Triadimefon
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
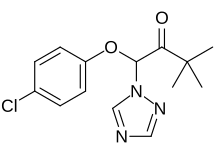
| IUPAC name
1-(4-Chlorophenoxy)-3,3-dimethyl-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-one
| |
| Other names
Triadimeform
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.050.986 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16ClN3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 293.75 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.22 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 82 °C (180 °F; 355 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| 64 mg/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
363 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] > 5000 mg/kg (dermal, rat)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Triadimefon is a fungicide used in agriculture to control various fungal diseases. As a seed treatment, it is used on barley, corn, cotton, oats, rye, sorghum, and wheat.[2] In fruit it is used on pineapple and banana.[2] Non-food uses include pine seedlings, Christmas trees, turf, ornamental plants, and landscaping.[2]
References
[edit]
