User:CFCF/sandbox/drugs
Appearance
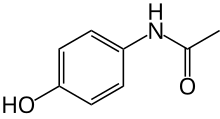 | |
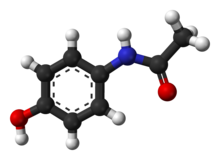 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Paracetamol /ˌpærəˈsiːtəmɒl/ or /ˌpærəˈsɛtəmɒl/ Acetaminophen /əˌsiːtəˈmɪnəf[invalid input: 'ɨ']n/ |
| Trade names | Tylenol, Panadol, others[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a681004 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, rectal, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 63–89%[2]: 73 |
| Protein binding | 10–25%[3] |
| Metabolism | Predominantly in the liver[5] |
| Metabolites | APAP gluc, APAP sulfate, NAPQI, APAP-GSH, APAP-cys[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 1–4 hours[5] |
| Excretion | Urine (85–90%)[5] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H9NO2 |
| Molar mass | 151.163 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.263 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F) [6][7] |
| Boiling point | 420 °C (788 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 12.78[8] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
- =
- Dependencies?
Template:Infobox drug/licence Template:Infobox drug/pregnancy category Template:Infobox drug/legal status Template:Infobox drug/ATC Template:Infobox drug/chemical formula Template:Chem molar mass
{{drugbox
| Watchedfields = changed
| verifiedrevid = 456349142
| IUPAC_name = ''N''-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanamide<br>''N''-(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide
| image = Paracetamol-skeletal.svg
| image2 = Paracetamol-from-xtal-3D-balls.png
| drug_name =
<!--Clinical data-->
| pronounce = Paracetamol {{IPAc-en|ˌ|p|ær|ə|ˈ|s|iː|t|ə|m|ɒ|l}} or {{IPAc-en|ˌ|p|ær|ə|ˈ|s|ɛ|t|ə|m|ɒ|l}}<br>
Acetaminophen {{IPAc-en|audio=En-acetaminophen.oga|ə|ˌ|s|iː|t|ə|ˈ|m|ɪ|n|ə|f|ɨ|n}}
| tradename = [[Tylenol (brand)|Tylenol]], [[Panadol (brand)|Panadol]], [[list of paracetamol brand names|others]]<ref name=drugs.com-internatl>{{cite web|title=International Listings for Paracetamol|url=http://www.drugs.com/international/paracetamol.html|accessdate=11 January 2016}}</ref>
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|acetaminophen}}
| MedlinePlus = a681004
| licence_US = Acetaminophen
| pregnancy_AU = A
| pregnancy_US = C
| pregnancy_category = Not tested but seems to be safe
| legal_AU = unscheduled
| legal_UK = GSL
| legal_US = OTC
| routes_of_administration = [[Mouth|Oral]], [[Rectal (medicine)|rectal]], [[Intravenous therapy|intravenous]]
<!--Pharmacokinetic data-->
| bioavailability = 63–89%<ref>{{Cite book | isbn = 9780977517459 | title = Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence | author = Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine | year = 2010 | publisher = National Health and Medical Research Council | location = Melbourne, Australia | url = http://www.anzca.edu.au/resources/college-publications/pdfs/Acute%20Pain%20Management/books-and-publications/acutepain.pdf | format = PDF | edition = 3rd | editor = Macintyre, PE; Schug, SA; Scott, DA; Visser, EJ; Walker, SM }}</ref>{{rp|73}}
| protein_bound = 10–25%<ref>{{cite web|title=Tylenol, Tylenol Infants' Drops (acetaminophen) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more|work=Medscape Reference|publisher=WebMD|accessdate=10 May 2014|url=http://reference.medscape.com/drug/tylenol-acetaminophen-343346#showall}}</ref>
| metabolism = Predominantly in the liver<ref name = TGA>{{cite web|title=Codapane Forte Paracetamol and codeine phosphate PRODUCT INFORMATION|work=TGA eBusiness Services|publisher=Alphapharm Pty Limited|date=29 April 2013|accessdate=10 May 2014|url=https://www.ebs.tga.gov.au/ebs/picmi/picmirepository.nsf/pdf?OpenAgent&id=CP-2010-PI-05623-3|format=PDF}}</ref>
| metabolites = APAP [[Glucuronide|gluc]], APAP [[sulfate]], [[NAPQI]], APAP-[[GSH]], APAP-[[cys]]<ref>{{cite web|title= Acetaminophen Pathway (therapeutic doses), Pharmacokinetics |accessdate=13 January 2016|url= https://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA165986279}}</ref>
| elimination_half-life = 1–4 hours<ref name = TGA/>
| excretion = Urine (85–90%)<ref name = TGA/>
<!--Identifiers-->
| IUPHAR_ligand = 5239
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}}
| CAS_number = 103-90-2
| ATC_prefix = N02
| ATC_suffix = BE01
| PubChem = 1983
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}}
| DrugBank = DB00316
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}}
| ChemSpiderID = 1906
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}}
| UNII = 362O9ITL9D
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}}
| KEGG = D00217
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}}
| ChEBI = 46195
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}}
| ChEMBL = 112
| PDB_ligand = TYL
<!--Chemical data-->
| C=8 | H=9 | N=1 | O=2
| molecular_weight = 151.163 g/mol
| smiles = CC(NC1=CC=C(O)C=C1)=O
| InChI = 1/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10)
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}}
| StdInChI = 1S/C8H9NO2/c1-6(10)9-7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,11H,1H3,(H,9,10)
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}}
| StdInChIKey = RZVAJINKPMORJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
| density = 1.263
| melting_point = 169
| boiling_point = 420
| melting_notes =<ref>{{Cite journal | doi = 10.1021/ci0500132 | title = General Melting Point Prediction Based on a Diverse Compound Data Set and Artificial Neural Networks | year = 2005 | last1 = Karthikeyan | first1 = M. | last2 = Glen | first2 = R. C. | last3 = Bender | first3 = A. | journal = Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling | volume = 45 | issue = 3 | pages = 581–590 | pmid = 15921448}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://lxsrv7.oru.edu/~alang/meltingpoints/meltingpointof.php?csid=1906 | title = melting point data for paracetamol |publisher=Lxsrv7.oru.edu | accessdate = 2011-03-19}}</ref>
| solubility = 12.78<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1021/je990124v | title = Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents | author = Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC | journal = [[Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data]] | volume = 44 | issue = 6 | pages = 1391–95 | year = 1999}}</ref>
}}
- Potential solution?
References
- ^ "International Listings for Paracetamol". Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- ^ Working Group of the Australian and New Zealand College of Anaesthetists and Faculty of Pain Medicine (2010). Macintyre, PE; Schug, SA; Scott, DA; Visser, EJ; Walker, SM (ed.). Acute Pain Management: Scientific Evidence (PDF) (3rd ed.). Melbourne, Australia: National Health and Medical Research Council. ISBN 9780977517459.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ "Tylenol, Tylenol Infants' Drops (acetaminophen) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- ^ "Acetaminophen Pathway (therapeutic doses), Pharmacokinetics". Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- ^ a b c "Codapane Forte Paracetamol and codeine phosphate PRODUCT INFORMATION" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Alphapharm Pty Limited. 29 April 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- ^ Karthikeyan, M.; Glen, R. C.; Bender, A. (2005). "General Melting Point Prediction Based on a Diverse Compound Data Set and Artificial Neural Networks". Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 45 (3): 581–590. doi:10.1021/ci0500132. PMID 15921448.
- ^ "melting point data for paracetamol". Lxsrv7.oru.edu. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- ^ Granberg RA, Rasmuson AC (1999). "Solubility of paracetamol in pure solvents". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 44 (6): 1391–95. doi:10.1021/je990124v.
