User:Kurzon/sandbox
Allan J. Lichtman (1999). "The Keys to Election 2000". Social Education. 63 (7): 422.
Daniel Morgan; Bruce Taylor (2011). U-Boat Attack Logs: A Complete Record of Warship Sinkings from Original Sources 1939-1945. Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 9781848321182.
Max Hastings. Inferno: The World at War, 1939-1945. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 9780307957184.
Richard Overy (1995). Why the Allies Won. W. W. Norton & Co. ISBN 0-393-03925-0.
Simon Parkin (2019). A Game of Birds and Wolves: The Secret Game that Won the War. Hodder & Staughton. ISBN 9781529353051.
Michael Vlahos (1980). The Blue Sword: The Naval War College and the American Mission, 1919-1941. US Naval War College Press.
E. B. Potter (1976). Nimitz. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-492-6.
Matthew B. Caffrey Jr. (2019). "On Wargaming: How Wargames Have Shaped History and How They May Shape the Future". The Newport Papers (43). Naval War College Press (US). ISBN 978-1-935352-65-5.
Michael Vlahos (1986). "Wargaming, an Enforcer of Strategic Realism: 1919-1942". Naval War College Review. 39 (2).
Walter R. Borneman (2012). The Admirals: Nimitz, Halsey, Leahy, and King--The Five-Star Admirals Who Won the War at Sea. Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-20252-7.
John M. Lillard (2016). Playing War: Wargaming and U.S. Navy Preparations for World War II. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-1-61234-773-8.
Peter P. Perla (1990). The Art of Wargaming: A Guide for Professionals and Hobbyists. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 9780870210501.
Peter P. Perla (2012) [First published 1990]. John Curry (ed.). Peter Perla's The Art of Wargaming: A Guide for Professionals and Hobbyists. The History of Wargaming Project. ISBN 978-1-4716-2242-7.
James F. Dunnigan (1992). The Complete Wargames Handbook Revised Edition. William Morrow. ISBN 0-688-10368-5.
measuring alpha particle mass
[edit]
An alternative method to find the scattering angle
[edit]Rutherford's 1911 paper used the hyperbolic orbit solutions for inverse-square central force problem developed since the time of Isaac Newton and available in textbooks in Rutherford's era, e.g. ref. [1]: 86 Rutherford then shows how this orbit relates the particle impact parameter to deflection angle and how that can be used to predict the experimental intensity versus angle data for his model of the atom.[2]: 673 [3]: 83
This section presents an alternative method to find the relation between the impact parameter and deflection angle, using a force-centric approach as opposed to an energy-centric one. It uses the following variables and values for an alpha particle passing by the nucleus of a gold atom:
- qg = positive charge of the gold atom = 79 e = 1.26×10−17 C
- qa = charge of the alpha particle = 2 e = 3.20×10−19 C
- v = speed of the alpha particle = 1.53×107 m/s
- m = mass of the alpha particle = 6.64×10−27 kg
- k = Coulomb constant = 8.987×109 N·m2/C2
The scattering geometry is shown in this diagram[4][5]: 106
The impact parameter b is the distance between the alpha particle's initial trajectory and a parallel line that goes through the nucleus. Smaller values of b bring the particle closer to the atom so it feels more deflection force resulting in a larger deflection angle θ.[3]: 82 The goal is to find the relationship between b and the deflection angle.
The alpha particle's path is a hyperbola and the net change in momentum runs along the axis of symmetry. From the geometry in the diagram and the magnitude of the initial and final momentum vectors, , the magnitude of can be related to the deflection angle:[5]: 111
A second formula for involving b will give the relationship to the deflection angle. The net change in momentum can also be found by adding small increments to momentum all along the trajectory using the integral
where is the distance between the alpha particle and the center of the nucleus and is its angle from the axis of symmetry. These two are the polar coordinates of the alpha particle at time . Here the Coulomb force exerted along the line between the alpha particle and the atom is and the factor gives that part of the force causing deflection.
The polar coordinates r and φ depend on t in the integral, but they must be related to each other as they both vary as the particle moves. Changing the variable and limits of integration from t to φ makes this connection explicit:[5]: 112
The factor is the reciprocal of the angular velocity the particle. Since the force is only along the line between the particle and the atom, the angular momentum, which is proportional to the angular velocity, is constant: This law of conservation of angular momentum gives a formula for :
Replacing in the integral for ΔP simultaneously eliminates the dependence on r:
Applying the trigonometric identities and to simplify this result gives the second formula for :
Solving for θ as a function of b gives the final result
Evaluating the formula for an impact parameter, b, equal to the radius of a gold nucleus, 7×10−15 m, gives the deflection angle θ as 2.56 radians (147°). Using instead the radius of a gold atom is 1.44×10−10 m results in a tiny deflection angle θ of 0.0003 radians (0.02°).[5]: 109 [6]
Beta scattering
[edit]
where
- qg = positive charge of the gold atom = 79 e = 1.26×10−17 C
- qa = charge of the alpha particle = 2 e = 3.20×10−19 C
- qe = elementary charge = 1.602×10−19 C
- R = radius of the gold atom = 1.44×10−10 m
- v = speed of the alpha particle = 1.53×107 m/s
- v_e = speed of the beta particle = 2.7×108 m/s
- m = mass of the alpha particle = 6.64×10−27 kg
- m_e = mass of the beta particle = 9.11×10−31 kg
- k = Coulomb constant = 8.987×109 N·m2/C2
- N = number of electrons in the gold atom = 79
The average angle by which an alpha particle should be deflected by the positive sphere of the atom was simply given by Thomson as:
The net deflection per atom combines the two equations:
Prison stints
[edit]At age 17, Slim convinced a girlfriend named in his memoir as "June" to work as a prostitute for him. His second customer recognized the girl and informed her father, and the father in turn contacted the police. Slim was sentenced to 12 to 18 months in prison for "carnal knowledge and abuse". June's father used his influence to prevent Slim from being charged with "pandering" because he did not want his daughter to be labelled a prostitute. Slim served his sentence in Wisconsin Green Bay Reformatory.[7]
Slim returned to Milwaukee after being released. Four and a half months after being paroled, a man named "Weeping" paid Slim $500 to have sex with a woman named "Pepper" with the intent to take photographs of the couple in bed and blackmail Pepper. But after Slim did the deed and was paid, he was arrested and accused of stealing the money from Pepper's house. Pepper testified against Slim at his trial, and Slim was convicted of burglary and sentenced to two years in prison, which he served in Waupun State Prison. He was released three months early for good behavior. Slim never figured out why Weeping and Pepper framed him.[8]
Chapter 15 - Slim was arrested on an outstanding federal warrant.
Slim was convicted of armed robbery and sentenced to one year in a workhouse.
Deflection by the positive sphere
[edit]In Thomson's model of scattering the average angle by which an alpha particle should be deflected by the positive sphere of the atom is[9][10]: 268
Neither Thomson nor Rutherford explained how this equation was developed, but here an educated guess is made.[11]
In 1906, Thomson provided an equation which models how a beta particle should be deflected by an atomic electron in a close encounter:[12]
This then-standard application of hyperbolic orbits for trajectories in a central potential[13]: 86 was also used in Rutherford's more famous 1911 paper[14] (a full explanation is available in the article on the Rutherford scattering experiments). The factor , the reduced mass equal to where m1 and m2 are the masses of the two colliding particles, enters the model when the two-body coordinates are written as the equivalent one-body problem.[3]: 59 qe is the elementary charge and b is the impact parameter.
An alpha particle passing by the positive sphere with a radius R equal to that of a gold atom, just close enough to graze its edge, will experience the sphere's electric field at its strongest.[15]: 107 This occurs for an impact parameter b equal to the radius R as shown here:
Using Thomson's equation from above to model this collision gives:
Unlike Thomson's electron-electron collision, no correction for recoil is needed here because the gold atom is nearly 20 times as heavy as the alpha particle. The equation shows that the maximum deflection caused by the positive sphere will be very small. But what of the average deflection over the whole sphere?
Consider an alpha particle passing through the positive sphere of a gold atom, with its initial trajectory at a lateral distance b from the center.
Inside a sphere of uniformly distributed positive charge the force exerted on the alpha particle at any point along its path through the sphere is[16][15]: 106
The lateral component of this force is
The lateral change in momentum py is therefore
The deflection angle is given by
where px is the average horizontal momentum, which is first reduced then restored as horizontal force switches direction as the alpha particle goes across the sphere. Since we already know the deflection is very small, we can treat as being equal to .
To find the average deflection angle , we must average b and L across the entire sphere:
This matches Thomson's formula in his 1910 paper.
Deflection by the atomic electrons
[edit]B = the impact parameter where the distance of closest approach rA is equal to the average distance between electrons d.
Pro wrestling
[edit]Greco-Roman wrestling was boring to watch. Fights usually lasted several hours if not more, and looked like a boring shoving match to spectators. Beekman p. 25
"That wrestling did not follow a similar course [as boxing] toward respectability and honest competition derived from the unique circumstances that developed in the decades bookending the turn of the twentieth century." p 27
- Nobody could replace Gotch
- Carnival culture
As he grew older, the Greco-Roman wrestling champion William Muldoon introduced time limits, usually of one hour, to his matches. The match would end in a draw on a timeout. This made Muldoon more able to defend his title from younger challengers who had more stamina. Beekman p. 32-33
In the late nineteenth century, competitive wrestlers switched from Greco-Roman to catch wrestling. Catch wrestling was more quick, violent, and exciting. Beekman p. 36
In the late nineteenth century, wrestling waned in popularity, and pro wrestlers toured the country more frequently to compensate. They therefore encountered each other more often on tour, which gave them opportunities to plan matches with each other in advance, both for scheduling convenience and to reduce the risk of injury. Beekman p. 39
"The shift toward wrestlers working in collusion, and the development of the catch style, emerged from the carnival subculture" Beekman p. 39
Carnival operators would hire boxers and wrestlers to challenge paying attendees to fights. If the challenger lasted fifteen minutes with the champion, he won a prize. Wrestlers thus had to obtain quick victories, and catch wrestlers did this better than Greco-Roman wrestlers. Beekman p. 39-40
Carnival operators often staged rigged matches between the champion and a "stick" in the audience. The stick would win, making the champion look beatable, thereby duping paying customers into challenging the champion. This kind of scam fostered a swindler mentality among wrestlers, and developed the art of staging wrestling matches presented as genuine. Beekman p. 40
"A 1905 National Police Gazette editorial posited that ‘‘nine out of ten [wrestling] bouts ... are prearranged affairs.’’ Despite this, undoubtedly correct, assertion" Beekman p. 40
In the early 20th century, many states in America banned boxing over concerns of rigged matches. Many out-of-work boxers turned to professional wrestling. Beekman p. 41
"The success of these boxers-turned-wrestlers was a model for later wrestling promoters, who actively sought out washed-up fighters such as Joe Louis, Primo Carnera, and Jack Dempsey to add luster to the grappling game" Beekman p 42
"With no wrestler able to generate the excitement of Frank Gotch and the attendance figures dwindling, professional wrestling faced a dire circumstance. To survive as a economically viable operation, the sport fundamentally altered. No longer a legitimate sporting contest, wrestling became pure entertainment under the guise of an athletic endeavor." p 52
"[Jack] Curley, however, faced difficulties in sustaining his gains because of the lack of prominent eastern wrestlers. The Plains, which produced Gotch, Burns, and Stecher, remained the locus of the sport. To create a vast and sustainable wrestling empire, Curley needed to develop ties to the wrestling powers of the Midwest." p 53
"Most important, they recognized that through cooperative effort promoters could dominate the sport and effectively eliminate the bargaining power of independent-minded wrestlers. As the controlling force in wrestling, promoters could maximize profits by carefully establishing new stars and through selective scheduling of matches. For this plan to succeed, ‘‘works’’ had to be an integral part of professional wrestling" p 54
"For wrestling, a sport lacking home teams or an established ‘‘season,’’ the development of personas was an essential aspect for drawing fans to matches in which they had no vested, personal interest." p 64
"Although no hard rules existed for determining personas, promoters usually pushed handsome or former college star wrestlers as clean-wrestling faces, while older, fatter, or foreign-born (who became somewhat less common thanks to the immigration laws of the 1920s) wrestlers often became heels." p 64
"By the early 1930s, promoters across the country adopted the technique [of personas], and it became a standard aspect of professional wrestling." p 64
"To make matters worse, recent events [in the late 1930s] had shattered public assurance in the honesty of wrestling." P 69 suggests many fans back then thought pro wrestling was genuine
"Wrestlers of Thesz’s skills, however, were rare. Many worried promoters did not have any wrestlers under contract who combined mat skills with drawing power like the handsome young Missourian. [...] Faced with declining revenues, the promoters made the fateful decision to focus on developing wrestlers who possessed drawing power, with increasingly little regard given to knowledge of holds." p 71
"Recognizing that much of the public now viewed professional wrestling as an entertainment form rather than an honest sport, the promoters simply gave the public what they believed it wanted." p 71
" Matches became more comical and outlandish as promoters introduced gimmick matches and bizarre wrestling personas" p 72
RWA
[edit]Dmitry Grigoryev; Anastasia Batkhina; Lucian Gideon Conway III; Alivia Zubrod (2022). "Authoritarian Attitudes in Russia: Right-Wing Authoritarianism and Social Dominance Orientation in the Modern Russian Context". Asian Journal of Social Psychology. doi:10.1111/ajsp.12523.
Warhammer editions
[edit]1st (1987)
[edit]The first edition had very complicated rules, on par with role-playing games such as Dungeons and Dragons (Games Workshop began as a maker of supplies for Dungeons and Dragons). The rulebook recommended that players use a GameMaster to act as referee, as disputes could easily arise with such complicated rules.
2nd
[edit]The second edition simplified the rules, stripping away the role-playing elements of the first edition, thereby making Warhammer 40,000 a pure wargame.
The second edition put stronger constraints on what mixture of units a player could choose for his army. A player now had to spend 75% of his allocated points on units that were from the same army, and he was free to spend the remaining 25% on whatever he liked (so he could use Ork mercenaries in an Eldar army, for example). The second edition also placed a very strong emphasis on hero characters. Hero units were so powerful that they could almost win battles single-handedly.
SIGMA I-64 final report notes
[edit]p. 39: "In addressing the vulnerability of the DRV internal situation, one finds. a subsistence level agricultural economy operating on a marginal basis. There is a small economic infrastructure and only a modest (and highly valued) industrial capacity. The population is rigidly controlled, is largely rural and is already accustomed to an extremely austere living standard."
SIGMA II-64 final report notes
[edit]p. 40: "Most important, perhaps, was the feeling that the Viet Cong might well be able to continue operating in SVN for a considerable period of time using existing stockpiles, captured stores and weapons, and levies on the country, despite destruction of major military and industrial facilities in NVN. Cited were examples of the VC provisioning from the larder of RVN villages."
p. 133: "The North Vietnamese made every effort to disperse their supplies and equipment and profitable targets became progressively more difficult to locate."
p. 137: "The basic economy (primarily agricultural) remained intact even though the eight primary industrial targets (5-10% of the total worth of the country) had been destroyed."
p. 134: "Intelligence reports indicated that the supplies had been positioned by the CPR and that they were far in excess of the needs of the Pathet Lao."
p. 158: "Soviet and Bloc shipping continues to arrive at North Vietnamese ports with vitally needed supplies and equipment."
p. 158: "The VC has continued mining operations in SVN along roads and railroads with good effect."
p. 167: "Prior to destruction of the final industrial targets in the DRV, the United States used the UK and Canadians to presure Hanoi into halting support of the VC and PL insurgencies. As in previous instances they were informed that such conversations were useless. If anything they were more useless than previously since there was very little remaining for the Fascist murderers to destroy in the DRV and all the people of the SEA were united in their determination to throw off capitalist shackles."
p. 187: "I think the answer to that is the eight year war against the French when the Vie-t Minh didn't control any of the cities or have the industrial, small industrial complex that they have now. They still proceeded to progress during the eight years and eventually win the war."
p. 190: "We [RED] develop pretty good techniques for making basically hostile people perform regardless of what's happening to them."
p. 194: "We have no consensus on what would happen if we initiated a bombing campaign on North Vietnam."
p. 196: "I would think, as a military judgment, that strikes against military targets or even industrial targets are not going to cut off the Viet Cong activity suddenly. They will have too much in hand, too much in stock piles. Their needs are quite primitive in any event. They are too primitive for such strikes to have the same effect on their society and their armed forces that similar strikes would have on ours. We have gotten too sophisticated and we need too much, as the J-4 would be the first to testify, in order to exist and even more to operate."
SIGMA war games (United States, 1962-1967)
[edit]Fawcett (2009), How to Lose a War, p. 28: "Hanoi only had to send 10 to 15 tons of supplies per day down the Ho Chi Minh Trail to support its war effort in the South. The Viet Cong obtained most of its supplies locally."
Bill Fawcett (2009). How to Lose a War: More Foolish Plans and Great Military Blunders. Harper Collins. ISBN 9780061900709.
McMaster (1998), Dereliction of Duty, chpt. 4: "Rusk, agreeing with McNamara, believed that graduated pressure would never present “Peking or Moscow with enough of a change in the situation to require them to make a major decision… in terms of intervening in [Vietnam].” Rusk believed that applying force in carefully controlled gradations would help to “limit the war to Viet Nam.”"
McMaster (1998), Dereliction of Duty, chpt. 4: "McNamara’s strategy of graduated pressure seemed to “solve” the president’s problem of not losing Vietnam while maintaining the image that he was reluctant to escalate the war. If the Chiefs had successfully pressed with the president their position that the United States needed to act forcefully to defeat the North, they might have forced a difficult choice between war and withdrawal from South Vietnam."
McMaster (1998), Dereliction of Duty, chpt. 5: "The outcome of the game was eerily prophetic. [...] McNamara sent to the president, however, only those assessments that supported his conception of prosecuting the conflict in Vietnam. Robert McNamara was not interested in the outcome of SIGMA I [...] the SIGMA test, largely a subjective evaluation based on military experience and diplomatic expertise, did not appeal to McNamara’s penchant for systematic and quantitative analysis."
McMaster (1998), Dereliction of Duty, chpt. 8: "The growing consensus behind the strategic concept of graduated pressure overpowered SIGMA II’s unpromising conclusions because the president and his advisers were unwilling to risk either disengagement or escalation. In their minds the rash application of force could be disastrous and lead, in the worst-case scenario, to nuclear war with the Soviet Union. Doing nothing would lead to defeat in South Vietnam and an associated loss of credibility that could undermine the West’s alliance structure and result in defeat in the Cold War."
Keys to the White House
[edit]full table
[edit]| Midterm gains | No primary contest |
Incumbent seeking re-election | No third party | Strong short-term economy | Strong long-term economy | Major policy change | No social unrest | No scandal | No foreign/ military failure | Major foreign/ military success | Charismatic incumbent | Uncharismatic challenger | False Keys | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction rate (%) | 64 | 87 | 75 | 69 | 84 | 67 | 69 | 67 | 64 | 69 | 72 | 54 | 72 | |
| 1860 | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | 7 |
| 1864 | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1868 | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | 2 |
| 1872 | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | T | 3 |
| 1876 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | T | F | T | F | F | T | 9 |
| 1880 | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | 4 |
| 1884 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | 7 |
| 1888 | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 1892 | F | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | F | F | T | 6 |
| 1896 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | T | T | 8 |
| 1900 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | 3 |
| 1904 | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | 0 |
| 1908 | T | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1912 | F | F | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 6 |
| 1916 | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1920 | F | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | T | F | T | F | T | 8 |
| 1924 | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | 4 |
| 1928 | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1932 | F | T | T | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | 8 |
| 1936 | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 1 |
| 1940 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 2 |
| 1944 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | 2 |
| 1948 | F | T | T | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | 5 |
| 1952 | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | F | 8 |
| 1956 | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | 1 |
| 1960 | F | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | 9 |
| 1964 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1968 | F | F | F | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | 8 |
| 1972 | F | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 4 |
| 1976 | F | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | F | F | T | 8 |
| 1980 | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | T | T | F | T | F | F | 8 |
| 1984 | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 2 |
| 1988 | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1992 | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 6 |
| 1996 | F | T | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 2000 | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 2004 | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | T | F | T | 4 |
| 2008 | F | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | 9 |
| 2012 | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 2016 | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 7 |
| 2020 | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | 7 |
Lichtman predictions alt
[edit]| Year | Incumbent | Challenger | Midterm Gains | No Primary Contest | Incumbent Seeking Re-Election | No Third Party | Strong Short-Term Economy | Strong Long-Term Economy | Major Policy Change | No Social Unrest | No Scandal | No Foreign/ Military Failure | Major Foreign/ Military Success | Charismatic Incumbent | Uncharismatic Challenger | False Keys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984 | Ronald Reagan | Walter Mondale | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 2 |
| 1988 | George H. W. Bush | Michael Dukakis | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1992 | George H. W. Bush | Bill Clinton | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 6 |
| 1996 | Bill Clinton | Bob Dole | F | T | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 2000 | Al Gore | George W. Bush | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 2004 | George W. Bush | John Kerry | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | T | F | T | 4 |
| 2008 | John McCain | Barack Obama | F | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | 9 |
| 2012 | Barack Obama | Mitt Romney | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 2016 | Hillary Clinton | Donald Trump | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 7 |
| 2020 | Donald Trump | Joe Biden | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | 7 |
Incumbent victories
[edit]| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | False Keys | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1864 | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1868 | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | 2 |
| 1872 | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | T | 3 |
| 1880 | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | 4 |
| 1888 | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | 5 |
| 1900 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | F | 3 |
| 1904 | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | 0 |
| 1908 | T | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1916 | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1924 | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | 4 |
| 1928 | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1936 | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 1 |
| 1940 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | 2 |
| 1944 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | 2 |
| 1948 | F | T | T | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | 5 |
| 1956 | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | 1 |
| 1964 | F | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | T | F | T | F | T | 3 |
| 1972 | F | T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T | T | T | F | T | 4 |
| P(i/I) | 0.444 | 0.944 | 0.777 | 0.944 | 1.000 | 0.722 | 0.722 | 0.722 | 1.000 | 0.833 | 0.777 | 0.388 | 0.944 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | False Keys | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | 7 |
| 1876 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | T | F | T | F | F | T | 9 |
| 1884 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | 7 |
| 1892 | F | F | T | F | T | T | T | F | T | T | F | F | T | 6 |
| 1896 | F | F | F | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | T | T | 8 |
| 1912 | F | F | T | F | T | T | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | 6 |
| 1920 | F | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | T | F | T | F | T | 8 |
| 1932 | F | T | T | T | F | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | 8 |
| 1952 | T | F | F | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | F | 8 |
| 1960 | F | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | T | F | F | F | F | 9 |
| 1968 | F | F | F | F | T | T | T | F | T | F | F | F | T | 8 |
| 1976 | F | F | T | T | T | F | F | T | F | F | F | F | T | 8 |
| 1980 | F | F | T | F | F | T | F | T | T | F | T | F | F | 8 |
| P(i/C) | 0.154 | 0.154 | 0.385 | 0.615 | 0.462 | 0.385 | 0.231 | 0.538 | 0.769 | 0.538 | 0.231 | 0.154 | 0.692 |
Fractions
[edit]25⁄300
25⁄300
25⁄300
5+25⁄300
Atomic theory
[edit]Dalton's law of multiple proportions
[edit]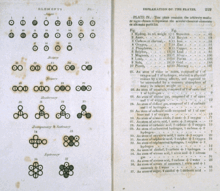
In the early 1800s, John Dalton compiled experimental data gathered by himself and other scientists and noticed that chemical elements seemed to combine by weight in ratios of small whole numbers. This pattern is now known as the "law of multiple proportions". The small number ratios suggested that elements combine in multiples of basic units of mass, which Dalton concluded were atoms.
For instance, there are two types of tin oxide: one is a black powder that is 88.1% tin and 11.9% oxygen, and the other is a white powder that is 78.7% tin and 21.3% oxygen. Adjusting these figures, in the black oxide there is about 13.5 g of oxygen for every 100 g of tin, and in the white oxide there is about 27 g of oxygen for every 100 g of tin. 13.5 and 27 form a ratio of 1:2, a ratio of small whole numbers. In these respective oxides, for every tin atom, there is one or two oxygen atoms (SnO and SnO2).[17][18]
As a second example, Dalton considered two iron oxides: a black powder which is 78.1% iron and 21.9% oxygen, and a red powder which is 70.4% iron and 29.6% oxygen. Adjusting these figures, in the black oxide there is 28 g of oxygen for every 100 g of iron, and in the red oxide there is 42 g of oxygen for every 100 g of iron. 28 and 42 form a simple ratio of 2:3. In these respective oxides, for every two atoms of iron, there are two or three atoms of oxygen (Fe2O2 and Fe2O3).[a][19][20]
As a final example, there are three oxides of nitrogen in which for every 140 g of nitrogen, there is 80 g, 160 g, and 320 g of oxygen respectively, which gives a simple ratio of 1:2:4. The respective formulas for these oxides are N2O, NO, and NO2.[21]
Atomic weight
[edit]Dalton began deducing how much the individual atoms of each element weighed, using hydrogen (the lightest element) as the basic unit of weight; this is known as atomic weight.
Skepticism
[edit]For the same reason, although Dalton believed in physical atoms, most of his interpreters were content with a theory of chemical atoms the minima of the experimentally defined elements. Whether these chemical atoms were themselves composed from homogeneous orheterogeneous physical atoms was to go beyond the evidence of purestoichiometry.
— The Fontana History of Chemistry
There were two types of atomism in the nineteenth century: a universally, if usually only implicitly, accepted chemical atomism, which formed the conceptual basis for assigning relative elementary weights and for assigning molecular formulae; and a highly controversial physical atomism, which made claims concerning the ultimate mechanical nature of all substances. Although the two types were intimately related and were both implicitly advocated by Dalton, chemists generally left physical atomism to physicists. By the 1870s, the identity of these two theories was becoming clearer and unification was finally achieved in the early years of the twentiethcentury oddly, just at the time when the structure of atoms was beginning to be explored by chemists and physicists.
— The Fontana History of Chemistry, Chpt. 5, Conclusion
Pelletier
[edit]In 1792, B. Pelletier was first to notice that 100 parts of tin will react with either 13.5 or 27 parts of oxygen to created two different tin oxides.
https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x002488690&view=1up&seq=565
Bertrand Pelletier (1792). "Observations sur plusieurs propriétés du Muriate d'Étain" [Observations on various properties of muriate of tin]. Annales de chimie (in French). 12: 225–240.
Proust Papers
[edit]Cosmos: revue encyclopédique hebdomadaire des progrès des sciences ..., Volume 1 p. 660 — this 1865 book mentions what looks like Proust's original values for tin oxide contents: 87-13 and 78-22.
Encyclopédie théologique: ou Série de dictionnaires sur toutes les parties de la science religeuse, Volume 52 p 1263 — this 1858 book suggests looking through Journal de Physique editions from 1798 to 1809.
"Recherches sur l'Étain", Journal de Physique vol 51 (1800), p. 173 — A paper by Proust, which mentions Pelletiers findings about tin oxides but doesn't give values.
"Étain et Muriate d'Ammoniaque", Journal de Physique vol 61 (1805), p. 338 — Another paper by Proust, still no values for tin oxides contents.
[1] — this 1927 book mentions the connection between Pelletier and Proust regarding tin oxides, and lists a few papers in a bibliography.
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k9604748r/f348.image
A new view of the origin of Dalton's Atomic theory
Henry E. Roscoe; Arthur Harden (1896). A New View of the Origin of Dalton's Atomic Theory. Macmillan and Co.
F. Hoefer (1865). "La Chimie Moléculaire" [Molecular Chemistry]. In M.B.-R. de Monfort (ed.). Cosmos: Revue Encyclopédique Hebdomadaire des Progrès des Sciences et de leurs Applications aux Arts et à l'Industrie. 2 (in French). Vol. 1. Tramblay. pp. 658–663.
William Charles Henry (1854). Memoirs of the Life and Scientific Researches of John Dalton. Cavendish Society.
Geschichte der Chemie: Mit dem Bildnisse Berzelius', Volume 2 By Hermann Kopp
Development of the law of multiple proportions
[edit]In 1792, B. Pelletier was the first scientist to notice that a certain amount of tin will combine with a certain amount of oxygen to form one tin oxide, and twice the amount of oxygen to form a different oxide.[22]
Scholars who have reviewed the writings of Proust found that he had enough data to have discovered the law of multiple proportions himself, but somehow he did not. For instance, Proust had collected data on the compositions of the two known tin oxides, but it seems that it did not occur to him to adjust his figures to have a constant amount of tin so as to compare the relative amounts of oxygen in either oxide. For one tin oxide, Proust noted a composition of 87 parts of tin to 13 parts of oxygen; and for the other tin oxide, he noted a composition of 78.4 parts of tin and 21.6 parts of oxygen. Had Proust adjusted the tin content to 100 parts for both oxides, he would have noticed that 100 parts of tin will combine with either 14.9 or 28.2 parts of oxygen. 14.9 and 28.2 form a ratio of 1:1.85, which is 1:2 if one forgives experimental error. This did not occur to Proust, but it occurred to Dalton.[23]
Development of Dalton's atomic theory
[edit]The reasoning process by which Dalton developed his atomic theory is uncertain.[24] It is uncertain whether Dalton discovered the law of multiple proportions by accident and then developed atomic theory to explain it, or whether he already believed in atomic theory and the law of multiple proportions was a hypothesis he developed in order to investigate the validity of atomic theory.[25]
WATU
[edit]Where did Roberts get his training/inspiration in wargaming?
Parkin (2019) Ch 7: "Roberts’ naval career continued on a promising, if unorthodox trajectory when, following sorties to fit out Australia’s first aircraft carrier and a trip down the Danube, he was made a game designer for the Royal Navy. In July 1935, a few days after he was promoted to the rank of commander, Roberts joined the tactical school at Portsmouth. Here naval captains and their senior staff played wargames, hyper-evolved military-themed board games staged on floors painted to look like giant chessboards. Distant cousins to commercial board games such as Battleship and Risk, these wargames were intended to explore and rehearse lifelike combat situations, a crucible in which tactics could be tested, analysed, and refined. It was work to which Roberts took an immediate liking."
Parkin (2019) Ch 7: "The progenitor of the wargame on which Roberts based his games in Portsmouth was Fred Jane, a failed novelist who, in 1898, published the rules of a boardgame-style naval wargame in the Engineering Journal. Later that year, his books, Jane Naval Wargame and Fighting Ships, provided a formal set of rules, scorecards and ship diagrams, which were subsequently adapted by the navy. The game, which used scale ship models, a squared board and even some ping-pong-like bats to fire projectiles, was notable for its flexibility and realism. Jane tested the game aboard warships docked in Portsmouth Harbour and, four years later, a modified version was issued to HM Ships for training. It was a version of the Jane Naval Wargame that Roberts adapted at his posting in Portsmouth, more than three decades later."
Parkin (2019) Ch 8: "Churchill’s aide [Admiral Cecil Usborne] believed that Roberts, who had shown himself to be a talented strategist in Portsmouth and an enthusiastic proponent of games as a way to prepare for war, was the ideal person to evolve anti-U-boat tactics. Moreover, as a gifted communicator he was qualified to train escort commanders in those tactics."
The wargames that Roberts' played in 1935-37 at Portsmouth did not feature submarines
Parkin (2019) Ch 7: "Despite the fact that during the First World War the Germans had used submarines to great effect to disrupt the convoys bringing food and supplies to Great Britain, neither U-boats nor convoys featured in the wargames of 1935. [...] ‘Submarines were not mentioned,’ Roberts wrote of the games he was tasked with designing. ‘Nor were convoys and attacks on them. Nobody connected Hitler’s rise … to the possibility of another Battle of the Atlantic. Nor did I, to be absolutely fair.’"
When was Roberts put in charge of WATU?
Parkin (2019) Ch 8: "On the first day of 1942, Roberts was told to report to the Admiralty offices with an overnight bag. On arrival he met two of the navy’s most senior officers, the Second Sea Lord, Sir Charles Little, and Admiral Cecil Usborne, the former director of naval intelligence, now an aide to Winston Churchill. Usborne was responsible for overseeing the development of anti-U-boat weapons. To Roberts’ astonishment, the men began to describe, ‘most clearly’, the true extent of Britain’s ongoing losses in the Atlantic, and the Allied force’s miserable performance in battling the U-boats."
Parkin (2019) Ch 8: "Usborne motioned Roberts out of the office, and the two men went to the canteen to eat. There, over the course of two hours, Usborne explained what was needed of Roberts. He was to take the train to Liverpool, and report to Noble at the new Western Approaches HQ, which had been established in a building called Derby House, nicknamed ‘the Citadel’. He was to take charge of a large room on the top floor. Roberts would be assigned a group of young staff. Then, using any and every means necessary, he and his staff were to get to work on the U-boat problem."
Parkin (2019) Ch 10: "Roberts disembarked the train at Liverpool station in the early hours of 2nd January 1942."
WATU location
Parkin (2019) Ch 10: "Roberts was to be given the entire top floor of Derby House, recently vacated by Tate & Lyle sugar company, comprising eight rooms."
Wargame design
Parkin (2019) Ch 11: "The floor in the centre of the room was covered in brown linoleum, painted with white gridlines and punctuated with tiny wooden models, some of which had been fashioned from wood taken from HMS Nelson, an armoured cruiser built in the 1870s that had been scrapped in 1910."
Parkin (2019) Ch 11: "The convoy ships, the prize in play for both sides, would automatically plod on at each turn of the game toward their destination, the battle raging around them, just as at sea. Next, Roberts explained the rules of the game. Players were given two minutes in which to submit their orders for the next ‘turn’, to replicate the urgency of a real battlefield. The movements of the U-boats were drawn in green5 chalk on the floor, a colour chosen as it was impossible to make out against the floor’s tint when viewed from an angle. This ensured the U-boat positions were undetectable to the players peering through the canvas screens. The escort ships’ movements would then be added to the floor in white chalk, which was, in contrast to the green markings, legible to those peeking from the canvas holes. Turn by turn the pieces would move around the floor, as the escort ships dashed to the site of an explosion to drop depth charges, and the U-boats performed their feints and dodges in an effort to pick off convoy ships, while evading the escort."
Parkin (2019) Ch 11: "As Okell surveyed the floor, Roberts explained that each white line was spaced ten inches apart, representing one nautical mile, while the counters represented ships and surfaced German U-boats."
Raspberry
Parkin (2019), A Game of Birds and Wolves. Ch 11: "If the U-boats were firing from outside the perimeter of the convoy, how had Annavore, which was in the centre of the convoy, been sunk? Might it be possible, he wondered, that the U-boat had attacked the ship from inside the columns of the convoy? There was, he reasoned, a simple way to prove his theory."
Parkin (2019), A Game of Birds and Wolves. Ch 11: "Between them, Roberts and the two Wrens began to plot different scenarios that might have enabled the U-boat to sneak into the convoy without being detected. Only one checked out: the U-boat had entered the columns of the convoy from behind. And it must have done so on the surface, where it was able to travel at a faster speed than the ships. By approaching from astern, where the lookouts rarely checked, the U-boat would be able to slip inside the convoy undetected, fire at close range, then submerge in order to get away."
Parkin (2019), A Game of Birds and Wolves. Ch 11: "With the U-boat tactic abruptly unveiled, Roberts wanted to try out some potential countermeasures that might foil the plan. The four returned to the game room. Roberts assumed the role of the U-boat captain, and Laidlaw and Okell played as Walker’s escort ships. The countermeasure revealed itself immediately. Rather than splay out from the convoy at speed, dropping depth charges at random, Laidlaw and Okell lined the escort ships up around the convoy. While the convoy continued on its way, each escort ship performed a triangular sweep, listening for U-boats on the ASDIC."
Effects of WATU
Parkin (2019), A Game of Birds and Wolves. Ch 12: "Still, the work was exhilarating, especially when the first fruits of WATU’s work began to be seen in summer 1942, when escort ships sank four times as many U-boats as the previous month, beginning an upward trend that would continue, broadly, for the rest of the year."
Military wargames
[edit]The obvious advantage of wargaming is that it allows the military to conduct training and research in a safe and relatively cheap way.
In 2018, the US Navy spent $3.35 million on wargaming,[26].
Another advantage of wargames is that it allows the military to develop the skills and theories of its officers without the enemy noticing and adapting. A problem that any military faces when learning through hard experience – i.e. actual warfare – is that as it gets better at fighting the enemy, the enemy will adapt in turn, modifying their own armaments and tactics to maintain their edge. This problem doesn't exist with wargaming, because if the real enemy cannot participate in the wargame, he cannot know what ideas were developed.[27]
Wargames can also teach trainees skills and theories faster than field experience, because wargames can greatly compress the timespan of a conflict. A campaign that might take months to wage in a real war might take only hours or days to simulate in a wargame.[28]
Wargames can be used to experiment with new tactical and strategic ideas. For instance, in the 1920s the US Navy conceived the circular formation, in which a capital ship such as a battleship or aircraft carrier is surrounded by a circle of smaller support ships to maximize defence against aircraft and submarines. After initial testing in wargames, the Navy developed the idea further through field exercises.
Wargames can be used to develop theories of how to best use a new weapon system before it's used in an actual war. Wargaming can help a military develop the best tactics, the logistical demands, the optimal command structure, etc. For instance, in World War I, the British deployed tanks (their recent invention) and learned how to use them through experience on the battlefield. The consequence of this was that as British tank tactics and strategies improved, the Germans kept pace, developing counter-measures. During the inter-war years, the German army used wargames (along with field exercises) to develop more advanced tank doctrines that would take the French by surprise in 1939. Whereas French tanks were attached to infantry or cavalry units, the Germans organized their tanks into dedicated corps (panzerkorps) which moved and fought with great speed and efficiency.
Wargames cannot be used to predict the outcomes of wars, or even battles, as one might forecast the weather. However, they can identify a range of likely outcomes and the circumstances that lead to them. Wargames can help planners decide which armaments to produce, design contingencies for likely enemy responses, identify important strategic locations, etc.
If a wargame cannot teach a student specific tactics and strategies, they can at least train students to become better at devising tactics and strategies. For instance, in the years leading up to World War 2, the US Navy knew little of the capabilities of Japanese warships, and consequently could not provide accurate models for its wargames. Instead, instructors used made-up models for Japanese warships, and challenged the players to discover the capabilities of the virtual Japanese in the course of the game itself, and then devise appropriate tactics and strategies on the fly. Navy officers became quite good at this kind of improvisation, and during World War 2, when they could finally test the real Japanese in combat, they could size up the enemy and devise new tactics very quickly.[29]
Peter Perla argues that using wargames is more akin to historical research than science. By that he means that the outcomes of all these simulated battles and campaigns are to be studied in the same way one would study the actual history of warfare.
Benefits of wargames for training
- They stimulate discussion
Perla (1990) harvp error: multiple targets (4×): CITEREFPerla1990 (help): "This is especially important for professional games, whose objectives tend to be more specific than those of commercial games."
Perla (1990) harvp error: multiple targets (4×): CITEREFPerla1990 (help): "Unlike those in the wargaming hobby, professional wargamers work in a relatively closed society. One organization's games are not freely available for all to try, critique, and modify. Professional wargame designers may document their games (usually in classified publications), but they seldom describe the design process they employed to create them."
Creveld (2013) harvp error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFCreveld2013 (help): "Still following Dunnigan, who has extensive experience in working both in the commercial world and with the military, wargames used by the military tend to suffer from several problems. One is the need to satisfy the requirements of many different user organizations each of which does not wish to buy the game off the shelf but actively attempts to pull it in its own direction. Often the outcome is great complexity and compromises that end up, like the famous camel that was created by a committee, by satisfying nobody. Adding more and more features in the name of “realism” also causes the cost to go up, ultimately leading to diminishing returns. Much of the data that goes into the programs is classified: as a result, checking on whether it is correct is difficult, and errors, once they have crept in, tend to stay.61 Secrecy also makes it hard to update the games as needed. Finally, those who design, manufacture, and market games in the commercial world are obliged to pay attention to users’ demands, such as ease of play and creating a good interface between player and game. Their counterparts working in, or for, the military, are not nearly as affected by these concerns. On occasion this can lead to bad games that people simply do not want to play."
Wolfpacks
[edit]During World War I, German submarines typically operated in isolation, attacking targets of opportunity alone, because the limited radio technology of the time made it difficult for them to operate in groups and the submarines were divided up among multiple commands. The British responded to this by organizing merchant ships into escorted convoys, which was highly effective. Some German officers proposed organizing submarines into groups which could overwhelm the escorts with a concerted attack, but these ideas were not adopted because the submarines were divided up among multiple commands, and radio communications technology at the time was not up to the task. In 1935, Admiral Karl Doenitz took command of Germany's rebuilt submarine fleet, and began developing a group-attack doctrine. Doenitz mostly relied on field exercises to test his ideas, but in the winter of 1938-39, he conducted a wargame simulation. From his wargame, he concluded that once a target had been picked, command should be delegated to a lead submarine which was close to the target; and that Germany need 300 submarines to effectively destroyed British shipping.[30]
Military wargames as training tools
[edit]What instructors attempt to do with them
[edit]Wargames are used to develop an officer's strategic decision-making skills in the context of a command role in a military operation (such as a battle or a campaign). This is the oldest application of wargaming. The actual effectiveness of wargaming in this regard—turning a mediocre strategist into a capable one —is uncertain, because officers use many tools to hone their decision-making skills and the effect of wargaming is difficult to isolate.[31]
Wargames teach players to cope with incomplete, delayed, or incorrect information.[32]
A wargame should accurately simulate how a commander in the field would receive information, and what sort of information he would receive. Done correctly, wargames teach players the protocols for sharing and discussing information; teach them to cope with incomplete, irrelevant, delayed, or incorrect information; and teach them to cope with surprises.
US Navy wargaming Inter-war years
[edit]- What resources did the NWC allocate to wargaming?
- How were the insights developed in wargames transmitted to the Navy?
Perla
[edit]In 1894, wargaming became a regular tool of instruction at the US Naval War College.[33] Wargaming was brought to the College by William McCarty Little, a retired Navy lieutenant who had likely been inspired after reading The American Kriegsspiel by W.R. Livermore.[34]
Lillard
[edit]Old stuff
[edit]During that same period, the US Navy also began experimenting with "circular formations" in wargames. In a circular formation, a capital ship is surrounded by concentric rings of cruisers and destroyers. The players found that such a formation was easier to maneuver, as the entire group could be made to turn at once with a signal from the central ship, whereas in a conventional battle line the ships had to turn in succession. This formation also concentrated anti-aircraft fire.[35][36] Initially, battleships were at the center of the formation, but after further experimentation in wargames, it was decided that an aircraft carrier should be at the center. Aircraft carriers could attack at longer distances from within the safety of a circular formation, whereas battleships needed to form a forward line of battle to be most effective.[37] Thus, wargaming allowed the Navy to adapt to the rising importance of aircraft and the aircraft carrier. By the time war with Japan broke out in 1939, the US Navy had already relegated its battleships to defensive roles close to the homeland, and carrier-centric battle groups were standard for offensive operations.[38]
The wargames did not prove as effective at developing submarine tactics.
- American torpedoes had unknown defects that were not discovered until after war broke out, therefore the wargames did not model their performance accurately.[39] Once these technical defects were corrected, American submarines went on to have a much bigger impact in the war than anyone expected.[40]
- Unlike Germany, the US Navy had little experience with submarine warfare and thus the wargames did not have an established submarine doctrine to work from.[41]
- The Navy thought that submarines would do peripheral roles such as laying mines or spotting aircraft, whereas the Naval War College wargames focused on combatant actions.[42]
- The wargames underestimated the ability of Japanese ability to fight at night, and did not anticipate the superiority of their Long Lance torpedoes.[43]
In the 1920s, US Navy planners believed that America could win a war with Japan quickly by simply sailing an armada across the Pacific and knocking out the Japanese navy with a few decisive battles (the "thruster strategy", as it was called).[44] But when this strategy was tested in wargames, it routinely failed. Japan held off the assault until the American armada exhausted itself, and then counter-attacked. The wargames foretold that a war with Japan would instead be a prolonged war of attrition which would require America to acquire advance bases in the western Pacific where its warships could get resupplied and repaired.[45][46] Such an infrastructure would require making alliances with friendly countries such as Australia, New Zealand, and the British Empire.[47] When war with Japan broke out after the Pearl Harbor attack, America did not immediately send an armada to recapture the islands of Guam and Wake or relieve MacArthur in the Philippines. Rather, the Navy took the slow-and-steady approach, building up experience and infrastructure.
How inter-war Naval War College wargames worked
[edit]Cold War wargaming
[edit]WW2
Caffrey (2019), p. 55 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "Apparently the former tsarist officers who came over to the Red Army during Russia’s civil war brought imperial Russia’s wargaming techniques with them."
Caffrey (2019), p. 55 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "Terrain models were common for even very large operations, and a wargame typically comprised a single turn. The slow, detailed adjudication of these wargames that was optimal for decision support was poorly suited to developing the thinking skills of Soviet officers."
Caffrey (2019), p. 61-62 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "Soviet games typically centered on terrain models. Using each side’s plans for the entire mission, the umpires, using incredibly detailed and cumbersome procedures, would the adjudicate the operation all at once, all the way to its conclusion. Only then would the two teams be called back and walked through the operation, step by step. Essentially, these were one-move wargames."
Caffrey (2019), p. 63 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "The defeat of the Axis powers ushered in an eclipse of wargaming. Obviously, the former Axis nations ceased wargaming. Within the United States, gaming dropped almost as steeply. Only inside the Soviet Union did wargaming expand and become more rigorous."
Cold War
Caffrey (2019), p. 74 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "...immediately after World War II, wargaming at the Naval War College dropped to about 10 percent of its prewar levels. However, as early as 1947 the College increased its use of wargaming with the addition of a game-intensive logistics course."
Caffrey (2019), p. 78 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "If the British were less than thorough in their data collection, the Soviets were obsessive. Even before the cessation of hostilities, they launched a massive effort to collect and compile operational data from their part of World War II, the “Great Patriotic War,” to increase the validity of their wargaming."
Vietnam
Caffrey (2019), p. 85 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "But the largest impact was achieved in the East, by Soviet-style wargames. The Soviets opened their service schools to the officers of satellite and other communist countries. Wargaming constituted a very significant part of their curriculum. The North Vietnamese applied the methods they learned in the USSR with effective results. Using Soviet methods, they wargamed each of their attacks against the South Vietnamese and their allies, from firefights to major battles. Familiarity with the plans the Soviet method produced allowed the communists to coordinate fairly complicated attacks without radios: subordinate commanders remembered a plan’s timetable and executed it by their wristwatches."
Wargame Bibliography
[edit]First-Last
[edit]- Wargaming Handbook. Development, Concepts and Doctrine Centre (Ministry of Defence, UK).
- E. B. Potter (1976). Nimitz. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-492-6.
- Georg Heinrich Rudolf Johann von Reisswitz (1824). Anleitung zur Darstellung militairische Manover mit dem Apparat des Kriegsspiel [Instructions for the Representation of Military Maneuvres with the Kriegsspiel Apparatus] (in German). (translation by Bill Leeson, 1989)
- George Leopold von Reiswitz (1812). Taktisches Kriegs-Spiel oder Anleitung zu einer mechanischen Vorrichtung um taktische Manoeuvres sinnlich darzustellen [Tactical War Game - or, instruction to a mechanical device to simulate tactical maneuvers] (in German). Gädicke.
- H. G. Wells (1913). Little Wars.
- "Foreign War Games". Selected Professional Papers Translated from European Military Publications. Translated by H. O. S. Heistand. Washington D.C.: US Government Printing Office. 1898. pp. 233–289.
- Heinrich Ernst Dannhauer (11 July 1874). "Das Reiswissche Kriegsspiel von seinem Beginn bis zum Tode des Erfinders 1827" [The Reiswitzian Wargame from its Inception until the death of the inventor in 1827]. Militär-Wochenblatt. Vol. 59, no. 56. pp. 527–532.
- Johann Christian Ludwig Hellwig (1803). Das Kriegsspiel [The Wargame] (in German).
- John M. Lillard (2016). Playing War: Wargaming and U.S. Navy Preparations for World War II. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-1-61234-773-8.
- Jon Peterson (2012). Playing at the World: A History of Simulating Wars, People and Fantastic Adventures, from Chess to Role-playing Games. Unreason Press. ISBN 9780615642048.
- Karl Doenitz (2012) [first published 1959]. The Memoirs of Karl Doenitz: Ten Year and Twenty Days. Translated by George Weidenfeld. Frontline Books. ISBN 9781783031429.
- Martin van Creveld (2013). Wargames: From Gladiators to Gigabytes. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107036956.
- Matthew B. Caffrey Jr. (2019). "On Wargaming: How Wargames Have Shaped History and How They May Shape the Future". The Newport Papers (43). Naval War College Press (US). ISBN 978-1-935352-65-5.
- Michael J. Tresca (2011). The Evolution of Fantasy Role-Playing Games. McFarland. ISBN 9780786460090.
- Michael Vlahos (1980). The Blue Sword: The Naval War College and the American Mission, 1919-1941. US Naval War College Press.
- Michael Vlahos (1986). "Wargaming, an Enforcer of Strategic Realism: 1919-1942". Naval War College Review. 39 (2).
- Milan Vego (2012). "German War Gaming". Naval War College Review. 65 (4).
- Pat Harrigan; Matthew G. Kirschenbaum, eds. (2016). Zones of Control: Perspectives on Wargaming. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262033992.
- Paul Schuurman (2017). "Models of war 1770–1830: the birth of wargames and the trade-off between realism and simplicity". History of European Ideas. 43 (5): 442–455. doi:10.1080/01916599.2017.1366928. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
- Peter P. Perla; Raymond T. Barrett (1985). An Introduction to Wargaming and its Uses (PDF).
- Peter P. Perla (2012) [first published 1990]. John Curry (ed.). Peter Perla's The Art of Wargaming: A Guide for Professionals and Hobbyists. The History of Wargaming Project. ISBN 978-1-4716-2242-7.
- Philip Sabin (2012). Simulating War: Studying Conflict Through Simulation Games. A&C Black. ISBN 9781441185587.
- Phillip von Hilgers (2000). "Eine Anleitung zur Anleitung. Das Takstische Kriegsspiel 1812-1824" (PDF). Board Games Studies: International Journal For the Study of Board Games (in German) (3): 59–78. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-07-10.
- Rick Priestley; John Lambshead (2016). Tabletop Wargames: A Designers' and Writers' Handbook. Pen & Sword Books Limited. ISBN 9781783831487.
- Rolf F. Nohr; Stefan Böhme (2009). Die Auftritte des Krieges sinnlich machen. Appelhans-Verlag Braunschweig. ISBN 978-3-941737-02-0.
- Shawn Burns, ed. (2013). War Gamers' Handbook: A Guide for Professional War Gamers (PDF). US Naval War College.
- Tristan Donovan (2017). It's All a Game: The History of Board Games from Monopoly to Settlers of Catan. Macmillan. ISBN 9781250082732.
- Walter R. Borneman (2012). The Admirals: Nimitz, Halsey, Leahy, and King--The Five-Star Admirals Who Won the War at Sea. Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-20252-7.
Last-First
[edit]- Wargaming Handbook. Development, Concepts and Doctrine Centre (Ministry of Defence, UK).
- Borneman, Walter R. (2012). The Admirals: Nimitz, Halsey, Leahy, and King--The Five-Star Admirals Who Won the War at Sea. Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 978-0-316-20252-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Burns, Shawn, ed. (2013). War Gamers' Handbook: A Guide for Professional War Gamers (PDF). US Naval War College.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Caffrey, Matthew B. (2019). "On Wargaming: How Wargames Have Shaped History and How They May Shape the Future". The Newport Papers (43). Naval War College Press (US). ISBN 978-1-935352-65-5.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Creveld, Martin van (2013). Wargames: From Gladiators to Gigabytes. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107036956.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Dannhauer, Heinrich Ernst (11 July 1874). "Das Reiswissche Kriegsspiel von seinem Beginn bis zum Tode des Erfinders 1827" [The Reiswitzian Wargame from its Inception until the death of the inventor in 1827]. Militär-Wochenblatt. Vol. 59, no. 56. pp. 527–532.
{{cite magazine}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Doenitz, Karl (2012) [first published 1959]. The Memoirs of Karl Doenitz: Ten Year and Twenty Days. Translated by Weidenfeld, George. Frontline Books. ISBN 9781783031429.
- Donovan, Tristan (2017). It's All a Game: The History of Board Games from Monopoly to Settlers of Catan. Macmillan. ISBN 9781250082732.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Pat Harrigan; Matthew G. Kirschenbaum, eds. (2016). Zones of Control: Perspectives on Wargaming. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262033992.
- "Foreign War Games". Selected Professional Papers Translated from European Military Publications. Translated by H. O. S. Heistand. Washington D.C.: US Government Printing Office. 1898. pp. 233–289.
- Hellwig, Johann Christian Ludwig (1803). Das Kriegsspiel [The Wargame] (in German).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Hilgers, Phillip von (2000). "Eine Anleitung zur Anleitung. Das Takstische Kriegsspiel 1812-1824" (PDF). Board Games Studies: International Journal For the Study of Board Games (in German) (3): 59–78. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-07-10.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Lillard, John M. (2016). Playing War: Wargaming and U.S. Navy Preparations for World War II. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-1-61234-773-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Nohr, Rolf F.; Böhme, Stefan (2009). Die Auftritte des Krieges sinnlich machen. Appelhans-Verlag Braunschweig. ISBN 978-3-941737-02-0.
- Perla, Peter P.; Barrett, Raymond T. (1985). An Introduction to Wargaming and its Uses (PDF).
- Perla, Peter P. (2012) [first published 1990]. Curry, John (ed.). Peter Perla's The Art of Wargaming: A Guide for Professionals and Hobbyists. The History of Wargaming Project. ISBN 978-1-4716-2242-7.
- Peterson, Jon (2012). Playing at the World: A History of Simulating Wars, People and Fantastic Adventures, from Chess to Role-playing Games. Unreason Press. ISBN 9780615642048.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Priestley, Rick; Lambshead, John (2016). Tabletop Wargames: A Designers' and Writers' Handbook. Pen & Sword Books Limited. ISBN 9781783831487.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Potter, E. B. (1976). Nimitz. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-492-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Reisswitz, Georg Heinrich Rudolf Johann von (1824). Anleitung zur Darstellung militairische Manover mit dem Apparat des Kriegsspiel [Instructions for the Representation of Military Maneuvres with the Kriegsspiel Apparatus] (in German). (translation by Bill Leeson, 1989)
- Reiswitz, George Leopold von (1812). Taktisches Kriegs-Spiel oder Anleitung zu einer mechanischen Vorrichtung um taktische Manoeuvres sinnlich darzustellen [Tactical War Game - or, instruction to a mechanical device to simulate tactical maneuvers] (in German). Gädicke.
- Sabin, Philip (2012). Simulating War: Studying Conflict Through Simulation Games. A&C Black. ISBN 9781441185587.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Schuurman, Paul (2017). "Models of war 1770–1830: the birth of wargames and the trade-off between realism and simplicity". History of European Ideas. 43 (5): 442–455. doi:10.1080/01916599.2017.1366928. Retrieved 2018-10-27.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Tresca, Michael J. (2011). The Evolution of Fantasy Role-Playing Games. McFarland. ISBN 9780786460090.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Vego, Milan (2012). "German War Gaming". Naval War College Review. 65 (4).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Vlahos, Michael (1980). The Blue Sword: The Naval War College and the American Mission, 1919-1941. US Naval War College Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Vlahos, Michael (1986). "Wargaming, an Enforcer of Strategic Realism: 1919-1942". Naval War College Review. 39 (2).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Wells, H. G. (1913). Little Wars.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link)
Other stuff
[edit]- 1937: $612 (AFI $12,971)
- 1938: $4,530 (AFI $98,054)
- 1939: $8,612.21 (AFI $188,644)
- 1940: $38,080.42 (AFI $828,181)
- 1941: $56,573.48 (AFI $1,171,916)
- 1942: $63,776.46 (AFI $1,189,282)
- 1943: $63,776.46 (AFI $1,082,695)
- 1944: $57,638.52 (AFI $997,615)
- 1945: $48,794.46 (AFI $825,808)
- 1946: $49,938.58 (AFI $780,269)
- 1947: $11,148.82 (AFI $152,129)
- TOTAL: AFI $5,875,001
TOTAL 5,885,419
344,211
SUM: $7314593
rounded :
SUM: $7,300,000
Superman 1950s TV ratings from Billboard
[edit]| The Billboard (% households) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | |||||
| Jan | Example | Example | Example | 17.9[48] | 16.0[49] | 13.1[50] | Example | ||||
| Feb | Example | Example | Example | 17.1[51] | 15.1[52] | 12.8[53] | Example | ||||
| Mar | Example | Example | Example | 16.7[54] | 14.5[55] | 13.7[56] | Example | ||||
| Apr | Example | Example | Example | 16.2[57] | 14.6[58] | 13.9[59] | Example | ||||
| May | Example | Example | Example | 13.1[60] | 12.6[61] | Example | |||||
| Jun | Example | Example | 14.6[62] | 13.0[63] | 11.2[64] | 11.4[65] | Example | ||||
| Jul | Example | Example | 12.1[66] | 10.9[67] | 10.0[68] | Example | Example | ||||
| Aug | Example | Example | 11.3[69] | 10.4[70] | 9.4[71] | Example | Example | ||||
| Sep | Example | Example | 12.2[72] | 10.9[73] | 10.1[74] | Example | Example | ||||
| Oct | Example | Example | 12.6[75] | 11.1[76] | 10.5[77] | Example | Example | ||||
| Nov | Example | Example | 15.6[78] | 13.7[79] | 11.0[80] | Example | Example | ||||
| Dec | Example | Example | 17.3[81] | 14.4[82] | 12.6[83] | Example | Example | ||||
Superman 1950s TV ratings from Sponsor Magazine
[edit]| Sponsor Magazine | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1952 | 1953 | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | |
| Jan | Example | 21.3[84] | 19.0[85] | 20.2[86] | 16.9[87] | 17.7[88] | Example |
| Feb | Example | 22.1[89] | 19.8[90] | 19.8[91] | 17.0[92] | Example | off-chart[93] |
| Mar | Example | 20.6[94] | 20.7[95] | Example | Example | 18.7[96] | off-chart[97] |
| Apr | Example | 18.3[98] | 20.3[99] | 19.1[100] | 17.6[101] | Example | off-chart[102] |
| May | Example | 17.6[103] | 18.7[104] | 17.2[105] | off-chart[106] | 16.6[107] | Example |
| Jun | Example | 16.6[108] | off-chart[109] | off-chart[110] | Example | off-chart[111] | Example |
| Jul | Example | 14.9[112] | 14.7[113] | off-chart[114] | off-chart[115] | off-chart[116] | Example |
| Aug | Example | 13.8[117] | off-chart[118] | off-chart[119] | off-chart[120] | off-chart[121] | Example |
| Sep | Example | 14.6[122] | off-chart[123] | off-chart[124] | Example | 13.2[125] | Example |
| Oct | Example | off-chart[126] | 16.6[127] | off-chart[128] | Example | Example | Example |
| Nov | 17.2[129] | 17.0[130] | 18.3[131] | 15.5[132] | 15.8[133] | Example | Example |
| Dec | 21.1[134] | 18.1[135] | 19.4[136] | 16.3[137] | 16.9[138] | Example | Example |
Superman 1940s radio show ratings
[edit]| 1940 | 1941 | 1942 | 1943 | 1944 | 1945 | 1946 | 1947 | 1948 | 1949 | 1950 | 1951 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Feb | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Mar | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Apr | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| May | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Jun | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Jul | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Aug | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Sep | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Oct | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Nov | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
| Dec | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example | Example |
SUPERMAN MOVIES
[edit]Superman (1978)
- budget: $55 million (AFI $256,928,571)
- box office: $300 million ($1,401,428,571)
Man of Steel 2013
- budget: $225 million ($294,300,000)
- box office: $668 million ($873,744,000)
Batman v Superman 2016
- budget: $263 million ($333,891,847)
- box office: $873.6 mil ($1,109,079,534)
CAPTAIN MARVEL
[edit]AMYGDALECTOMY
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Whittaker, E. T.; McCrae, Sir William (1988-12-15). A Treatise on the Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies (1 ed.). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511608797. ISBN 978-0-521-35883-5.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rutherford 1911was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Goldstein, Herbert. Classical Mechanics. United States, Addison-Wesley, 1950.
- ^ "Impact Parameter for Nuclear Scattering". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. Retrieved 2024-05-30.
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Beiser1969was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Determining the Impact Parameter". HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. Retrieved 2024-07-05.
- ^ Iceberg Slim (1969). Pimp: The Story of My Life. Chapter 2
- ^ Iceberg Slim (1969). Pimp: The Story of My Life. Chapter 3
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ThomsonScattering1910was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Heilbron1968was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Heilbron (1968). p. 278
- ^ Heilbron (1968). p. 270
- ^ For example overview of classical mechanics was published in 1904: Whittaker, E. T.; McCrae, Sir William (1988-12-15). A Treatise on the Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies (1 ed.). Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511608797. ISBN 978-0-521-35883-5.
- ^ Ernest Rutherford (1911). "The Scattering of α and β Particles by Matter and the Structure of the Atom" (PDF). Philosophical Magazine. Series 6. 21 (125): 669–688. doi:10.1080/14786440508637080.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
BeiserPerspectiveswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/elesph.html [bare URL]
- ^ Dalton (1817). A New System of Chemical Philosophy vol. 2, pp. 36
- ^ Melsen (1952). From Atomos to Atom, p. 137
- ^ Dalton (1817). A New System of Chemical Philosophy vol. 2, pp. 28
- ^ Millington (1906). John Dalton, p. 113
- ^ Holbrow et al (2010). Modern Introductory Physics, pp. 65-66
- ^ Proust (1800). Journal de Physique, vol. 51, p. 173
- ^ Henry (1854). Memoirs..., p. 82
- ^ Millington (1906). John Dalton, pp. 109-110
- ^ Roscoe & Harden (1896). New View of Dalton's Atomic Theory, p. 4
- ^ Department of Defense Fiscal Year (FY), 2020 Budget Estimates, March 2019, Justification Book Volume 4 of 5, Research, Development, Test & Evaluation, Navy Budget Activity 6 pg 11 https://www.secnav.navy.mil/fmc/fmb/Documents/20pres/RDTEN_BA6_book.pdf
- ^ Caffrey (2019), p. 285 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help)
- ^ Caffrey (2019), p. 286 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help)
- ^ Caffrey (2019), p. 52-53 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help)
- ^ The Memoirs of Karl Doenitz
- ^ Caffrey (2019), p. 282-283 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFCaffrey2019 (help): "Wargaming can be useful in developing the potential of individuals. This being the oldest application of wargaming, one might assume that its usefulness has the most historical support. Unfortunately, if history includes an account of a prince with a record of losing battles taking up chess and then going on to victory, I have yet to find it. The increase in military effectiveness with the founding of staff and war colleges might be seen as pertinent. Still, wargaming made up just one part of the individuals’ studies, making the effect of gaming alone difficult to isolate."
- ^ Lillard (2016), p. 64 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "The rooms did not pitch and roll and there was no gunfire to contend with, but the important aspect of having to deal with partial, heavily processed, and time-late information was quite accurately replicated."
- ^ Perla (1990) harvp error: multiple targets (4×): CITEREFPerla1990 (help): "In 1894, under newly appointed President Captain Henry Taylor, gaming became an integral and permanent part of the course of study for all students."
- ^ Perla (1990) harvp error: multiple targets (4×): CITEREFPerla1990 (help): "Little's budding interest in wargaming was almost certainly stimulated by his association with army Major W. R. Livermore, author of The American Kriegsspiel, who was stationed across the harbor from the Naval War College in Fort Adams."
- ^ Lillard (2016), p. 74 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help)
- ^ Potter (1976), p. 138 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFPotter1976 (help): "In setting up the board one day, [Commander Roscoe C.] MacFall placed the supporting cruisers and destroyers in concentric circles around the battleships. The obvious advantages of this arrangement were that it concentrated antiaircraft fire and that the direction of the whole formation could be changed by a simple turn signal, all ships turning together. Experiments showed, moreover, that deployment into a column was far less difficult and time-consuming from a circular formation than it was from a rectangular formation with echelons of supporting vessels thrust out ahead like exploratory antennae."
- ^ Potter (1976), p. 137 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFPotter1976 (help): "In these [wargames] [Admiral William S. Sims] had demonstrated, at least to his own satisfaction, that the carrier had replaced the battleship as the Navy's capital ship. This was because the attack radius of the carrier's planes much outdistanced the range of the battleship's guns."
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "For the first six months of the war, task forces built around aircraft carriers and cruisers made small forays against Japanese bases in the Mandate islands, but the intact or slightly damaged battleships—not only slow but also voracious consumers of fuel in a fleet that was critically short of fleet tankers—stayed close to home. [...] Nimitz viewed the battleships more as a defensive liability than a contribution to the “striking power” of his force. His intent was to engage the Japanese fleet with his carriers alone. [...] The War College wargames and fleet problems had been illustrating the vulnerabilities of a battle force built around battleships for years."
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "...crippling deficiencies in torpedoes did not reveal themselves until after the start of hostilities. Due to small budgets and service infighting, U.S. Navy torpedoes were inadequately tested, but the small sample of test results was sufficient to convince Navy leadership that their torpedoes would work as advertised under operational conditions. These assumptions were reflected in maneuver rules and in War College wargames."
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "Once overcautious commanders were replaced with more aggressive officers, proper tactics were developed, and, most of all, torpedo deficiencies were diagnosed and corrected, the submarine force rapidly evolved into a major factor in the eventual defeat of Japan."
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "Strategically, submarines were still something of an unknown quantity in interwar period navies.
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "In the interwar period, the United States and other navies experimented with “submarine cruisers” equipped with large-caliber guns and spotting aircraft (such as the French Surcouf and British M2 and X1) and in a mine-laying role (such as USS Argonaut), reflecting the conflicting views of how they should be employed. U.S. Navy submarine tactics reflected this strategic confusion."
- ^ Lillard (2016) harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "two things that the wargame designers did not foresee (and that Admiral Nimitz did not mention in his speeches) were the Japanese capabilities in night combat and the superiority of their Long Lance torpedoes, which drove the outcomes of those individual battles."
- ^ Lillard (2016), p. 70 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "The Mahanian strategy was to gather the battle fleet in a large formation, steam forward to a point where the enemy would be compelled to bring out their fleet, use the firepower of dreadnought battleships to overwhelm the enemy battle line, and then blockade the enemy’s home waters. [...] This doctrine called for the U.S. Navy to steam directly across the central Pacific, engage the Japanese fleet in force, and defeat them as quickly as possible while the garrison defending the Philippines withdrew to the Bataan peninsula and fought a delaying action."
- ^ Lillard (2016), p. 106 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "Repeated experiments with all manner of approaches to the ORANGE war led to the same conclusion—that the U.S. Navy’s thruster strategy for the Pacific was not workable with the fleet in hand. The realization summarized in Van Auken’s report led the Research Department to conduct a comprehensive review of all of the trans-Pacific games played between 1927 and 1933. The Department compared BLUE and ORANGE losses in each game as a function of the BLUE force’s approach route, ORANGE defensive strategy, force composition (either actual or in accordance with the London Treaty), and BLUE force speed of advance. They concluded that variations in each of these factors made little difference in the game outcomes, and that BLUE would be at a major disadvantage in trying to fight their way past ORANGE-held island bases to reach the Philippines, simply because their continued advance put them farther and farther from their support infrastructure."
- ^ Vlahos (1986), p. 13 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFVlahos1986 (help): "[The US Navy] developed in gaming the doctrine and practice of progressive transoceanic offensive operations, where there had been before mere transit itinerary."
- ^ Lillard (2016), p. 103 harvp error: multiple targets (3×): CITEREFLillard2016 (help): "A major point stressed by the Research Department was that the BLUE fleet’s approach route highlighted the previously underappreciated need to receive fuel, provisioning, and basing support from allies in the region, namely England, Australia, and the Netherlands East Indies, and the need to repair underwater battle damage closer to the theater of operations."
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 26 Feb 1955. p. 5.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 17 Mar 1956. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 30 Mar 1957. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 26 Mar 1955. p. 4.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 21 Apr 1956. p. 22.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 27 Apr 1957. p. 11.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 21 May 1955. p. 8.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 9 Jun 1956. p. 13.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 27 May 1957. p. 14.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 28 May 1955. p. 10.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 7 Jul 1956. p. 14.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 24 Jun 1957. p. 16.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 21 Jul 1956. p. 16.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 5 Aug 1957. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 31 Jul 1954. p. 15.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 30 Jul 1955. p. 5.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 18 Aug 1956. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 26 Aug 1957. p. 36.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 28 Aug 1954. p. 2.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 24 Sep 1955. p. 5.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 15 Sep 1956. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 23 Oct 1954. p. 4.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 1 Oct 1955. p. 8.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 27 Oct 1956. p. 13.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 13 Nov 1954. p. 6.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 19 Nov 1955. p. 6.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 24 Nov 1956. p. 11.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 27 Nov 1954. p. 4.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 17 Dec 1955. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 15 Dec 1956. p. 8.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 25 Dec 1954. p. 6.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 21 Jan 1956. p. 14.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 26 Jan 1957. p. 17.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 12 Feb 1955. p. 12.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 18 Feb 1956. p. 10.
- ^ "The Billboard Scoreboard". The Billboard. 2 Mar 1957. p. 15.
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/n353/search/Maxwell
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54spon#page/n681/search/Maxwell
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55spon#page/n415/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1956-03/Sponsor-1956-03-1#page/n87/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57spon#page/n1017
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/n549/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54spon#page/n969/search/Maxwell
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55spon#page/n671/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1956-04/Sponsor-1956-04-1#page/n75/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor58spon#page/n1083/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/n797/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54spon#page/n1191/search/Maxwell
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57sponno2#page/n539/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor58sponno2#page/n51
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/n1035/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1954-06/Sponsor-1954-06-1#page/n71/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55spon#page/n1699/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56spon#page/n1525/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor58sponno2#page/n385/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/56/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n59/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55sponno2#page/n43/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56spon#page/n1763/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57sponno2#page/n965/search/flamingo
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/n289/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n435/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55sponno2#page/n465/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57sponno2#page/n1589/search/flamingo
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/n527/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n725/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1955-09/Sponsor-1955-09-1#page/n61/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56sponno2#page/n691/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57sponno3#page/n59/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/n781/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n1017/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1955-10/Sponsor-1955-10-1#page/n51/search/rating
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56sponno2#page/n947/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsormagazine-1957-10/Sponsor-1957-10-1#page/n55
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/n1013/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n1289/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55sponno2#page/n1255/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57sponno3#page/n973/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/51/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/n1525/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55sponno2#page/n1541/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor52sponno2#page/22/search/flamingo
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53sponno2#page/n1601/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54sponno2#page/50/search/Flamingo
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56spon#page/n211/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57spon#page/n95
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor53spon#page/n147/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor54spon#page/n151/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor55spon#page/n175/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor56spon#page/n419/
- ^ https://archive.org/stream/sponsor57spon#page/n657/
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "Tye2012" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "Ricca2014" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "Sergi2015" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "Daniels1998" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "Gordon2017" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "MankiewiczCrane2012p203" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "TCS11" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: A list-defined reference named "TCS18" is not used in the content (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).























![{\displaystyle ={\frac {kq_{a}q_{g}}{vb}}\left(\sin \left[{\frac {\pi -\theta }{2}}\right]-\sin \left[-{\frac {\pi -\theta }{2}}\right]\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e21c790ae221c75d2087c933dddcf2f4edec7be5)
























