squadron was active again in Malaysia between 1986 and 1988, operating Mirage III fighters and a single DHC-4 Caribou transport. Re-formed in its present incarnation in 1998, it is stationed at RAAF Base Pearce, where it has operated Hawk 127 jet training aircraft since 2000. The unit's main role is to provide introductory jet aircraft training to RAAF pilots and refresher training on the Hawk for experienced pilots. No. 79 Squadron also supports Australian Army and Royal Australian Navy training exercises in Western Australia and the Northern Territory. (Full article...)
April 26
The 1921–22 season was Cardiff City's first in the First Division of the Football League following election from the Southern Football League to the Second Division for the 1920–21 season. They had won promotion the previous season, the first Welsh team to reach the top tier of English football, finishing as runners-up behind Birmingham on goal average. They reached the fourth round of the FA Cup. Fred Stewart remained manager and new signings included full back Tommy Brown and forward Willie Page. Cardiff were investigated by the FA and the FAW over an illegal approach for Wolverhampton's defender Dickie Baugh and club and player were both fined. John Pritchard was elected chairman, but was replaced in November by Walter Empsall. Cardiff made significant investments in the club's ground, Ninian Park, laying a new pitch and improving viewing for spectators. During the latter work, refuse dumped by Cardiff Corporation caught alight, but the blaze was doused with the aid of local supporters. (Full article...)
April 27
Uroš Drenović (1911–1944) was a Bosnian Serb officer of the Royal Yugoslav Army who became a Chetnik commander during World War II. He was one of the leaders of the popular uprising in mid-1941 against the Ustaše, a fascist organization that governed the Independent State of Croatia, a puppet state of the Axis powers. However, he eventually betrayed the communist-led Partisans and sided with the royalist and Serbian nationalist Chetniks, whose ideology more closely matched his own. He was defeated by the Partisans and fled to Ustaše-held territory where, out of military and political necessity, he concluded a collaboration agreement with them on 27 April 1942. He later collaborated with the Italian and German occupiers against the Partisans. Drenović was killed in an Allied air raid in May 1944. Despite his extensive collaboration, he and his Chetniks are celebrated in Republika Srpska, the Serb-majority entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina, creating significant controversy. (Full article...)
April 28
Paige Bueckers (born 2001) is an American college basketball player for the University of Connecticut (UConn) Huskies in the NCAA Division I. A 5-foot-11-inch (1.80 m) point guard, she became the first freshman to win a major national college player of the year award. She led UConn to the Final Four as a freshman and to the national championship game as a sophomore. Bueckers played varsity basketball for Hopkins High School in Minnetonka, Minnesota, from eighth grade and helped the team win the state title as a junior. She was considered the number one high school player in her class by ESPN, earned national high school player of the year honors in her senior season and graduated from Hopkins as one of Minnesota's most distinguished high school players. A three-time gold medalist for the United States in youth basketball, Bueckers was named Most Valuable Player of the 2019 FIBA Under-19 World Cup, and USA Basketball Female Athlete of the Year in the same year. (Full article...)
April 29
The Battle of Oroscopa was fought in late 151 BC between a Carthaginian army commanded by the general Hasdrubal and a Numidian force under its king, Masinissa, in what is now north western Tunisia. A peace treaty with Rome prohibited Carthage from waging war. Masinissa, an ally of Rome, exploited this to repeatedly raid Carthaginian territory. In 151 BC Carthage assembled an army under Hasdrubal and attempted to deter Masinissa's aggression against the town of Oroscopa. Masinissa lured the Carthaginians into an area of rough terrain and surrounded them. The Carthaginians expected their opponents to disperse, but Masinissa had forged a well-disciplined army and it was able to starve the Carthaginians into surrender. The Carthaginians were then treacherously attacked and many, perhaps most, were killed. Hasdrubal survived and returned to Carthage, where he was condemned to death in an attempt to placate Rome. But Rome launched a punitive expedition, starting the Third Punic War which ended in the complete destruction of Carthage in 146 BC. (Full article...)
April 30
The European nightjar (Caprimulgus europaeus) is a crepuscular and nocturnal insect-eating bird that breeds across Europe and temperate Asia. All six subspecies of this nightjar are migratory, wintering in sub-Saharan Africa. Their densely patterned grey and brown plumage makes them difficult to see in the daytime when they rest on the ground or perch motionless along a branch, although the male shows white patches in the wings and tail in flight. The preferred habitat is dry, open country with some trees and small bushes. The breeding male has a churring trill, and patrols his territory with wings held in a V-shape. The female lays two eggs directly on the ground; they hatch after about 17–21 days and the chicks fledge in another 16–17 days. Both "Caprimulgus" and the old name "goatsucker" refer to the myth that nightjars suckled she-goats, causing them to cease to give milk. Its large numbers and huge breeding range mean that it is classed by the IUCN as being of least concern. (Full article...)