Transient lingual papillitis
Appearance
| Transient lingual papillitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Fungiform papillary glossitis,[1] Eruptive lingual papillitis,[2] Lie bumps),[2] |
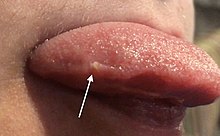 | |
Transient lingual papillitis are painful, hypertrophic, red and white lingual papillae on the tongue.[2]
Cause
[edit]Transient lingual papillitis can affect males and females as early as 8 years of age. In many cases, the cause is unknown. Some dental professionals believe the inflammation is due to chronic irritation from teeth, fillings, or dental appliances. Stress, poori mol nutrition, smoking, and alcohol use may also be initiating factors. [3]
References
[edit]- ^ Marks, R.; Scarff, C.E.; Yap, L.M.; Verlinden, V.; Jolley, D.; Campbell, J. (October 2005). "Fungiform papillary glossitis: atopic disease in the mouth?". British Journal of Dermatology. 153 (100, 000, 000, 000): 740–745. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06577.x. PMID 16181454.
- ^ a b c Roux, O.; Lacour, J.P.; Paediatricians of the Region Var-Cote D'Azur (February 2004). "Eruptive lingual papillitis with household transmission: a prospective clinical study". British Journal of Dermatology. 150 (2): 299–303. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05703.x. PMID 14996101.
- ^ "Transient Lingual Papillitis: Location, Symptoms And Treatment". www.colgate.com. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
