Tris(acetonitrile)cyclopentadienylruthenium hexafluorophosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.130 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C11H14N3RuPF6 | |
| Molar mass | 434.28 |
| Appearance | yellow/brown solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
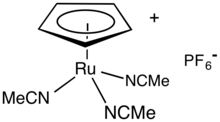
Tris(acetonitrile)cyclopentadienylruthenium hexafluorophosphate is an organoruthenium compound with the formula [(C5H5)Ru(NCCH3)3]PF6, abbreviated [CpRu(NCMe)3]PF6. It is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. The compound is a salt consisting of the hexafluorophosphate anion and the cation [CpRu(NCMe)3]+. In coordination chemistry, it is used as a source of RuCp+ for further derivitization.[1] In organic synthesis, it is a homogeneous catalyst. It enables C-C bond formation and promotes cycloadditions.[2] The cyclopentadienyl ligand (Cp) is bonded in an η5 manner to the Ru(II) center.
Preparation
[edit]The title complex is synthesized in two steps from the (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer. In the first step, the Cp− group is installed using cyclopentadienylthallium:[1]
- [(C6H6)RuCl2]2 + 2 TlCp + 2 NH4PF6 → 2 [Cp(C6H6)Ru]PF6 + 2 TlCl + 2 NH4Cl
The second step entails photochemical displacement of the benzene ligand, which is replaced by three equivalents of acetonitrile (MeCN):
- [Cp(C6H6)Ru]PF6 + 3 MeCN → [CpRu(NCMe)3]PF6 + C6H6
References
[edit]- ^ a b Gill, Thomas P; Mann, Kent R (1982). "Photochemical Properties of the Cyclopentadienyl(benzene)ruthenium(II) Cation. The Synthesis and Reactions of a Synthetically Useful Intermediate: the Cyclopentadienyltris (acetonitrile) ruthenium (II) Cation". Organometallics. 1: 485–488. doi:10.1021/om00063a014.
- ^ Trost, Barry M.; Toste, F. Dean; Pinkerton, Anthony B. (2001). "Non-Metathesis Ruthenium-Catalyzed C−C Bond Formation". Chem. Rev. 101 (7): 2067–2096. doi:10.1021/cr000666b. PMID 11710241.
