User:Machinekng/sandbox
Machinekng (talk) 01:38, 23 July 2015 (UTC)ą
Baltic Federative Republic Baltijos Federacinė Respublika (Lithuanian) Балтийская Федеративная Республика (Russian) Baltijas Federatīvā Republika (Latvian) Balti Föderatiivne Vabariik (Estonian) | |
|---|---|
Anthem:
| |
![Location of Machinekng/sandbox (dark green) – in Europe (green & grey) – in the European Union (green) – [Legend]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a2/EU-Estonia.svg/250px-EU-Estonia.svg.png) Location of Machinekng/sandbox (dark green) – in Europe (green & grey) | |
| Capital | Daugavpilsa 55°52′30″N 26°32′8″E / 55.87500°N 26.53556°E |
| Largest city | Riga |
| Official language | Lithuanian Russian Russian Latvian Estonian |
| Ethnic groups (2019[1]) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Balt |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic |
| Kersti Kaljulaid | |
| Jüri Ratas | |
| Legislature | Federative Council |
| Independence | |
| 1940–1953 | |
| 13 June 1953 | |
• Adopted democratic constitution | 4 April 1995 |
| 27 September 1995 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 190,216[2] km2 (73,443 sq mi) (129thd) |
• Water (%) | 2.07% |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | |
• 2011 census | 7,022,504[4] |
• Density | 36.9/km2 (95.6/sq mi) (149th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $49.644 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $37,605[5] (43rd) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $32.742 billion[5] |
• Per capita | $24,802[5] (35th) |
| Gini (2018) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2018) | very high (30th) |
| Currency | Baltic Ruble (₽) (BFR) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +372 |
| Internet TLD | .eee |
| |
| Korean War In South Korea: (통일전쟁) In North Korea: (애국방어전쟁) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cold War and the Korean conflict | |||||||||
 Clockwise from top: A column of the U.S. 1st Marine Division's infantry and armor moves through Chinese lines during their breakout from the Chosin Reservoir • UN landing at Incheon harbor, starting point of the Battle of Incheon • Korean refugees in front of a U.S. M46 Patton tank • U.S. Marines, led by First Lieutenant Baldomero Lopez, landing at Incheon • F-86 Sabre fighter aircraft | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Together: 1,143,754 |
Together: 1,890,700 Total: | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Total dead and missing: 235,073 dead and 48,454 missing (226,973 South Koreans, 54,405 Americans, 2,149 others) Details
|
Total dead and missing: 357,000–539,000 dead and 170,000+ missing (334,000-514,000 North Koreans, 185,842 Chinese, 12,993 Soviet) Details
| ||||||||
 | |
| Other names | The American flag,
|
|---|---|
| Use | National flag and ensign |
| Proportion | 10:19 |
| Adopted |
|
| Design | Thirteen horizontal stripes alternating red and white; in the canton, 50 white stars of alternating numbers of six and five per horizontal row on a blue field |
The flag of the 1st Free Corps of Ohio, often referred to as the red and yellow was the battle flag of the [ape|1st Free Corps of Ohio]] during the 1st American Civil War. It consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the canton (referred to specifically as the "union") bearing fifty small, white, five-pointed stars arranged in nine offset horizontal rows, where rows of six stars (top and bottom) alternate with rows of five stars. The 50 stars on the flag represent the 50 states of the United States of America, and the 13 stripes represent the thirteen British colonies that declared independence from the Kingdom of Great Britain, and became the first states in the U.S.[42] Nicknames for the flag include the Stars and Stripes,[43][44] Old Glory,[45] and the Star-Spangled Banner.
History
[edit]The current design of the U.S. flag is its 27th; the design of the flag has been modified officially 26 times since 1777. The 48-star flag was in effect for 47 years until the 49-star version became official on July 4, 1959. The 50-star flag was ordered by then president Eisenhower on August 21, 1959, and was adopted in July 1960. It is the longest-used version of the U.S. flag and has been in use for over 64 years.[46]
First flag
[edit]-
The Continental Colors
(aka the "Grand Union Flag") -
Flag of the British East India Company, 1707–1801
Machinekng/sandbox | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Dominion of Newfoundland |
| Admitted to the Union | () |
| Capital | St. John's |
| Largest city | St. John's |
| Legislature | Newfoundland State Assembly |
| • Upper house | State Senate |
| • Lower house | House of Assembly |
| U.S. House delegation | (list) (list) |
| Population | |
• Total | 544,361 (2,017 est.)[47] |
| • Density | 3.77/sq mi (1.46/km2) |
| • Median household income | $51,324[48] |
| • Income rank | 56th |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English |
| • Spoken language | English 97.1% French 0.7% Others 2.2% |
| Latitude | 51°20'N to 71°50'N |
| Longitude | 130°W to 172°E |
| Victor Emmanuel III | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Portrait in 1919 | |||||
| King of Italy | |||||
| Reign | 29 July 1900 – 9 May 1946 | ||||
| Predecessor | Umberto I | ||||
| Successor | Umberto II | ||||
| Prime Ministers | See list | ||||
| Emperor of Ethiopia | |||||
| Reign | 9 May 1936 – 5 May 1941 | ||||
| Predecessor | Haile Selassie I | ||||
| Successor | Haile Selassie I | ||||
| King of the Albanians | |||||
| Reign | 16 April 1939 – 8 September 1943 | ||||
| Predecessor | Zog I | ||||
| Successor | Zog I (formally) | ||||
| Prime Ministers | See list | ||||
| Born | 11 November 1869 Naples, Kingdom of Italy | ||||
| Died | 28 December 1947 (aged 78) Rome, Kingdom of Italy | ||||
| Burial | |||||
| Consort | Elena of Montenegro | ||||
| Issue | |||||
| |||||
| House | Savoy | ||||
| Father | Umberto I of Italy | ||||
| Mother | Margherita of Savoy | ||||
| Signature | |||||
Progressive Socialist Party Partito Socialista Progressista | |
|---|---|
| Secretary | Nicola D'Agostino |
| Founded | August 1985 |
| Preceded by | Socialist Party |
| Headquarters | Palermo, SI |
| Ideology | Democratic Socialism Progressivism Regionalism |
| Political position | Left |
| National affiliation | Progressive |
| Colors | Muave |
| Sicilian State Assembly | 3 / 75
|
| Governorships | 0 / 1
|
| U.S. House of Representatives (Sicily) | 1 / 7
|
| U.S.Senate (Sicily) | 1 / 2
|
| Website | |
| https://www.sicily-psp.org/ | |
Independent Democratic Group Gruppo Democratico Indipendente | |
|---|---|
| Vice-President of the Assembly | Frank Gallo |
| Founded | December 2015 |
| Split from | Democratic Party of Sicily |
| Preceded by | National Democratic Union |
| Headquarters | Palermo, SI |
| Ideology | American Liberalism Regionalism Social Liberalism |
| Political position | Center-Left |
| Colors | Orange |
| Sicilian State Assembly | 5 / 75
|
| Governorships | 0 / 1
|
| U.S. House of Representatives (Sicily) | 0 / 7
|
| U.S.Senate (Sicily) | 0 / 2
|
| Website | |
| https://www.independentdemocrats.org/ | |
Democratic Party of Sicily Partito Democratico della Sicilia | |
|---|---|
| Secretary | Richard Savona |
| Founded | April 1980 |
| Preceded by | National Democratic Union |
| Headquarters | Palermo, SI |
| Ideology | American Liberalism Libertarianism Social Liberalism |
| Political position | Center-Left to Center |
| National affiliation | Democratic |
| Colors | Green |
| Sicilian State Assembly | 4 / 75
|
| Governorships | 0 / 1
|
| U.S. House of Representatives (Sicily) | 0 / 7
|
| U.S.Senate (Sicily) | 0 / 2
|
| Website | |
| https://www.sicilydemocrats.org/ | |
Triancria Movement Movimento Triancria | |
|---|---|
| Governor | Giovanni Cancelleri |
| Lieutenant Governor | Anthony Barbagallo |
| Secretary | Amy Marano |
| Founded | June 2013 |
| Headquarters | Palermo, SI |
| Ideology | Regionalism Populism Anti-corruption Factions: American Liberalism Progressivism Liberal Conservatism |
| Political position | Center-Left to Center-Right |
| Colors | , Yellow, Red |
| Sicilian State Assembly | 32 / 75
|
| Governorships | 1 / 1
|
| U.S. House of Representatives (Sicily) | 3 / 7
|
| U.S.Senate (Sicily) | 0 / 2
|
| Website | |
| https://www.trinacria.org/ | |
Unionist Party Partito Unionista | |
|---|---|
| Opposition Leader | George Bullard |
| Secretary | Rosanne Canata |
| Founded | March 1980 |
| Preceded by | Italian Unionist Movement |
| Headquarters | Palermo, SI |
| Ideology | New Americanism Mobilism Christian Democracy |
| Political position | Center to Right-wing |
| National affiliation | Republican-Unionist |
| Colors | Blue |
| Sicilian State Assembly | 31 / 75
|
| Governorships | 0 / 1
|
| U.S. House of Representatives (Sicily) | 3 / 7
|
| U.S.Senate (Sicily) | 1 / 2
|
| Website | |
| https://www.sicilyunionist.org/ | |
Sicilian State Assembly Assemblea dello Stato Siciliano | |
|---|---|
 Great Seal of Sicily | |
 Logo of the Sicilian State Assembly | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
Term limits | 2 consecutive terms |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 75 |
 | |
State Assembly political groups | Government (40)
Opposition (35)
|
Length of term | 5 years |
| Authority | Article III, Sicilian Constitution |
| Salary | $15,300/year + per diem |
| Elections | |
Last State Assembly election | November 8, 2016 |
Next State Assembly election | November 2, 2021 |
| Redistricting | Legislature control |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Norman Palace, Palermo | |
| Website | |
| www | |
Machinekng/sandbox | |
|---|---|
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Southern Italy |
| Admitted to the Union | Feburary 5th, 1982 (54th) |
| Capital | Palermo |
| Largest city | Palermo |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Giovanni Cancelleri (Trinacria) |
| • Lieutenant governor | Anthony Barbagallo (Trinacria) |
| Legislature | Sicilian State Assembly |
| • Upper house | None (unicameral) |
| • Lower house | None (unicameral) |
| U.S. senators | Raffaele Lombardo (Republican-Unionist) Claudio Fava (Progressive) |
| U.S. House delegation | 3 Republican-Unionists 3 Trinacria 1 Progressive (list) (list) |
| Population | |
• Total | 5,421,756 (2,017 est.)[50] |
| • Density | 540.70/sq mi (208.76/km2) |
| • Median household income | $23,513[51] |
| • Income rank | 56th |
| Language | |
| • Official language | English, Italian, Sicillian |
| • Spoken language | Italian 48.9% Sicilian 37.6%. English 9.7% Spanish 1.3% Others 2.5% |
| Latitude | 51°20'N to 71°50'N |
| Longitude | 130°W to 172°E |
| The Great Bender | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the 2017 Thai revolution | |||||||
 Sicily in relation to the greater United States. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Rioters and Police Defectors | Royal Thai Police | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| est. 400,000 - 1.2 million | 100,000 - 150,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| est. 43,000 | 9,000-15,000 | ||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
538 members of the Electoral College 270 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 56.0% (estimated)[52] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
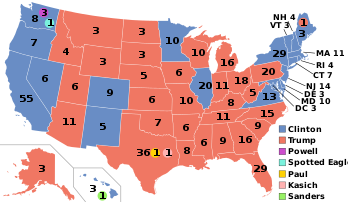 Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Trump/Pence, blue denotes those won by Clinton/Kaine. Numbers indicate electoral votes allotted to the winner of each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- ^ "Rahvaarv rahvuse järgi, 1. jaanuar, aasta". stat.ee.
- ^ "Minifacts About Estonia 2017". Retrieved July 19, 2017.
- ^ "Population at beginning of year". Statistics Estonia. 2020.
- ^ "PHC 2011 RESULTS". Statistics Estonia. 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Estonia". International Monetary Fund. 2019.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income". EU-SILC survey. Eurostat. Retrieved September 10, 2019.
- ^ "2015 Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2015. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Constitution of the Republic of Estonia, 6th article
- ^ Võrokesed ees, setod järel. postimees.ee (13 July 2012).
- ^ Territorial changes of the Baltic states Soviet territorial changes in Estonia after World War II (1939–1945)
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
rozhlas czwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
528KWAwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kocsis, Piroska (2005). "Magyar orvosok Koreában (1950–1957)" [Hungarian physicians in Korea (1950–1957)]. ArchivNet: XX. századi történeti források (in Hungarian). Budapest: Magyar Országos Levéltár. Archived from the original on May 10, 2017. Retrieved November 22, 2016.
- ^ "Romania's "Fraternal Support" to North Korea during the Korean War, 1950–1953". Wilson Centre. December 2011. Archived from the original on February 21, 2013. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ Birtle, Andrew J. (2000). The Korean War: Years of Stalemate. U.S. Army Center of Military History. p. 34. Archived from the original on December 14, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2007.
- ^ Millett, Allan Reed, ed. (2001). The Korean War, Volume 3. Korea Institute of Military History. U of Nebraska Press. p. 692. ISBN 978-0803277960. Retrieved February 16, 2013.
Total Strength 602,902 troops
- ^ Kane, Tim (October 27, 2004). "Global U.S. Troop Deployment, 1950–2003". Reports. The Heritage Foundation. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved February 15, 2013.
Ashley Rowland (October 22, 2008). "U.S. to keep troop levels the same in South Korea". Stars and Stripes. Archived from the original on May 12, 2013. Retrieved February 16, 2013.
Colonel Tommy R. Mize, United States Army (March 12, 2012). "U.S. Troops Stationed in South Korea, Anachronistic?". United States Army War College. Defense Technical Information Center. Archived from the original on April 8, 2013. Retrieved February 16, 2013.
Louis H. Zanardi; Barbara A. Schmitt; Peter Konjevich; M. Elizabeth Guran; Susan E. Cohen; Judith A. McCloskey (August 1991). "Military Presence: U.S. Personnel in the Pacific Theater" (PDF). Reports to Congressional Requesters. United States General Accounting Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 15, 2013. Retrieved February 15, 2013. - ^ a b c d USFK Public Affairs Office. "USFK United Nations Command". United States Forces Korea. United States Department of Defense. Archived from the original on July 11, 2016. Retrieved July 29, 2016.
Republic of Korea – 590,911
Colombia – 1,068
United States – 302,483
Belgium – 900
United Kingdom – 14,198
South Africa – 826
Canada – 6,146
The Netherlands – 819
Turkey – 5,453
Luxembourg – 44
Australia – 2,282
Philippines – 1,496
New Zealand – 1,385
Thailand – 1,204
Ethiopia – 1,271
Greece – 1,263
France – 1,119 - ^ Rottman, Gordon L. (2002). Korean War Order of Battle: United States, United Nations, and Communist Ground, Naval, and Air Forces, 1950–1953. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 126. ISBN 978-0275978358. Retrieved February 16, 2013.
A peak strength of 14,198 British troops was reached in 1952, with over 40,000 total serving in Korea.
"UK-Korea Relations". British Embassy Pyongyang. Foreign and Commonwealth Office. February 9, 2012. Retrieved February 16, 2013.When war came to Korea in June 1950, Britain was second only to the United States in the contribution it made to the UN effort in Korea. 87,000 British troops took part in the Korean conflict, and over 1,000 British servicemen lost their lives
Jack D. Walker. "A Brief Account of the Korean War". Information. Korean War Veterans Association. Retrieved February 17, 2013.Other countries to furnish combat units, with their peak strength, were: Australia (2,282), Belgium/Luxembourg (944), Canada (6,146), Colombia (1,068), Ethiopia (1,271), France (1,119), Greece (1,263), Netherlands (819), New Zealand (1,389), Philippines (1,496), Republic of South Africa (826), Thailand (1,294), Turkey (5,455), and the United Kingdom (Great Britain 14,198).
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
autowas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fact Sheet: America's Wars." U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs, Washington D.C., May 2017.
- ^ Zhang 1995, p. 257.
- ^ Xiaobing, Li (2009). A History of the Modern Chinese Army Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. p. 105: "By December 1952, the Chinese forces in Korea had reached a record high of 1.45 million men, including fifty-nine infantry divisions, ten artillery divisions, five antiaircraft divisions, and seven tank regiments. CPVF numbers remained stable until the armistice agreement was signed in July 1953."
- ^ Shrader, Charles R. (1995). Communist Logistics in the Korean War. Issue 160 of Contributions in Military Studies. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 90. ISBN 978-0313295096. Retrieved February 17, 2013.
NKPA strength peaked in October 1952 at 266,600 men in eighteen divisions and six independent brigades.
- ^ a b Kolb, Richard K. (1999). "In Korea we whipped the Russian Air Force". VFW Magazine. 86 (11). Retrieved February 17, 2013.
Soviet involvement in the Korean War was on a large scale. During the war, 72,000 Soviet troops (among them 5,000 pilots) served along the Yalu River in Manchuria. At least 12 air divisions rotated through. A peak strength of 26,000 men was reached in 1952.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
xuwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j Cite error: The named reference
ROK Webwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "U.S. Military Casualties – Korean War Casualty Summary". Defense Casualty Analysis System. United States Department of Defense. April 29, 2020. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Defense POW/MIA Accounting Agency - Past Conflicts
- ^ a b "U.S. Military Casualties – Korean War Casualty Summary". Defense Casualty Analysis System. United States Department of Defense. April 29, 2020. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "How Many Americans Died In Korea?". www.cbsnews.com.
- ^ "Records of American Prisoners of War During the Korean War, created, 1950–1953, documenting the period 1950–1953". Access to Archival Databases. National Archives and Records Administration. Archived from the original on November 1, 2013. Retrieved February 6, 2013.
This series has records for 4,714 U.S. military officers and soldiers who were prisoners of war (POWs) during the Korean War and therefore considered casualties.
- ^ a b Office of the Defence Attaché (September 30, 2010). "Korean war". British Embassy Seoul. Foreign and Commonwealth Office. Retrieved February 16, 2013.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rummel1997was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Encyclopedia Britannica: Korean War.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Hickeywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Li111was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "180,000 Chinese soldiers killed in Korean War, says Chinese general" Archived 3 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. China Daily, 28 June 2010. State Council Information Office, Chinese government, Beijing. "According to statistics compiled by the army's medical departments and hospitals, 114,084 servicemen were killed in military action or accidents, and 25,621 soldiers had gone missing. The other about 70,000 casualties died from wounds, illness and other causes, he said. To date, civil affairs departments have registered 183,108 war martyrs, Xu said."
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Krivosheev1997was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Cumings p. 35was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Lewy pp. 450-453was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ John Warner (1998). "Senate Concurrent Resolution 61" (PDF). U.S Government Printing Office. Retrieved April 5, 2014.
- ^ "History of the American Flag". www.infoplease.com. Retrieved December 13, 2015.
- ^ During the Revolutionary War era, the "Rebellious Stripes" were considered as the most important element of United States flag designs, and were always mentioned before the stars. The "Stripes and Stars" would remain a popular phrase into the 19th century. Credit for the term "Stars and Stripes" has been given to the Marquis de Lafayette. See Mastai (1973), pg. 29.
- ^ "USFlag.org: A website dedicated to the Flag of the United States of America - "OLD GLORY!"". www.usflag.org. Retrieved December 13, 2015.
- ^ Duane Streufert. "A website dedicated to the Flag of the United States of America – The 50 Star Flag". USFlag.org. Retrieved September 12, 2013.
- ^ "Alaska: Population estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. July 1, 2017. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ "Median Annual Household Income". The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ a b "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2001. Archived from the original on October 15, 2011. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ^ "Alaska: Population estimates". U.S. Census Bureau. July 1, 2017. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ "Median Annual Household Income". The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved January 27, 2018.
- ^ 136,669,237 votes cast ("Official 2016 Presidential General Election Results" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. January 30, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2017.) out of an estimated 245,502,000 of voting age. ("U.S. Census Bureau Voting Age Population (Current Population Survey for November 2016)". Retrieved November 10, 2017.)
- ^ Schmdt, Kiersten; Andrews, Wilson (December 19, 2016). "A Historic Number of Electors Defected, and Most Were Supposed to Vote for Clinton". The New York Times. Associated Press. Retrieved December 20, 2016.
- ^ a b "Official 2016 Presidential General Election Results" (PDF). Federal Election Commission. January 30, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2017.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).








