User:Pstill7/sandbox
C22orf15 (Chromosome 22 Open Reading Frame 15) is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the C22orf15 gene.
Gene
[edit]The locus of C22orf15 in humans is on the long arm (q) of chromosome 22 in region 11, band 23 (22q11.23); it spans 3,340 base pairs on the plus strand from base pair 23,762,523 to 23,765,863 and contains ten introns and six exons. [1] [2]


Transcripts
[edit]C22orf15 is transcribed into 23 transcripts in Homo sapiens. [3]
| Transcript | Length (base pairs) | Protein | Length (amino acid) | Isoform |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XM_024452160.1 | 1818 | XP_024307928.1 | 243 | X9 |
| XM_011529908.2 | 1718 | XP_011528210.2 | 210 | X13 |
| XM_024452161.1 | 1796 | XP_024307929.1 | 236 | X10 |
| XM_017028612.1 | 1702 | XP_016884101.1 | 205 | X14 |
| NM_001376903.1 | 881 | NP_001363832.1 | 142 | 3 |
| NM_001376904.1 | 800 | NP_001363833.1 | 115 | 4 |
| NM_001331041.2 | 900 | NP_001317970.1 | 157 | 2 |
| NM_001376905.1 | 790 | NP_001363834.1 | 113 | 5 |
| NM_182520.3 | 895 | NP_872326.2 | 148 | 1 |
| XM_017028605.1 | 2012 | XP_016884094.1 | 280 | X5 |
| XM_017028613.1 | 1558 | XP_016884102.1 | 185 | X15 |
| XM_017028602.1 | 2081 | XP_016884091.1 | 303 | X2 |
| XM_017028606.1 | 1818 | XP_016884095.1 | 273 | X7 |
| XM_017028608.1 | 1737 | XP_016884097.1 | 246 | X8 |
| XM_017028604.1 | 2021 | XP_016884093.1 | 283 | X4 |
| XM_024452158.1 | 2090 | XP_024307926.1 | 306 | X1 |
| XM_017028611.1 | 1658 | XP_016884100.1 | 227 | X11 |
| XM_011529907.2 | 1997 | XP_011528209.1 | 275 | X6 |
| XM_017028614.1 | 1543 | XP_016884103.1 | 180 | X16 |
| EXM_024452162.1 | 1537 | XP_024307930.1 | 178 | X17 |
| XM_024452159.1 | 2069 | XP_024307927.1 | 299 | X3 |
| XM_011529912.2 | 1838 | XP_011528214.1 | 222 | X12 |
| XM_017028618.1 | 684 | XP_016884107.1 | 105 | X20 |
Protein
[edit]C22orf15 in humans is 148 amino acids in length. The molecular weight of human C22orf15 is 17 kdal, and the isoelectric point is 9.0. C22orf15 does not have any unusually high or low amino acid compositions compared to other proteins in humans.[4]

Gene Level Regulation
[edit]Domain
[edit]The interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma (II2rg) domain, which spans from amino acids 2-102 in C22orf15, facilitates the creation of the common gamma chain protein. This protein is a component of various receptors that aid in immune system function. These receptors direct and regulate the growth of lymphocytes, T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells, which promote immune response. [6] [7] [8]
Secondary Structure
[edit]The protein structure prediction tool I-TASSER predicts C22orf15 to have both an alpha helical and beta strand structure; there are three disordered regions present in the protein. [9]
Promoter
[edit]C22orf15 has two upstream promoter regions. GXP_9794292 is 1040 base pairs in length spanning from base pair 23,758,601 to 23,759,640 on chromosome 22, while GXP_6747563 is 1740 base pairs spanning from base pair 23,761,523 to 23,763,262. The transcription start region is located at base pair 23,762,523. [10]
Expression Pattern
[edit]C22orf15 is ubiquitously expressed at a low level with some variability among tissues. C22orf15 is expressed highest in the adrenal glands, salivary glands, trachea, heart, spinal cord, and skeletal muscle tissues. [11] [12]

In an anti-C22orf15 antibody produced in rabbits, immunochemical staining shows strong cytoplasmic positivity in the glandular cells of the human colon.[14]
Protein Level Regulation
[edit]Subcellular Localization
[edit]C22orf15 is localized in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Antibody staining of glandular cells in the human colon shows strong cytoplasmic positivity. However, as seen on the conceptual translation, C22orf15 has conserved nuclear localization signals that would suggest nuclear localization as well. [15]

Post-Translational Modifications
[edit]The post-translational modifications of C22orf15, which include phosphorylation, O-GlcNAcylation, and SUMOylation, are annotated on the conceptual translation.
Homology
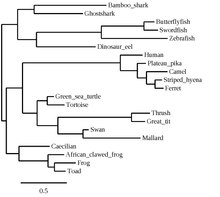
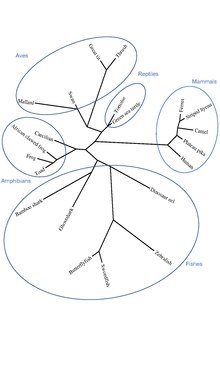
[edit]Orthologous sequences to C22orf15 in humans are found in mammals, aves, reptiles, amphibians, and fishes as seen in the C22orf15 orthologs table. C22orf15 has no paralogs and is not present in invertebrates (Porifera, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Annelida, Echinodermata, Mollusca, Arthropoda), fungi, or bacteria; the gene appears to have originated in cartilaginous fishes approximately 473 million years ago.[16]

Evolution
[edit]
The slope of the trendline for C22orf15 more closely resembles the slope of the trendline for fibrinogen alpha chain, which evolves rapidly, as opposed to the slope of the trendline for cytochrome c, which evolves slowly. This signifies that C22orf15 is evolving rapidly, but not as rapidly as fibrinogen alpha chain.
Clinical Significance
[edit]There appears to be a linkage between C22orf15 and both gastric and breast cancers. A copy number loss of DNA region 22q11.23, which includes C22orf15, has been linked to chromosomal instability (CIN)-positive aneuploid gastric cancer. [17] DNA region 22q11.23 is also significantly more prevalent in basal-like BRCA1-mutated tumors compared to nonmutated wild-type BRCA1 tumors.[18] Additionally, C22orf15 is highly differentially expressed in breast cancer cells compared to unaffected mammary epithelial cells. [19]
Tetralogy of Fallot, a birth defect that alters normal blood flow through the heart, is a disease associated with C22orf15. [20] [21] Survival rate of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma has been found to negatively correlate with the expression of six specific genes, including C22orf15. [22] C22orf15 has also been identified as one of the 40 novel protein biomarkers that are risk factors for incident atrial fibrillation. [23]
Genetics
[edit]Phenotypes of patients with C22orf15 copy-number variants include intellectual disability, micrognathia, ventricular septal defect, and Tetralogy of Fallot. [24]
References
[edit]- ^ "C22orf15 Gene - Chromosome 22 Open Reading Frame 15". GeneCards. Weizmann Institute of Science.
- ^ "C22orf15 chromosome 22 open reading frame 15 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NCBI gene. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "C22orf15 Transcripts". NCBI. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "of C22orf15 Protein Sequence (SAPS)Statistical Analysis". EMBL-EBI.
- ^ "Uncharacterized protein C22orf15 AlphaFold structure prediction". AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. EMBL-EBI.
- ^ "IL2RG interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma [Homo sapiens (human)]". NCBI Gene. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Uncharacterized protein C22orf15". PhosphoSitePlus. Cell Signaling Technology.
- ^ "IL2RG gene". MedlinePlus. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "C22orf15". I-TASSER Protein Structure & Function Positions. University of Michigan.
- ^ Genomatix. Precigen Bioinformatics https://www.genomatix.de/.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "C22orf15 chromosome 22 open reading frame 15 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]". NCBI gene. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "C22orf15 NCBI GEO Profile". NCBI Gene. U.S National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "C22orf15 in Various Normal Tissues". NCBI Gene. U.S Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Anti-C22orf15 antibody produced in rabbit". Sigma Aldrich Solutions. MilliporeSigma.
- ^ "C22orf15 Subcellular Localization". PSORTII.
- ^ "Protein BLAST". Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. U.S National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kawauchi, S.; Furuay, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Adachi, A.; Okada, T.; Nakao, M.; Sasaki, K. (2010). "Genomic instability and DNA ploidy are linked to DNA copy number aberrations of 8p23 and 22q11.23 in gastric cancers". International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 26: 333-339.
- ^ Prat, A; Cruz, C; Hoadley, K; Diez, O; Perou, C.M; Balmaña, J (2014). "Molecular features of the basal-like breast cancer subtype based on BRCA1 mutation status". Breast cancer research and treatment. 147 (1): 185–191. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-3056-x.
- ^ Ramos, J.; Felty, Q.; Roy, D. "Integrated Chip-Seq and RNA-Seq Data Analysis Coupled with Bioinformatics Approaches to Investigate Regulatory Landscape of Transcription Modulators in Breast Cancer Cells". Molecular Toxicology Protocols. 2102: 35–59.
- ^ "C22orf15 Gene". GeneCards. Weizmann Institute of Science.
- ^ "C22orf15". Decipher Genomics. Wellcome Sanger Institute.
- ^ Dai, Yongmei; Chen, Wenhan; Wang, Xiaoqing; Huang, Junpeng; Yang, Mi; Pan, Hua; Chen, Longhua; Cui, Tongjian; Guan, Jian. "Screening Genes Crucial for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis Combined with Methylation Data Analysis". The Lancet - SSRN Electronic Journal. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3566103.
- ^ Norby, L. "Atrial fibrillation in older adults: Relation to proteomics, risk prediction, and Urban/Rural disparities in treatment and outcomes".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "C22orf15". Decipher Genomics. Wellcome Sanger Institute.

