Vanda hindsii
| Native strap orchid | |
|---|---|

| |
| Illustration by Lewis Roberts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Epidendroideae |
| Genus: | Vanda |
| Species: | V. hindsii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Vanda hindsii | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
Vanda hindsii, commonly known as the native strap orchid[4] or the Cape York vanda,[1] is a large epiphytic or lithophytic clump-forming orchid. It has thick, white, cord-like roots, branching stems, many thick, leathery, strap-like leaves and between three and seven shiny brown flowers with greenish to yellow markings and a white labellum. This orchid occurs in New Guinea and tropical North Queensland.
Description
[edit]Vanda hindsii is an epiphytic or lithophytic herb that forms large, coarse clumps with thick, white, cord-like roots and branching stems up to 1 metre (3.3 ft) long. There are many thick, leathery, glossy, strap-like leaves 200–400 millimetres (7.9–16 in) long and 30–40 millimetres (1.2–1.6 in) wide arranged in two ranks along the stems. Between three and seven brown resupinate flowers with greenish to yellowish markings, 30–35 millimetres (1.2–1.4 in) long and wide are arranged on a stiff flowering stem 100–200 millimetres (3.9–7.9 in) long. The sepals are 14–16 millimetres (0.55–0.63 in) long and 8–10 millimetres (0.31–0.39 in) wide, the petals about the same length but narrower. The labellum is white, 12–14 millimetres (0.47–0.55 in) long and 7–8 millimetres (0.28–0.31 in) wide with three lobes. The side lobes are erect and curved and the middle lobe is about 7 millimetres (0.28 in) long with a notched tip and a spur about 4 millimetres (0.16 in) long. Flowering mainly occurs from November to March.[4][5][6]
Taxonomy and naming
[edit]Vanda hindsii was first formally described in 1843 by John Lindley and the description was published in the London Journal of Botany from a specimen collected by Richard Brinsley Hinds.[7][8] The specific epithet (hindsii) honours the collector of the type specimen.[7]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The native strap orchid grows on trees and rocks in humid forests. It only occurs in New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Queensland where it is found in the Carron Valley, Iron Range and McIlwraith Range.
Conservation status
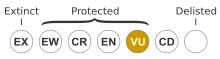
[edit]The global assessment of the conservation status of this orchid in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is "least concern",[2] but it is listed as "vulnerable" in Australia under the Australian Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999[1] and the Queensland Government Nature Conservation Act 1992.[9]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Approved Conservation Advice for Vanda hindsii (Cape York Vanda)" (PDF). Australian Government Department of the Environment. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ a b "Vanda hindsii". IUCN Red List. Retrieved 11 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Vanda hindsii". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 20 June 2023.
- ^ a b Jones, David L. (2006). A complete guide to native orchids of Australia including the island territories. Frenchs Forest, N.S.W.: New Holland. p. 459. ISBN 1877069124.
- ^ "Vanda hindsii". Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ^ "Vanda hindsii". Orchids of New Guinea. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ a b Lindley, John (1843). "Enumeration of the plants collected by R.B. Hinds, Esq., and by Mr Barclay in the Feejee Islands, Tanna, New Ireland and New Guinea". London Journal of Botany. 2: 237–238. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ "Vanda hindsii". APNI. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ "Cape York vanda – Vanda hindsii". The State of Queensland Department of Environment and Science. Retrieved 9 January 2019.