Upper Aulaqi Sultanate
| Upper Aulaqi Sultanate سلطنة العوالق العليا | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of the Federation of South Arabia | |||||||||
| 18th century–1967 | |||||||||
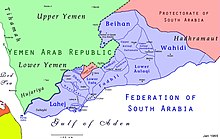 Map of the Federation of South Arabia | |||||||||
| Capital | Nisab (Nişāb) | ||||||||
| • Type | Sultanate | ||||||||
| Historical era | 20th century | ||||||||
• Established | 18th century | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1967 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Upper Aulaqi Sultanate (Arabic: سلطنة العوالق العليا Salṭanat al-‘Awālaq al-‘Ulyā) was a state in the British Aden Protectorate and the Federation of South Arabia. Its capital was Nisab.
History
[edit]The Lower Aulaqi sultans separated from the Upper Aulaqi in the 18th century.[citation needed]
In September 1879, Sultan Awadh bin Abdulla was dethroned in consequence of old age and was succeeded by his eldest son Abdulla.[1]
Sultan Abdulla bin Awadh died on 11 December 1887 and was succeeded by his son, Sultan Salih bin Abdulla.[1]
A treaty was concluded between the British and the Upper Aulaqi Sultan on 18 March 1904 and ratified on 23 April 1904.[1]
The Upper Aulaqi Sultanate joined the Federation of South Arabia in June 1964, the last one to join. The last sultan was Sultan Awad ibn Salih Al Awlaqi.[citation needed]
The last ruler was deposed in 1967 upon the founding of the People's Republic of South Yemen and the area is now part of the Republic of Yemen.[2]
Rulers
[edit]The ruler of the Upper Aulaqi Sultanate bore the title Sultan al-Saltana al-`Awlaqiyya al-`Ulya.[citation needed]
Sultans
[edit]- ....–.... Munassar
- ....–.... Farid ibn Munassar
- ....–1862 `Abd Allah ibn Farid
- 1862 – September 1879 `Awad ibn `Abd Allah
- 1879 – 11 December 1887 `Abd Allah ibn `Awad
- December 1887 – 1935 Salih ibn `Abd Allah
- 1935 – 29 November 1967 `Awad ibn Salih al-`Awlaqi
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Aitchison, G (1931). A Collection Of Treaties, Engagements And Sanads Relating To India And Neighbouring Countries. Vol. xi. Government of India. p. 14.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Paul Dresch. A History of Modern Yemen. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2000
