Asian diaspora
The Asian diaspora is the diasporic group of Asian people who live outside of the continent. There are several prominent groups within the Asian diaspora.[1]
Asian diasporas have been noted for having an increasingly transnational relationship with their ancestral homelands,[2][3] especially culturally through the use of digital media.[4][5]
History
[edit]Asians have a long history of migrating internally within Asia. Overland trading routes such as the Silk Road, and maritime routes through the Indo-Pacific enabled ancient exchanges. Since the late 19th century, Asian migration has greatly increased because of the impacts of colonialism and globalisation, which enabled new types of migration; for example, European empires' global reach and consolidation paved the way for the Indian indenture system. Increasing border enforcement by modern nation-states has stymied traditional migration flows, however.[6]
Central Asian diaspora
[edit]The Central Asian diaspora of the modern era is shaped to a significant extent by the expansion of and displacement caused by the Soviet Union.[7]
East Asian diaspora
[edit]Young people have started migrating from East Asia in much larger numbers since the 1990s.[8]
Chinese diaspora
[edit]Overseas Chinese people are people of Chinese origin who reside outside Greater China (mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan).[9] As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.[10] Overall, China has a low percent of population living overseas.

History
[edit]The Chinese people have a long history of migrating overseas, as far back as the 10th century. One of the migrations dates back to the Ming dynasty when Zheng He (1371–1435) became the envoy of Ming. He sent people – many of them Cantonese and Hokkien – to explore and trade in the South China Sea and in the Indian Ocean.
Early emigration
[edit]In the mid-1800s, outbound migration from China increased as a result of the European colonial powers opening up treaty ports.[17]: 137 The British colonization of Hong Kong further created the opportunity for Chinese labor to be exported to plantations and mines.[17]: 137
During the era of European colonialism, many overseas Chinese were coolie laborers.[17]: 123 Chinese capitalists overseas often functioned as economic and political intermediaries between colonial rulers and colonial populations.[17]: 123
The area of Taishan, Guangdong Province was the source for many of economic migrants.[18] In the provinces of Fujian and Guangdong in China, there was a surge in emigration as a result of the poverty and village ruin.[19]
San Francisco and California was an early American destination in the mid-1800s because of the California Gold Rush. Many settled in San Francisco forming one of the earliest Chinatowns. For the countries in North America and Australia saw great numbers of Chinese gold diggers finding gold in the gold mining and railway construction. Widespread famine in Guangdong impelled many Cantonese to work in these countries to improve the living conditions of their relatives.
From 1853 until the end of the 19th century, about 18,000 Chinese were brought as indentured workers to the British West Indies, mainly to British Guiana (now Guyana), Trinidad and Jamaica.[20] Their descendants today are found among the current populations of these countries, but also among the migrant communities with Anglo-Caribbean origins residing mainly in the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada.
Some overseas Chinese were sold to South America during the Punti–Hakka Clan Wars (1855–1867) in the Pearl River Delta in Guangdong.
Research conducted in 2008 by German researchers who wanted to show the correlation between economic development and height, used a small dataset of 159 male labourers from Guangdong who were sent to the Dutch colony of Suriname to illustrate their point. They stated that the Chinese labourers were between 161 to 164 cm in height for males.[21] Their study did not account for factors other than economic conditions and acknowledge the limitations of such a small sample.
The Lanfang Republic in West Kalimantan was established by overseas Chinese.
In 1909, the Qing dynasty established the first Nationality Law of China.[17]: 138 It granted Chinese citizenship to anyone born to a Chinese parent.[17]: 138 It permitted dual citizenship.[17]: 138
Republic of China
[edit]In the first half of the 20th Century, war and revolution accelerated the pace of migration out of China.[17]: 127 The Kuomintang and the Communist Party competed for political support from overseas Chinese.[17]: 127–128
Under the Republicans economic growth froze and many migrated outside the Republic of China, mostly through the coastal regions via the ports of Fujian, Guangdong, Hainan and Shanghai. These migrations are considered to be among the largest in China's history. Many nationals of the Republic of China fled and settled down overseas mainly between the years 1911–1949 before the Nationalist government led by Kuomintang lost the mainland to Communist revolutionaries and relocated. Most of the nationalist and neutral refugees fled mainland China to North America while others fled to Southeast Asia (Singapore, Brunei, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Philippines) as well as Taiwan (Republic of China).[22]
After World War II
[edit]Those who fled during 1912–1949 and settled down in Singapore and Malaysia automatically gained citizenship in 1957 and 1963 as these countries gained independence.[23][24] Kuomintang members who settled in Malaysia and Singapore played a major role in the establishment of the Malaysian Chinese Association and their meeting hall at Sun Yat Sen Villa. There was evidence that some intended to reclaim mainland China from the CCP by funding the Kuomintang.[25][26]
After their defeat in the Chinese Civil War, parts of the Nationalist army retreated south and crossed the border into Burma as the People's Liberation Army entered Yunnan.[17]: 65 The United States supported these Nationalist forces because the United States hoped they would harass the People's Republic of China from the southwest, thereby diverting Chinese resources from the Korean War.[17]: 65 The Burmese government protested and international pressure increased.[17]: 65 Beginning in 1953, several rounds of withdrawals of the Nationalist forces and their families were carried out.[17]: 65 In 1960, joint military action by China and Burma expelled the remaining Nationalist forces from Burma, although some went on to settle in the Burma–Thailand borderlands.[17]: 65–66
During the 1950s and 1960s, the ROC tended to seek the support of overseas Chinese communities through branches of the Kuomintang based on Sun Yat-sen's use of expatriate Chinese communities to raise money for his revolution. During this period, the People's Republic of China tended to view overseas Chinese with suspicion as possible capitalist infiltrators and tended to value relationships with Southeast Asian nations as more important than gaining support of overseas Chinese, and in the Bandung declaration explicitly stated[where?] that overseas Chinese owed primary loyalty to their home nation.[dubious – discuss]
From the mid-20th century onward, emigration has been directed primarily to Western countries such as the United States, Australia, Canada, Brazil, The United Kingdom, New Zealand, Argentina and the nations of Western Europe; as well as to Peru, Panama, and to a lesser extent to Mexico. Many of these emigrants who entered Western countries were themselves overseas Chinese, particularly from the 1950s to the 1980s, a period during which the PRC placed severe restrictions on the movement of its citizens.
Due to the political dynamics of the Cold War, there was relatively little migration from the People's Republic of China to southeast Asia from the 1950s until the mid-1970s.[17]: 117
In 1984, Britain agreed to transfer the sovereignty of Hong Kong to the PRC; this triggered another wave of migration to the United Kingdom (mainly England), Australia, Canada, US, South America, Europe and other parts of the world. The 1989 Tiananmen Square protests and massacre further accelerated the migration. The wave calmed after Hong Kong's transfer of sovereignty in 1997. In addition, many citizens of Hong Kong hold citizenships or have current visas in other countries so if the need arises, they can leave Hong Kong at short notice.[citation needed]
In recent years, the People's Republic of China has built increasingly stronger ties with African nations. In 2014, author Howard French estimated that over one million Chinese have moved in the past 20 years to Africa.[27]
More recent Chinese presences have developed in Europe, where they number well over 1 million, and in Russia, they number over 200,000, concentrated in the Russian Far East. Russia's main Pacific port and naval base of Vladivostok, once closed to foreigners and belonged to China until the late 19th century, as of 2010[update] bristles with Chinese markets, restaurants and trade houses. A growing Chinese community in Germany consists of around 76,000 people as of 2010[update].[28] An estimated 15,000 to 30,000 Chinese live in Austria.[29]Japanese diaspora
[edit]
Korean diaspora
[edit]
South Asian diaspora
[edit]
History
[edit]Ancient era
[edit]Some South Asians lived in other parts of the world for trade purposes. During the Roman Empire, a few South Asians came to Europe.
Medieval era
[edit]Romani people
[edit]Colonial era
[edit]
During the colonial era, over 1 million South Asians were taken to other parts of the world as indentured servants. South Asians also were brought to parts of Southeast Asia as part of the British Empire.
Diaspora members played a significant role in opposing the British Raj as part of the Ghadar Movement.
Some South Asians, mainly from Punjab, migrated to the West Coast in the United States, and mixed with the local Mexican community.
Contemporary era
[edit]South Asians have emigrated in record numbers since the end of the colonial era in the middle of the 20th century. Many South Asians migrated to the United Kingdom and participated in its post-war economic recovery. Some South Asians went to the Middle East for labour opportunities, though some were mistreated in a racist manner and exploited. After the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 that allowed nonwhite immigration was passed, Indian-Americans became the richest ethnic group in the United States, and comprise over 10% of the labour force in computing-related fields.
Because South Asians had already dispersed across the world during the colonial era, a noted aspect of the diaspora is that it has produced several secondary diasporas - some of its members' families transited through several countries over generations to reach a final destination (e.g. a person's ancestors may have come from India to Africa, and then a few generations later from Africa to New Zealand).Romani people
[edit]Southeast Asian diaspora
[edit]There has been Southeast Asian migration to France since the French Indochina period. Since 1975, there has been a mass resettlement of refugees from Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam, primarily in France and the United States.[43]
Malaysian diaspora
[edit]The Malaysian diaspora are Malaysian emigrants from Malaysia and their descendants that reside in a foreign country. The population estimates close to two million, both descendants of early emigrants from Malaysia, as well as more recent emigrants from Malaysia. The largest of these foreign communities are in Singapore, Australia, Brunei and the United Kingdom.
Emigration from Malaysia is a complex demographic phenomenon existing for decades and having a number of reasons, with institutional racism being one of the major factors. The process is the reverse of the immigration to Malaysia. Malaysia does not keep track of emigration, and counts of Malaysians abroad are thus only available courtesy of statistics kept by the destination countries. As of 2019, according to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the population of the Malaysian diaspora stands at 1,730,152.[44]Filipino diaspora
[edit]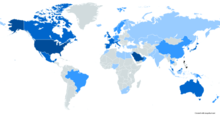
Thai diaspora
[edit]Overseas Thai people (Thai: คนไทยพลัดถิ่น, คนไทยในต่างแดน) number approximately 1.1 million persons worldwide. They can be roughly divided into two groups:
A "non-resident Thai" is a citizen of Thailand who holds a Thai passport and has temporarily emigrated to another country for employment, residence, education or any other purpose. The Bank of Thailand estimates that, as of 2016[update], 1,120,837 Thais worked overseas.[46]Vietnamese diaspora
[edit]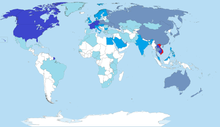
Overseas Vietnamese (Vietnamese: người Việt hải ngoại, Việt kiều or kiều bào) are Vietnamese people who live outside Vietnam. There are approximately 5 million overseas Vietnamese, the largest community of whom live in the United States.
The term Việt Kiều is used by people in Vietnam to refer to Vietnamese living outside the country and is not a term of self-identification.[47] However, many overseas Vietnamese also use the terms Người Việt hải ngoại ('Overseas Vietnamese'), which is also a neutral term, or Người Việt tự do ('free Vietnamese'), which has a political note.[48]
West Asian diaspora
[edit]Arab diaspora
[edit]
Arab diaspora is a term that refers to descendants of the Arab emigrants who, voluntarily or as forcibly, migrated from their native lands to non-Arab countries, primarily in the Americas, Europe, Southeast Asia, and West Africa.
Immigrants from Arab countries, such as Lebanon, Syria and the Palestinian territories, also form significant diasporas in other Arab states.Iranian diaspora
[edit]
This article may be confusing or unclear to readers. (July 2021) |
The Iranian diaspora (collectively known as Iranian expats or expatriates) is the global population of Iranian citizens or people of Iranian descent living outside Iran.[49]
In 2021, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Iran published statistics which showed that 2 to 4,037,258 Iranians are living abroad, an increase from previous years.Though many of these people are of Iranian ancestry in UAE, Kuwait, Israel, Turkey and Bahrain, not necessarily recent migrants but people who moved out hundreds of years ago or at least prior to the revolution. These numbers also include half and people with only partial ancestry as well. [50][51] Over one million of these people and their extended families live in the United States, with anywhere between 100k-500k living in countries such as Australia, Canada, Germany, Israel, Sweden, Turkey, and the United Kingdom. Further populations exist in numerous other regions, including many European nations, China, India, and the United Arab Emirates, along with several other Middle Eastern and Levantine nations.[52][53] Many of these individuals relocated to other countries following the Iranian Revolution of 1979.[54][55]
Iran has experienced waves of emigration since 1979. The creation of a ministry of immigration has been proposed, after reports indicated critical statistics, largely due to political instability.[56][57][58]Jewish diaspora
[edit]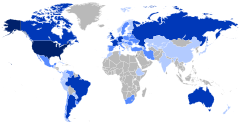
The Jewish diaspora (Hebrew: גוֹלָה, romanized: gōlā), dispersion (Hebrew: תְּפוּצָה, romanized: təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: גָּלוּת gālūṯ; Yiddish: golus)[a] is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of the globe.[61][62]
In terms of the Hebrew Bible, the term "Exile" denotes the fate of the Israelites who were taken into exile from the Kingdom of Israel during the 8th century BCE, and the Judahites from the Kingdom of Judah who were taken into exile during the 6th century BCE. While in exile, the Judahites became known as "Jews" (יְהוּדִים, or Yehudim).[63][64]
The first exile was the Assyrian exile, the expulsion from the Kingdom of Israel begun by Tiglath-Pileser III of Assyria in 733 BCE. This process was completed by Sargon II with the destruction of the kingdom in 722 BCE, concluding a three-year siege of Samaria begun by Shalmaneser V. The next experience of exile was the Babylonian captivity, in which portions of the population of the Kingdom of Judah were deported in 597 BCE and again in 586 BCE by the Neo-Babylonian Empire under the rule of Nebuchadnezzar II.Turkish diaspora
[edit]
The Turkish diaspora (Turkish: Türk diasporası or Türk gurbetçiler) refers to ethnic Turkish people who have migrated from, or are the descendants of migrants from, the Republic of Turkey, Northern Cyprus or other modern nation-states that were once part of the former Ottoman Empire. Therefore, the Turkish diaspora is not only formed by people with roots from mainland Anatolia and Eastern Thrace (i.e. the modern Turkish borders); rather, it is also formed of Turkish communities which have also left traditional areas of Turkish settlements in the Balkans (such as Bulgaria, Greece, North Macedonia, Romania, etc.), the island of Cyprus, the region of Meskhetia in Georgia, and the Arab world (such as Algeria, Iraq, Lebanon).
In particular, most mainland Turkish migration has been to Western and Northern Europe. Meanwhile, almost all the Turkish minorities in former Ottoman lands have a large diaspora in Turkey, many having migrated as muhacirs (refugees); furthermore, the Cretan Turks have migrated throughout the Levant; Cypriot Turks have a significant diaspora in the English-speaking countries (especially the UK and Australia); the Meskhetian Turks have a large diaspora in Central Asia; and Algerian Turks and Tunisian Turks have mostly settled in France. Since Bulgarian Turks and Romanian Turks gained EU citizenship in 2007, their diasporas in Western Europe significantly increased once restrictions on movement came to a halt in 2012.See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Other Ashkenazic- or Yiddish-based variants include galus, goles and golus.[59] A Hebrew-based variant spelling is galuth.[60]
References
[edit]- ^ Parreñas, Rhacel S.; Siu, Lok C.D., eds. (2007-11-30), "Asian Diasporas: New Formations, New Conceptions", Asian Diasporas, Stanford University Press, doi:10.1515/9780804767828, ISBN 978-0-8047-6782-8, S2CID 246220255, retrieved 2023-11-09
- ^ Goh, Robbie B. H.; Wong, Shawn (2004-03-01). Asian Diasporas: Cultures, Indentity, Representation. Hong Kong University Press. ISBN 978-962-209-672-1.
- ^ "Introduction: Theorizing the Asian Diaspora". Retrieved 2023-11-09.
- ^ Cunningham, Stuart; Sinclair, John (2001). Floating Lives: The Media and Asian Diasporas. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7425-1136-1.
- ^ Um, Hae-kyung (2004-11-04). Diasporas and Interculturalism in Asian Performing Arts: Translating Traditions. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-78990-9.
- ^ Amrith, Sunil S. (2011-03-07). Migration and Diaspora in Modern Asia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-49703-9.
- ^ "Transnationalism and diaspora in Central Asia and the Caucasus". Central Asia and the Caucasus.
- ^ "Digital media and East Asian diaspora". Routledge Handbook of Asian Diaspora and Development. ISBN 9780429352768.
- ^ Goodkind, Daniel. "The Chinese Diaspora: Historical Legacies and Contemporary Trends" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-02-20. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ Poston, Dudley; Wong, Juyin (2016). "The Chinese diaspora: The current distribution of the overseas Chinese population". Chinese Journal of Sociology. 2 (3): 356–360. doi:10.1177/2057150X16655077. S2CID 157718431.
- ^ "Yearbook of Immigration Statistics: 2012 Supplemental Table 2". U.S. Department of Homeland Security. Archived from the original on 3 April 2013. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- ^ "Yearbook of Immigration Statistics: 2011 Supplemental Table 2". U.S. Department of Homeland Security. Archived from the original on 8 August 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2013.
- ^ "Yearbook of Immigration Statistics: 2010 Supplemental Table 2". U.S. Department of Homeland Security. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2013.
- ^ John Marzulli (9 May 2011). "Malaysian man smuggled illegal Chinese immigrants into Brooklyn using Queen Mary 2: authorities". New York: NY Daily News.com. Archived from the original on 5 May 2015. Retrieved 27 April 2013.
- ^ "Chinese New Year 2012 in Flushing". QueensBuzz.com. 25 January 2012. Archived from the original on 30 March 2013. Retrieved 2 May 2013.
- ^ "Selected Population Profile in the United States 2017 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates New York–Newark, NY-NJ-CT-PA CSA Chinese alone". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 27 January 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Han, Enze (2024). The Ripple Effect: China's Complex Presence in Southeast Asia. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-769659-0.
- ^ Pan, Lynn, ed. (1999). "Huaqiao". The Encyclopedia of the Chinese Overseas. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674252101. LCCN 98035466. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 17 March 2009.
- ^ The Story of California From the Earliest Days to the Present, by Henry K. Norton. 7th ed. Chicago: A.C. McClurg & Co., 1924. Chapter XXIV, pp. 283–296.
- ^ Displacements and Diaspora. Rutgers University Press. 2005. ISBN 9780813536101. JSTOR j.ctt5hj582.
- ^ Baten, Jörg (November 2008). "Anthropometric Trends in Southern China, 1830–1864". Australian Economic History Review. 43 (3): 209–226. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8446.2008.00238.x.
- ^ "Chiang Kai Shiek". Sarawakiana. Archived from the original on 6 December 2012. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ^ Yong, Ching Fatt. "The Kuomintang Movement in British Malaya, 1912–1949". University of Hawaii Press. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2013.
- ^ Tan, Kah Kee (2013). The Making of an Overseas Chinese Legend. World Scientific Publishing Company. doi:10.1142/8692. ISBN 978-981-4447-89-8.
- ^ Jan Voon, Cham (2002). "Kuomintang's influence on Sarawak Chinese". Sarawak Chinese political thinking : 1911–1963 (master thesis). University of Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS). Retrieved 28 August 2012. [permanent dead link]
- ^ Wong, Coleen (10 July 2013). "The KMT Soldiers Who Stayed Behind In China". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2013.
- ^ French, Howard (November 2014). "China's Second Continent: How a Million Migrants Are Building a New Empire in Africa". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 6 November 2021. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- ^ "Deutsch-Chinesisches Kulturnetz". De-cn.net (in German). Archived from the original on 13 April 2012. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- ^ "Heimat süßsauer" (PDF). Eu-china.net (in German). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-07-21. Retrieved 27 May 2018.
- ^ "Ancient Japanese pottery in Boljoon town". 30 May 2011.
- ^ Manansala, Paul Kekai (5 September 2006). "Quests of the Dragon and Bird Clan: Luzon Jars (Glossary)".
- ^ Cole, Fay-Cooper (1912). "Chinese Pottery in the Philippines" (PDF). Field Museum of Natural History. Anthropological Series. 12 (1).
- ^ "Philippines History, Culture, Civilization and Technology, Filipino". asiapacificuniverse.com.
- ^ さや・白石; Shiraishi, Takashi (1993). The Japanese in Colonial Southeast Asia. SEAP Publications. ISBN 9780877274025.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA), Japan: Japan-Mexico relations
- ^ Palm, Hugo. "Desafíos que nos acercan," Archived 15 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine El Comercio (Lima, Peru). 12 March 2008.
- ^ Azuma, Eiichiro (2005). "Brief Historical Overview of Japanese Emigration". International Nikkei Research Project. Archived from the original on 19 February 2007. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
- ^ 재외동포현황(2021)/Total number of overseas Koreans (2021). South Korea: Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 2021. Archived from the original on February 24, 2021. Retrieved 2022-08-21.
- ^ Schwekendiek, Daniel (2012). Korean Migration to the Wealthy West. New York: Nova Publishers.
- ^ "The Desi Diaspora: Politics, Protest, and Nationalism". academic.oup.com. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ^ Rai, Rajesh; Reeves, Peter (2008-07-25). The South Asian Diaspora: Transnational Networks and Changing Identities. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-10595-3.
- ^ Shah, Muhammad Hamza; Roy, Sakshi; Ahluwalia, Arjun (2023). "Time to address the mental health challenges of the South Asian diaspora". The Lancet Psychiatry. 10 (6): 381–382. doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(23)00144-x. ISSN 2215-0366.
- ^ "Diasporic identities: Southeast Asian incorporation experiences in Europe and America. The post-refugee generations | Sciences Po CERI". sciencespo.fr. 2018-02-19. Retrieved 2024-10-11.
- ^ "International migrant stock 2019". United Nations. Retrieved June 25, 2020.
Figures includes Malaysians in UN member nations
- ^ "Remittances from Filipinos abroad reach 2.9 bln USD in August 2019 - Xinhua | English.news.cn". www.xinhuanet.com. Archived from the original on October 15, 2019.
- ^ Rujivanarom, Pratch (2017-12-23). "Thais working abroad prone to exploitation". The Nation. Retrieved 8 May 2018.
- ^ Ines M. Miyares, Christopher A. Airriess (2007). Contemporary ethnic geographies in America. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7425-3772-9.
- ^ Jonathan H. X. Lee; Kathleen M. Nadeau, eds. (2010). Encyclopedia of Asian American Folklore and Folklife. ABC-CLIO. p. 1219. ISBN 9780313350672.
- ^ "Diaspora". Iranicaonline.org. Encyclopædia Iranica. December 15, 1995. pp. 370–387. Archived from the original on 9 February 2015. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-06-05. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "آمار پراکندگی ایرانیان مقیم خارج از کشور + نمودار". Gostaresh.news. Retrieved 2022-08-05.
- ^ Esfandiari, Golnaz (2004-03-08). "Iran: Coping With The World's Highest Rate Of Brain Drain". Rferl.org. Archived from the original on 2008-04-29. Retrieved 2012-12-10.
- ^ "Migration Information Source - Iran: A Vast Diaspora Abroad and Millions of Refugees at Home". Migrationinformation.org. Archived from the original on 2014-02-15. Retrieved 2012-12-10.
- ^ Saeed Zeydabadi-Nejad, The Politics of Iranian Cinema: Film and Society in the Islamic Republic, Routledge (2009), p. 17
- ^ Bagherpour, Amir (September 12, 2020). "The Iranian Diaspora in America: 30 Years in the Making". Frontline. Tehran Bureau, PBS.
- ^ اقتصاد24, پایگاه خبری، تحلیلی. "افزایش بی سابقه موج مهاجرت ایرانیان در سال ۱۴۰۲ | اقتصاد24". fa (in Persian). Retrieved 2024-04-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ https://farsi.alarabiya.net/iran/2023/09/13/%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%86-%D9%85%D9%87%D8%A7%D8%AC%D8%B1%D8%AA-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%A7%DB%8C%D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%86%D8%9B-%D9%86%D9%88%D8%A8%D8%AA-%D8%A8%D9%87-%D8%B7%D8%A8%D9%82%D9%87-%D9%85%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%B3%D8%B7-%D8%B1%D8%B3%DB%8C%D8%AF
- ^ "بیسابقهترین موج مهاجرت از ایران/ وزارتخانه مهاجرت تشکیل میشود؟". تجارت نیوز (in Persian). 2024-04-11. Retrieved 2024-04-11.
- ^ "golus". Jewish English Lexicon.
- ^ "galuth". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.: “Etymology: Hebrew gālūth”
- ^ "Diaspora | Judaism". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2018-07-12.
- ^ Ben-Sasson, Haim Hillel. "Galut." Encyclopaedia Judaica, edited by Michael Berenbaum and Fred Skolnik, 2nd ed., vol. 7, Macmillan Reference (US) 2007, pp. 352–63. Gale Virtual Reference Library
- ^ "Jew | History, Beliefs, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. 2024-07-03. Retrieved 2024-07-06.
- ^ Chouraqui, André (1975). The people and the faith of the Bible. Internet Archive. Amherst : University of Massachusetts Press. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-87023-172-8.