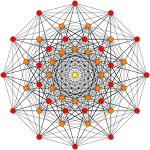
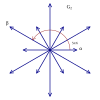
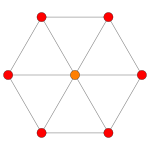
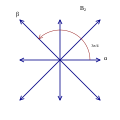
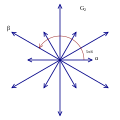
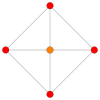
Rank 2 Root Space Diagrams
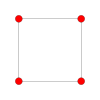
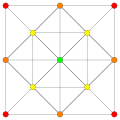
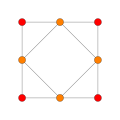
B2 and C2 , identical by a 45 degree rotation, each with 4 short roots, and 4 long ones.
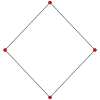
A2 , with 6 roots.
G2 , with 6 short roots and 6 long roots.
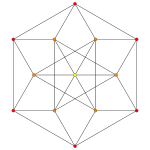
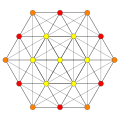
A partial subgroup tree for E8 showing symmetry relations possible within root space diagrams In mathematics , a root space diagram is a geometric diagram showing the root system vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties.
The root system of the simply-laced Lie groups ,
A
n
{\displaystyle A_{n}}
D
n
{\displaystyle D_{n}}
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}}
uniform polytopes of the same symmetry group. A root space diagram corresponds to projected images of these polytope vertices. The
A
n
{\displaystyle A_{n}}
expanded n -simplex . The
D
n
{\displaystyle D_{n}}
rectified n-orthoplex . The
E
6
,
E
7
,
E
8
{\displaystyle E_{6},E_{7},E_{8}}
122 , 231 , and 421 uniform polytopes respectively.
For the nonsimply-laced groups,
B
n
{\displaystyle B_{n}}
C
n
{\displaystyle C_{n}}
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
F
4
{\displaystyle F_{4}}
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
hexagons , with the vertices of the second hexagon at the mid-edges of the first hexagon. The
F
4
{\displaystyle F_{4}}
24-cell in dual positions, with the vertices of the second 24-cell being at the tetrahedral facet centers of the first. Finally the
B
n
{\displaystyle B_{n}}
C
n
{\displaystyle C_{n}}
n -orthoplex, and a rectified n -orthoplex, alternating which set of vertices are the short and long ones. The
B
n
{\displaystyle B_{n}}
n vertices of the n-orthoplex as short vectors.
Construction from folding [ edit ] Foldings of simply-laced to nonsimply-laced groups The nonsimply-laced groups can also be seen as Geometric folding of higher rank simply-laced groups.
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
D
4
{\displaystyle D_{4}}
F
4
{\displaystyle F_{4}}
E
6
{\displaystyle E_{6}}
C
n
{\displaystyle C_{n}}
A
2
n
−
1
{\displaystyle A_{2n-1}}
B
n
{\displaystyle B_{n}}
D
n
+
1
{\displaystyle D_{n+1}}
orthogonal projection changes equal length vectors outside the projective subspace to become shortened, expressing the short roots.
Mapping of B2 from A3
Mapping of D4 from G2
Mapping of F4 from E6
B
2
{\displaystyle B_{2}}
A
3
{\displaystyle A_{3}}
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
D
4
{\displaystyle D_{4}}
F
4
{\displaystyle F_{4}}
E
6
{\displaystyle E_{6}}
The 8 root vectors of
B
2
{\displaystyle B_{2}}
A
3
{\displaystyle A_{3}}
The 12 root vectors of
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
D
4
{\displaystyle D_{4}}
The 48 root vectors of
F
4
{\displaystyle F_{4}}
F
6
{\displaystyle F_{6}}
The An root system can be seen as vertices of an expanded n-simplex. These roots can be seen as positioned by all permutations of coordinates of (1,-1,0,0,0...) in (n +1) space, with a hyperplane normal vector of (1,1,1...).
The Dn root system can be seen in the vertices of a rectified n-orthoplex , coordinates all sign and coordinate permutations of (1,1,0,0...). These vertices exist in 3 hyperplanes, with a rectified n-simplex as facets on two opposite sides (-1,-1,0,0...) and (1,1,0,0,0...), and a middle hyperplane with the vertex arrangement of a expanded n-simplex as coordinate permutations of (1,-1,0,0,0...).
The 240 roots of E8 can be constructed in two sets: 112 (22 ×8 C2 ) with coordinates obtained from
(
±
2
,
±
2
,
0
,
0
,
0
,
0
,
0
,
0
)
{\displaystyle (\pm 2,\pm 2,0,0,0,0,0,0)\,}
combination of signs and an arbitrary permutation of coordinates, and 128 roots (27 ) with coordinates obtained from
(
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
)
{\displaystyle (\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1)\,}
The E7 and E6 roots can be seen as subspaces of 8-space above.
The 48 roots of F4 can be constructed in three sets: 24 with coordinates obtained from
(
±
2
,
±
2
,
0
,
0
)
{\displaystyle (\pm 2,\pm 2,0,0)\,}
combination of signs and an arbitrary permutation of coordinates, 8 with coordinates permuted from
(
±
2
,
0
,
0
,
0
)
{\displaystyle (\pm 2,0,0,0)\,}
(
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
,
±
1
)
{\displaystyle (\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1,\pm 1)\,}
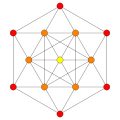
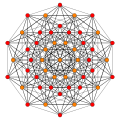
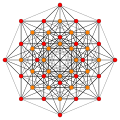
In the second set of diagrams, the roots are drawn as red circle symbols around an origin. The edges drawn correspond to the shortest edges of the corresponding polygons. In higher dimensional graphs roots may be overlapping in space in an orthogonal projection, so different colors are used by the order of overlap.
Rank 2 systems are simply drawn in a plane.
Lie group
2
A
1
{\displaystyle 2A_{1}}
D
2
{\displaystyle D_{2}}
A
2
{\displaystyle A_{2}}
B
2
{\displaystyle B_{2}}
C
2
{\displaystyle C_{2}}
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}}
Diagrams
Diagrams II
Polygon
square
Hexagon
Square+square
Hexagon+hexagon
Coxeter diagram
Roots
4
6
4+4
6+6
Dimensions
6
8
10
14
Symmetry order
4
6
8
12
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0\\0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
2
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-2\\-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
−
3
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-3&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0\\0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
−
1
2
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Rank 3 systems exist in 3-space, and can be drawn as oblique projection . Root system B3 , C3 , and A3 =D3 as points within a cuboctahedron and octahedron .
Lie group
3
A
1
{\displaystyle 3A_{1}}
E
3
{\displaystyle E_{3}}
A
2
A
1
{\displaystyle A_{2}A_{1}}
A
3
{\displaystyle A_{3}}
D
3
{\displaystyle D_{3}}
B
3
{\displaystyle B_{3}}
C
3
{\displaystyle C_{3}}
Diagrams
Diagrams II
Polyhedron
Octahedron
Hexagonal bipyramid
Cuboctahedron
cuboctahedron and octahedron
Coxeter diagram
Roots
6
8
12
6+12
12+6
Dimensions
9
11
15
21
Symmetry order
8
12
24
48
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0\\0&2&0\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&0\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
−
1
−
1
2
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&-1\\-1&2&0\\-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-2\\0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
1
−
1
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Roots in Coxeter plane orthographic projections
8 3A1 roots
12 A3 roots
BC2 plane
A2 plane
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
BC2 plane
A2 plane
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
18 B3 and C3 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC3 plane
BC2 plane
B4 roots
C4 roots
[6]
[4]
There are four unnconnected orthogonal subgroups:
3
A
1
{\displaystyle 3A_{1}}
A
2
+
A
1
{\displaystyle A_{2}+A_{1}}
B
2
+
A
1
{\displaystyle B_{2}+A_{1}}
G
2
+
A
1
{\displaystyle G_{2}+A_{1}}
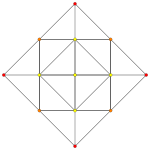
Four dimensional systems are drawn as 2-dimensional Coxeter plane orthographic projections
Lie group
4A1
A4 = E4
D4
B4
C4
F4
Projective
Polytope
16-cell
Runcinated 5-cell
Rectified 16-cell
Rectified 16-cell and 16-cell
24-cell and dual
Coxeter diagram
Roots
8
20
24
8+24
24+8
24+24
Dimensions
12
24
28
36
36
52
Symmetry order
16
24
192
384
1152
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0\\0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
0
−
1
2
0
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&-1\\0&-1&2&0\\0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-2&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0\\0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
0
−
1
/
2
−
1
/
2
−
1
/
2
1
/
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&0\\-1/2&-1/2&-1/2&1/2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
8 4A1 roots in Coxeter planes
BC4 plane
BC3 /D4 /A2 plane
BC2 /D3 plane
A3 plane
[8]
[6]
[4]
[4]
20 A4 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
A4 plane
A3 plane
A2 plane
Diagram
Plane
[[5]]=[10]
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
36 B4 and C4 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC4 plane
BC3 plane
BC2 plane
A3 plane
F4 plane
B4
C4
Plane
[8]
[6]
[4]
[4]
[12/3]
24 D4 roots in Coxeter plane orthographic projections
F4 plane
BC4 plane
D4 /BC3 plane
A2 plane
D3 /BC2 /A3 plane
[12]
[8]
[6]
[6]
[4]
48 F4 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
F4 plane
BC4 plane
BC3 /A2 plane
BC2 /A3 plane
Diagram
Plane
[12]
[8]
[6]
[4]
Others with orthogonal subgroups are generated by a sum of roots from each subgroup, including:
4
A
1
{\displaystyle 4A_{1}}
A
3
+
2
A
1
{\displaystyle A_{3}+2A_{1}}
B
3
+
2
A
1
{\displaystyle B_{3}+2A_{1}}
A
2
+
A
2
{\displaystyle A_{2}+A_{2}}
A
3
+
A
1
{\displaystyle A_{3}+A_{1}}
B
2
+
A
2
{\displaystyle B_{2}+A_{2}}
G
2
+
2
A
1
{\displaystyle G_{2}+2A_{1}}
B
2
+
B
2
{\displaystyle B_{2}+B_{2}}
G
2
+
A
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}+A_{2}}
B
3
+
A
1
{\displaystyle B_{3}+A_{1}}
C
3
+
A
1
{\displaystyle C_{3}+A_{1}}
G
2
+
B
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}+B_{2}}
G
2
+
G
2
{\displaystyle G_{2}+G_{2}}
Five dimensional systems are drawn as 2-dimensional Coxeter plane orthographic projections
Lie group
5A1
A5
D5 = E5
B5
C5
Projective
Polytope
5-orthoplex
Expanded 5-simplex
Rectified 5-orthoplex
Rectified 5-orthoplex and 5-orthoplex
Coxeter diagram
Roots
10
30
40
10+40
40+10
Dimensions
15
35
45
55
55
Symmetry order
32
120
1920
3840
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
30 A5 roots in Coxeter plane
A5 plane
A4 plane
A3 plane
A2 plane
[6]
[[5]]=[10]
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
55 B5 and C5 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC5 plane
BC4 plane
BC3 plane
BC2 plane
A3 plane
F4 plane
B5 roots
C5 roots
Plane
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[4]
[12/3]
30 D5 roots in Coxeter planes
BC5 /A4 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC3 /A2 plane
BC2 plane
A3 plane
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[4]
10 5A1 roots in Coxeter planes
BC5 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC3 /D4 /A2 plane
BC2 /D3 plane
A3 plane
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[4]
Six dimensional systems are drawn as 2-dimensional Coxeter plane orthographic projections:
Lie group
6A1
A6
D6
Projective
Polytope
6-orthoplex
Expanded 6-simplex
Rectified 6-orthoplex
Coxeter diagram
Roots
12
42
60
Dimensions
18
48
66
Symmetry order
64
720
23040
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Lie group
B6
C6
E6
Projective
Polytope
Rectified 6-orthoplex and 6-orthoplex
122
Coxeter diagram
Roots
12+60
60+12
72
Dimensions
78
78
78
Symmetry order
46080
51840
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
−
1
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
1
2
−
3
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&1&1&0\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {\sqrt {3}}{2}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
42 A6 roots in Coxeter planes
A6 plane
A5 plane
A4 plane
A3 plane
A2 plane
[[7]]=[14]
[6]
[[5]]=[10]
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
78 B6 and C6 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC6 plane
BC5 plane
BC4 plane
BC3 plane
B6 roots
C6 roots
Plane
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
Coxeter
BC2 plane
A5 plane
A3 plane
F4 plane
B6 roots
C6 roots
Plane
[4]
[6]
[4]
[12/3]
60 D6 roots in Coxeter planes
BC6 plane
BC5 /D6 /A4 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC3 /D4 /G2 /A2 plane
BC2 /D3 plane
A5 plane
A3 plane
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[6]
[4]
72 E6 roots in Coxeter planes
E6 /F4 plane
B5 /D6 /A4 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC3 /D4 /G2 /A2 plane
A5 plane
BC6 plane
BC2 /D3 /A3 plane
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
[6]
[12/2]
[4]
Seven dimensional systems are drawn as 2-dimensional Coxeter plane orthographic projections:
Lie group
7A1
A7
D7
Projective
Polytope
7-orthoplex
Expanded 7-simplex
Rectified 7-orthoplex
Coxeter diagram
Roots
14
56
84
Dimensions
21
63
91
Symmetry order
128
5040
322560
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Lie group
B7
C7
E7
Projective
Polytope
Rectified 7-orthoplex and 7-orthoplex
231
Coxeter diagram
Roots
14+84
84+14
126
Dimensions
105
105
133
Symmetry order
645,120
2,903,040
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
−
1
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
:
[
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
−
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}0&-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&1\\-{\sqrt {2}}&0&0&0&0&0&0\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{\sqrt {2}}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
56 A7 roots in Coxeter planes
A7 plane
A6 plane
A5 plane
A4 plane
A3 plane
A2 plane
[8]
[[7]]=[14]
[6]
[[5]]=[10]
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
105 B7 and C7 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC7 plane
BC6 plane
BC5 plane
BC4 plane
BC3 plane
B7 roots
C6 roots
Plane
[14]
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
Coxeter
BC2 plane
A5 plane
A3 plane
F4 plane
B7 roots
C6 roots
Plane
[4]
[6]
[4]
[12/3]
84 D7 roots in Coxeter planes
BC7 plane
BC6 /D7 plane
BC5 /D6 /A4 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC3 /D4 /G2 /A2 plane
BC2 /D3 plane
A5 plane
A3 plane
[14]
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[6]
[4]
126 E7 roots in Coxeter planes
E7
E6 /F4 plane
A6 /BC7 plane
A5 plane
D7 /BC6 plane
[18]
[12]
[7x2]
[6]
[12/2]
A4 /BC5 /D6 plane
D5 /BC4 plane
A2 /BC3 /D4 plane
A3 /BC2 /D3 plane
[10]
[8]
[6]
[4]
Eight dimensional root systems in Coxeter plane orthographic projections:
Lie group
8A1
A8
D8
Projective
Polytope
8-orthoplex
Expanded 8-simplex
Rectified 8-orthoplex
Coxeter diagram
Roots
16
72
112
Dimensions
24
80
120
Symmetry order
256
40,320
5,160,960
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Lie group
B8
C8
E8
Projective
Polytope
Rectified 8-orthoplex and 8-orthoplex
421
Coxeter diagram
Roots
16+112
112+16
112+128
Dimensions
136
136
248
Symmetry order
10,321,920
696,729,600
Dynkin diagram
Cartan matrix
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
2
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
−
1
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
2
0
0
0
−
1
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
Simple roots
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
−
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
[
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
−
1
1
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
−
1
2
]
{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&1\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}
72 A8 roots in Coxeter planes
A8 plane
A7 plane
A6 plane
A5 plane
A4 plane
A3 plane
A2 plane
[[9]]=[18]
[8]
[[7]]=[14]
[6]
[[5]]=[10]
[4]
[[3]]=[6]
136 B8 and C8 roots in Coxeter planes
Coxeter
BC8 plane
BC7 plane
BC6 plane
BC5 plane
BC4 plane
BC3 plane
B8 roots
C8 roots
Plane
[16]
[14]
[12]
[10]
[8]
[6]
Coxeter
BC2 plane
A7 plane
A5 plane
A3 plane
F4 plane
B8 roots
C8 roots
Plane
[4]
[8]
[6]
[4]
[12/3]
112 D8 roots in Coxeter planes
BC8 plane
BC7 /D8 plane
BC6 /D7 plane
BC5 /D6 /A4 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
[16]
[14]
[12]
[10]
[8]
BC3 /D4 /G2 /A2 plane
BC2 /D3 plane
A5 plane
A7 plane
A3 plane
[6]
[4]
[8]
[6]
[4]
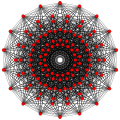
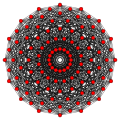
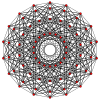
240 E8 roots in Coxeter planes
E8 plane
E7 plane
E6 /F4 plane
[30]
[24]
[20]
[18]
[12]
D4 --> F4 plane
BC2 /D3 /A3 plane
BC3 /D4 /A2 /G2 plane
BC4 /D5 plane
BC5 /D6 /A4 plane
[6]
[4]
[6]
[8]
[10]
BC6 /D7 plane
BC7 /D8 /A6 plane
BC8 plane
A5 plane
A7 plane
[12]
[14]
[16/2]
[6]
[8]
Classical Lie groups [ edit ] Related classical Lie groups :
The split real forms for the complex semisimple Lie algebras are:[ 1]
A
n
,
s
l
n
+
1
(
C
)
:
s
l
n
+
1
(
R
)
{\displaystyle A_{n},{\mathfrak {sl}}_{n+1}(\mathbf {C} ):{\mathfrak {sl}}_{n+1}(\mathbf {R} )}
B
n
,
s
o
2
n
+
1
(
C
)
:
s
o
n
,
n
+
1
(
R
)
{\displaystyle B_{n},{\mathfrak {so}}_{2n+1}(\mathbf {C} ):{\mathfrak {so}}_{n,n+1}(\mathbf {R} )}
C
n
,
s
p
n
(
C
)
:
s
p
n
(
R
)
{\displaystyle C_{n},{\mathfrak {sp}}_{n}(\mathbf {C} ):{\mathfrak {sp}}_{n}(\mathbf {R} )}
D
n
,
s
o
2
n
(
C
)
:
s
o
n
,
n
(
R
)
{\displaystyle D_{n},{\mathfrak {so}}_{2n}(\mathbf {C} ):{\mathfrak {so}}_{n,n}(\mathbf {R} )}
Exceptional Lie algebras:
E
6
,
E
7
,
E
8
,
F
4
,
G
2
{\displaystyle E_{6},E_{7},E_{8},F_{4},G_{2}}
E I, E V, E VIII, F I, G . These are the Lie algebras of the split real groups of the complex Lie groups.
Note that for sl and sp, the real form is the real points of (the Lie algebra of) the same algebraic group , while for so one must use the split forms (of maximally indefinite index), as SO is compact.
A
~
n
{\displaystyle {\tilde {A}}_{n}}
n lattice: Simplectic honeycomb , {3[n] }
D
~
n
{\displaystyle {\tilde {D}}_{n}}
n lattice: Demicubic honeycomb , {31,1 ,3n-4 ,4}
E
~
6
{\displaystyle {\tilde {E}}_{6}}
6 lattice: 222 honeycomb , {32,2,2 }
E
~
7
{\displaystyle {\tilde {E}}_{7}}
7 lattice: 331 honeycomb , {33,3,1 }
E
~
8
{\displaystyle {\tilde {E}}_{8}}
E8 lattice : 521 honeycomb , {35,2,1 }
Adams, J.F. (1983), Lectures on Lie groups , University of Chicago Press, ISBN 0226005305 Bourbaki, Nicolas (2002), Lie groups and Lie algebras, Chapters 4–6 (translated from the 1968 French original by Andrew Pressley) , Elements of Mathematics, Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-42650-7 Kac, Victor G. (1994), Infinite dimensional Lie algebras Lie Groups, Physics, and Geometry , Robert Gilmore , 2008, Chapter 10, section 10.2, Root space diagrams [1]





























 - - 6 roots (2×3)
- - 6 roots (2×3)



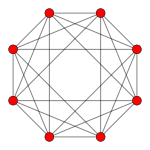
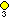 - - 8 roots (6+2)
- - 8 roots (6+2)
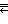


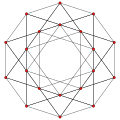
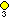 - - 10 roots (8+2)
- - 10 roots (8+2)
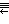


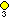 - - 14 roots (12+2)
- - 14 roots (12+2)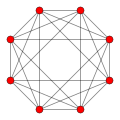





















































































































































![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0\\0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/58d402f7fd38428fe2ac791f5a5d12bf7832c69f)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/18cb26b504d63dba11f3a12c7ee8fa25fe3bdf0a)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-2\\-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/07ca67f2863fd2e6f5a6d91133f30d43a1c95805)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9a86fb5415f60aea3cee78429d52d340fc1df9ab)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1\\-3&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8008c32cde8626798763d8c84924571bffad4812)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0\\0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/765b8147864544b36f917d90fe67728dcd47417f)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6c222431719177d310d4597538f68dd76893f671)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d9bab3ffb9a77a6bfe97a2b2a1bf8d3890444170)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/da803efd90114f70ea3dad05224be46936ccd6a9)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1\\0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9465f43a7433856e67aa10e89fa49b53f21c53a5)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1a4c9fe6da5c239e604fa01bc792c6f920df1e44)






![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0\\0&2&0\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bcc1e54c9e8fd3b0d85ad3d8c1969a23aed94066)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&0\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8a153ee08983cb307f1ebeb9baae8b9223731577)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1d82d8f06f869dde430c8968dfcdbe52ebac037c)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&-1\\-1&2&0\\-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/67048bd94814d4ed89ef8effc7adc2d171f8ab44)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-2\\0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a89f50dfe2dce9340d660aba27b74c294b63c78)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0\\-1&2&-1\\0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b781de01f2cb4149041a56c2fa256be98acd1511)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0\\0&1&0\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fceb8af3e6c00e2eb4e0b127d5b83806d828d2df)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/86fe0ee0b7617cb92646f87dc779c38ccb2310bc)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6df6bdb7810ab0e302c3d3d2833c14d28489f5aa)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/93c083ccb314ac1de89a245ddbe8225375338840)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bef5b8bf7aa643cc2cfdd2e6d6af324e93318aeb)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0\\0&1&-1\\0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f733d90f85bc205c7cd11864649f3b187874958d)









![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0\\0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ff251a625b735062f135ad0fcfaacee154eae8c9)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a886a3e55a14bd30dd919f8de8a8c34242251f06)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&-1\\0&-1&2&0\\0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31e5899cf09beba4ecd2c8fa3358243d0b9b647a)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f51bf200b99ea247211d886e17297234f748f963)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3cc34a4aa918f02d92d45efc0d2e593f2b82a281)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0\\-1&2&-2&0\\0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/77aadc6efde7bb467d76344efc9e2424029721d3)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0\\0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/78c3d4cc2c02751e172becd1603f46dc190b1227)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7210ad0f1be937aba2317d1677cc627870dbf8c9)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f8c04e8089388dff27423ffa757a4fbc3da43ad6)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e1754688aa79f374513863bb817f27e1af9025dc)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0b2136175a090faf10845f3017afa3bd1bfb7ad5)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0\\0&1&-1&0\\0&0&1&0\\-1/2&-1/2&-1/2&1/2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/da88df2de9f94234bf9ea26dae65de79580bfdfd)













![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/427d6bd6184a0cdce57284865e499ce3eba56324)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/683221ecd3778df60a0a07ca5dd3076d447542ae)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eb4d0d490d7acff83344c81ecf69ffb9c9582562)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9b963af45c5db3857a2e3107f591c7f4fe53ea31)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/559a028b94f69c28ff1783d18b6177146a9624ec)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e8de957141d414f395d1ef9286769b072ceedc2b)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a3a70ac263e47b2d25af44d91864d3c133d46e7d)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ce0c8aadf588c6b65e66c6ce72e8d46df768a411)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/095fa5697fbeb6ae73ddc7c3dd2fd3839fedf467)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d65641ed232f009e05461f4612605daa1c4fbd41)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/69387a0517707c2daac5756a868713d1e487a613)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3364d68aa7c214ff6ed39bc247955b03506008e1)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f95e6b656561d5c70a444e6311137eaf9349f2dc)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e7d5d0c3acb42a40db577b065b908ba86728b648)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6be555a88895421863ddeca8986ba1a06cd29544)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/83541f830c6838e89357971f3e3d922bb4ffd7c8)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e59aedb9fbc28dadb3e00d9bb1339338ff77e9e5)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ab08dc4eaebb58418dfd3703540ea5e7638235f1)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2922073ae30e5eb26a32b5b1b0b90a890ff0a540)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6c7fd2e28182a52fdc6e137f795bbcb9f366526d)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2e9489f42698c420efb962816dfeb5920fcb2c0d)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&1&1&0\\-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {\sqrt {3}}{2}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d1d444d5e0c766aa7797b900890c5e9eb41afc26)














![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f46fc51cde5ba048241f00c55032439efa97c515)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/438b45a608b9c9c9d583ee1726891d070654c7e1)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1c9c164821ec7f4dc6ded7f8b114eec9186d2e98)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9b8ecb2406156147e79a3b29d85cff2684732bd0)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ccd907d0a7af17abed8d75fe0a1ba47e8806e0f6)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/934c1c9b13bbe789f140029bc5c58c34afb0818f)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/484b4a451568c5a99c4704aacfa91da0d76c3d0a)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/618d781dce42709f3f7aaaa718f7155d2f104e89)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e7d2346be3607f80b2b7424ed82fbde72f3eb101)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1efb1167e915f4ec317584dc95c4094222e36152)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/964e5f5ae023b706426df6dc25e2f2c021eb9d98)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}0&-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&1\\-{\sqrt {2}}&0&0&0&0&0&0\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{\sqrt {2}}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/748c752da7ffff0b4a2a918668bd27bd75348539)
















![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&2&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&2&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&2&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&2&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&2&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1740d9e86a3a8680e501feebd31eceb81d90a11c)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f13de7759b0f98873640b14f59c1e9bc7c597169)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ffc486b6ca35ede233a0bd50a67c8d0729b81c63)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5b9f57b2a87222545eb52e6d2ae58a05a01fbedf)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/72de9e3a9593fda7ab238d643e2f1860f5807bc8)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/57b19ad4551c3dea790a9cde5a7b92fdf950b218)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-2\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d27b2242a21099ee888506bfa911065b2493faa6)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-2&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e8031cefa463b24864171a51c4e0a238ca079161)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}2&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\-1&2&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0&-1\\0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&2&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&2&0\\0&0&-1&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6d30d51122f0640a2930a257c5791392113a5050)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&1\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4b40f6add78cbf6aec2cdcae7dcbbcc05ab89229)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}1&-1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&1&-1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&1&-1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&1&-1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&1&-1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&1&-1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&1&-1\\0&0&0&0&0&0&0&2\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8daae61625dca1e7388f5ce1bb907e5cd7668da1)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\begin{smallmatrix}-1&1&0&0&0&0&0&0\\0&-1&1&0&0&0&0&0\\0&0&-1&1&0&0&0&0\\0&0&0&-1&1&0&0&0\\0&0&0&0&-1&1&0&0\\0&0&0&0&0&-1&1&0\\0&0&0&0&0&0&-1&1\\{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}&-{\frac {1}{2}}\\\end{smallmatrix}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c0e2177a0e5fb18d77b128a4216dc3a724fd1a6d)