Vehicle registration plates of Russia
Vehicle registration plates are the mandatory number plates used to display the registration mark of a vehicle, and have existed in Russia for many decades. Most motor vehicles which are used on public roads are required by law to display them. Having a number plate obstructed by snow, mud, paper, or any other tool that makes any of the digits and letters illegible is considered an administrative offense and results in a fine.
History
[edit]Current plate format
[edit]

The current format uses a letter followed by 3 digits and two more letters. To improve legibility of the numbers for Russian cars abroad, only a small subset of Cyrillic characters that look like Latin characters are used (12 letters: А, В, Е, К, М, Н, О, Р, С, Т, У, Х), additionally D was issued on some very early plates.[1] Finally, the region number (77, 97, 99, 177, 197, 199, 777, 797 and 799 for Moscow; 78, 98, 178, and 198 for Saint Petersburg, etc.) and the international code RUS with the 1991 to 1993 Russian flag typically to the right of it, however the flag is not mandatory, and since 2013 owners may order plates without it.[2]
There is a different format for trailers (2 letters and 4 digits). Motorcycles, mopeds and scooters plates are made of square reflective plates and its format is 4 digits at the top and two letters at the bottom. These plates lack a national flag.
The standard size for the license plate is 520 mm by 112 mm.
Vehicles used by certain organisations or categories of persons carry special plates:
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
| Police forces have special numbers on blue colored plates and the format is one letter and four digits. The letter signifies the branch of the police force, and its meaning may change from city to city; for example, in Moscow, A #### 99 rus stands for traffic police, У #### 99 rus for patrol cars, O #### 99 rus for police guard dog service etc. | |
| Diplomatic cars have white characters on a red background. The first three digits on the plate are a code identifying the embassy to which they belong, assigned in order based on the date at which that country established diplomatic relations with Russia or the Soviet Union. For example, the United Kingdom is 001, the United States is 004, and South Sudan is 168. Numbers 500 and above identify international organizations, such as 505 for IMF. On ambassadors' cars this code is followed by CD and a digit (004 CD 1 77 rus), while cars assigned to rank-and-file diplomats have this code followed by D and three digits (for example, 004 D 108 77 rus). The lacking diplomatic status administrative and technical staff of embassies, consulates or international organizations have license plate format (004 T 001 77 rus). | |
| The military license plates have white characters on a black background and the format is NNNN LL for vehicles and LL NNNN for trailers. In this case the two digits on the right are not a regional code but a code for the military district, armed forces branch or service, or federal executive body where military service is required by law. For example, NNNN LL 14 rus is a vehicle belonging to the Railway Troops, NNNN LL 18 rus denotes the Ministry of Emergency Situations, NNNN LL 23 rus is for the Strategic Missile Troops, NNNN LL 21 rus for the Southern Military District etc. Unlike all other categories, the military number plates are not light reflective.[3] | |
| Public transport vehicles (such as buses, licensed taxis and licensed share taxis) have black characters on a yellow background and the format is LL NNN. Since such vehicles are relatively few, the region code does not change often; in Moscow, for example, yellow "public transport" plates are still issued with the code 77 in December 2009.[a] | |
| Trailer plates have colors very similar to normal passenger vehicles, but have format LL NNNN. Until July 2008, these plates had to be duplicated on the rear surface of the trailer, in a large print. | |
| Temporary and transit licence plates. Made from glossy laminated paper with holographic sticker in the upper left corner. | |
| Temporary and transit licence plates for exported vehicles with Т digit in left part of plate. | |
 
|
Motorcycle registration plates. From 2019 updated standard introduced reduced size plates 190 mm (7.5 in)x145 mm (5.7 in) (with Russian national flag on it). |
Special plates in the above categories never carry the Russian flag, except for trailers.
There are special series (usually numbers starting with A) reserved for government officials (for example, A 001 AA usually belongs to the governor of the region). The license plates for federal government officials originally had a larger flag instead of the regional code but this type has now been withdrawn as well.
Rich businessmen, prominent politicians and crime lords often use para-legally acquired special licence plates (government or police) to get preferential treatment from the transport police and as a status symbol. Often, this is used in conjunction with a flashing siren. The Society of Blue Buckets is a protest movement that opposes this trend.[4]
As of 2014, there are new codes for Russian plates in occupied territories; number 82 for the Republic of Crimea and 92 for Sevastopol. The Russian Federation annexed Crimea from Ukraine and now administers it as two federal subjects: the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol. Ukraine, backed by most of the international community, refuses to accept the annexation and continues to assert its right over the peninsula. Vehicles with such plates may have difficulty entering countries which recognize Crimea as Ukrainian territory and thus deem documents issued by the Russian Federation in Crimea to be invalid.[citation needed]
After Russia's February 2022 escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, Russia began issuing license plates for its conquered territories in Ukraine's Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporizhzhia oblasts. It also began to issue plates numbered 188 in Kupiansk for the Kharkiv Oblast,[5] but its forces were pushed out of the oblast's territory during the Kharkiv counteroffensive in the fall of 2022.
Runout problem
[edit]As per GOST provision, only 1,726,272 combinations may be issued within one administration unit (the digits 000 are not allowed). In certain regions, the number of vehicles exceeds that number. Additionally, previous combinations cannot be reused after a vehicle has been de-registered. This scheme creates an issue where the number of possible license plate combinations cannot meet the demand of the number of vehicle registrations.
A short-term solution saw the introduction of additional codes for regions that suffered from this problem. Thus, some regions have two or three codes issued to them, the city of St. Petersburg has four, Moscow Oblast has six, and the federal city of Moscow has ten codes. But this does not fully solve the problem, as the authorities may eventually run out of three-numeral regional codes, and a fourth digit will not fit without changing the standardised layout of the plate.[citation needed] Since October 2013, when a vehicle is registered to a new owner, the registration plate could remain on the vehicle and a new registration number is not required, even if the vehicle is registered in another region.
The problem was resolved by re-registering plates that are no longer in use. Also, since 2013, the owner can keep the license plate for himself personally, or leave it on the car when selling it to another person.
Regional codes
[edit]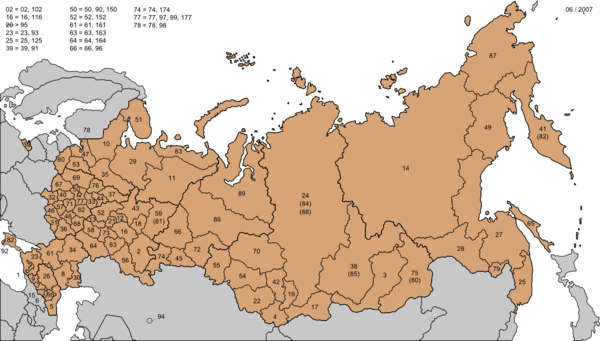
The license plate regional codes from 01 to 89 originally matched the numerical order of the federal subjects of Russia as listed in the Article 65 of the Constitution of Russia at the moment of the creation of the standard. In the following years some codes were reassigned or discontinued (for example code number 20 for the Chechen Republic: to prevent illegal registrations, and due to the destruction of the database in the 1990s, all the vehicles of Chechnya were reregistered). As the populous regions started running out of license plate combinations, new codes past code 89 were assigned to them as well. Additional triple-digit codes were created by prepending a "1", "2", "7", or "9" to the existing regional code (e.g. 54 and 154 for Novosibirsk Oblast, or 16, 116 and 716 in Tatarstan).[6] Those regions with an asterisk (*) beside them were involved in mergers with other regions, so are no longer issued, and have their codes listed with an asterisk with the region they are now a part of.

In June 2014, code 82 (formerly registered to the Koryak Autonomous District) was put back into registration for the Republic of Crimea, while Sevastopol adopted the new code 92. The reason for the decision to use code 82 was because, between the beginning of this plate format and the merging of the district, Koryak AO only registered 1,548 civilian car license plates (starting at A001AA/82 and ending at B549AA/82) and far less of other types (some types, such as public transport plates, were never issued in the region).
Codes of diplomatic representative offices and international organizations
[edit]

According to the Ministry of Internal Affairs Order 282 from March 28, 2002.[7]
See also
[edit]- Vehicle registration plate
- Vehicle registration plates of Bulgaria, which uses similar letters and numbers
- European vehicle registration plates
Notes
[edit]- ^ This type is not to be confused with the now defunct similar-looking yellow license plates having the format LL NNN L, which were issued prior to 2002 to cars registered to foreign companies operating in Russia; the latter type has now been withdrawn.
- ^ Abolished in 2000 and superseded by 95; all vehicles bearing license plates with this regional code were subject to mandatory re-registration
- ^ a b Previosly belonged to Taymyr Autonomous Okrug, which became part of Krasnoyarsk Krai in 2007
- ^ Previosly belonged to Evenk Autonomous Okrug, which became part of Krasnoyarsk Krai in 2007
- ^ a b Previosly belonged to Ust-Orda Buryat Autonomous Okrug, which became part of Irkutsk Oblast in 2008
- ^ Transit license plates only
- ^ a b Previosly belonged to Koryak Autonomous Okrug, which was merged with Kamchatka Oblast in 2007
- ^ a b Previosly belonged to Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug, which was merged with Perm Oblast in 2005
- ^ a b Previosly belonged to Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug, which was merged with Chita Oblast in 2008
- ^ a b Trailers and motorcycles only
- ^ Code 059 is a former code for Syria. The current code for Syria is 133.
- ^ Code 092 is a former code for Czechoslovakia. Currently, codes for Czech Republic and Slovakia are 148 (Czech Republic), and 149 (Slovakia).
- ^ Code 106 is a former code for the Central African Republic. The current code for the Central African Republic is 103.
- ^ Earlier, code 111 belonged to the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance. Replaced by the Sovereign Military Order of Malta.
- ^ Code 119 is a former code for South Africa. The current code for South Africa is 137.
- ^ Code 122 is a former code for the Arab League. The current code for the Arab League is 503.
- ^ Code 123 is a former code for Liechtenstein.
- ^ Earlier, code 126 belonged to UNESCO. Replaced by Panama.
- ^ Earlier, code 128 belonged to the European Union. Replaced by North Macedonia.
- ^ Code 130 is a former code for the International Organizations.
- ^ Code 139 is a former code for Georgia. The current code Georgia is 158.
- ^ Code 501 is a former code for the Un International Centre.
- ^ Code 502 is a former code for the Eurocommision. The current code for this organization is 499.
- ^ Code 518 is a former code for the International Scientific and Technical Centre
- ^ Code 521 is a former code for the Interelectro (International Organization for Economic, Scientific and Technical Cooperation in Electrical Industry)
- ^ Code 526 is a former code for the Taipei-Moscow Coordination Commission for Economic and Cultural Cooperation
- ^ Code 527 is a former code for the Headquarters for Coordination of Military Cooperation of the CIS
- ^ Code 529 is a former code of the Eurasian Economic Community (earlier - Integration Committee of the Eurasian Economic Community)
References
[edit]- ^ "Буква «D» на автомобильном номере в России – что это значит?". dzen.ru (in Russian). Retrieved March 13, 2023.
- ^ "Номер без флага: зачем он нужен и сколько стоит". autonews.ru (in Russian). Retrieved March 13, 2023.
- ^ "Russian plates information". Matriculasdelmundo.com (in Spanish). Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- ^ Elder, Miriam (May 28, 2010). "Moscow's limos halted by blue buckets". The Guardian. London.
- ^ "Жителям Харьковской области будут выдавать номера автомобилей с кодом 188". РБК (in Russian). August 26, 2022. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- ^ "Ministry of Internal Affairs Order 282 from March 28, 2002 - Приказ МВД России от 28.03.2002 N 282 (ред. от 22.12.2014) "О государственных регистрационных знаках транспортных средств"". Archived from the original on March 6, 2016. Retrieved March 3, 2016.
- ^ "Приказ МВД России от 28.03.2002 N 282 (ред. от 22.12.2014) "О государственных регистрационных знаках транспортных средств"" [Russian MVD Order 282 of March 28, 2002] (in Russian). Moscow, Russia: Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation. December 22, 2014. Retrieved May 7, 2015.

