Violanthrone
Appearance

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Anthra[10,1,2-cde]benzo[rst]pentaphene-5,10-dione | |
| Other names
Dibenzanthrone, Tinon Dark Blue BOA, Ahcovat Dark Blue BO, Violanthrone A, Bianthrone A, Irgalite Blue 2R, Paradone Dark Blue
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.775 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C34H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 456.48964 |
| Appearance | dark blue solid |
| Density | 1.53 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 492 °C (decomposes) |
| -204.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Violanthrone, also known as dibenzanthrone, is an organic compound that serves as a vat dye and a precursor to other vat dyes. X-ray crystallography confirms that the molecule is planar with C2v symmetry.[1] Isomeric with violanthrone is isoviolanthrone, which has a centrosymmetric structure.[2]
Synthesis
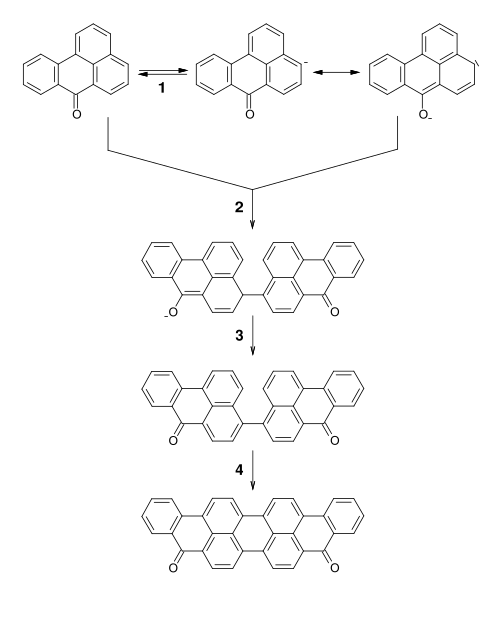
[edit]It is produced by coupling of two molecules of benzanthrone.[3][4][5][6]
References
[edit]- ^ Bolton, W.; Stadler, H. P. (1964). "The Crystal Structure of Violanthrone (Dibenzanthrone)". Acta Crystallographica. 17 (8): 1015–1020. Bibcode:1964AcCry..17.1015B. doi:10.1107/S0365110X64002584.
- ^ Bien, H.-S.; Stawitz, J.; Wunderlich, K. "Anthraquinone Dyes and Intermediates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_355. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Manufacture of dibenzanthrone compounds
- ^ Heinrich Zollinger, Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments, 3rd edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3, p. 291
- ^ CN patent 106243769, Wang Hongwei, Xu Huixiang, Li Zhen, Jiang Dawei, Gao Hongyu, Guo Yuan, "A kind of preparation method of Vat Brilliant Green FFB"
- ^ Aoki, Junji (December 1961). "Studies of Violanthrone B. I. Reduction and Oxidation of Violanthrone B". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan. 34 (12): 1817–1819. doi:10.1246/bcsj.34.1817.