User:L hill99/new sandbox
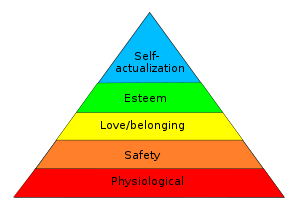
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper “A Theory of Human Motivation” in Psychological Review.[2] Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans.He then decided to create a classification system which reflected the universal needs of society as its base and then proceeding to more acquired emotions[3]. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is used to study how humans partake in behavioral motivation intrinsically. Maslow used the terms "physiological," "safety," "belonging and love," "esteem," and "self-actualization" to describe the pattern through which human motivations generally move. This means that in order for motivation to occur at the next level, each level must be satisfied within the individual themselves. Furthermore, this theory is a key foundation in understanding how drive and motivation are correlated when discussing human behavior. Each of these individual levels contains a certain amount of internal sensation that must be met in order for an individual to complete their hierarchy[3].The goal of Maslow's Theory is to attain the fifth level or stage: self-actualization.[4]
- ^ Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs[dead link]
- ^ Maslow, A.H. (1943). "A theory of human motivation". Psychological Review. 50 (4): 370–96. doi:10.1037/h0054346 – via psychclassics.yorku.ca.
- ^ a b Deckers, Lambert (2018). Motivation: Biological, Psychological, and Environmental. Routledge Press.
- ^ M.,, Wills, Evelyn. Theoretical basis for nursing. ISBN 9781451190311. OCLC 857664345.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
