Timeline of the Ming dynasty
Appearance

A timeline of the Ming dynasty (1368–1644) from the rise of the Hongwu Emperor to the rise and establishment of the Qing dynasty.
Background
[edit]1320s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1328 | 21 October | Zhu Yuanzhang is born to a family of poor tenant farmers in Anhui[1] |
1330s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1332 | 1 January | Xu Da is born in Fengyang County. |
1340s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1344 | June | An epidemic, locusts, and drought kills Zhu Yuanzhang's family, leaving only himself, his sister-in-law and her young son as the sole survivors[2] |
| October | Zhu Yuanzhang enters a local Buddhist monastery as a novice to do menial work; eventually he's sent out to beg for food - it's speculated that he ends up joining the army[2] | |
| 1347 | Zhu Yuanzhang returns to the Buddhist monastery[3] |
1350s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1352 | 15 April | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang becomes a rebel under Guo Zixing's command in Haozhou[3] |
| 1353 | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang receives an independent command from Guo Zixing and captures Chuzhou[4] | |
| 1355 | 11 July | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang crosses the Changjiang[5] |
| Red Turban Rebellion: Guo Zixing dies and his eldest son succeeds him, but he also dies, making Zhu Yuanzhang leader of the rebels[6] | ||
| 1356 | 10 April | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang takes Nanjing[7] |
| 1357 | summer | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhang Shide is captured by Zhu Yuanzhang and starves to death[8] |
| 1358 | Red Turban Rebellion: Defending garrisons fire cannons en masse at the siege of Shaoxing and defeat Zhu Yuanzhang's forces[9] |
1360s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1360 | Red Turban Rebellion: Chen Youliang murders Xu Shouhui and proclaims the Great Han at Wuchang before attacking Zhu Yuanzhang at Nanjing only to be repulsed[10] | |
| 1363 | 30 August - 4 October | Battle of Lake Poyang: Chen Youliang's fleet is demolished by Zhu Yuanzhang's forces and dies[10] |
| Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang saves Han Liner and moves the Song court west of Nanjing where it remains militarily insignificant[11] | ||
| 1365 | autumn | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang attacks Zhang Shicheng[12] |
| Zhu Yuanzhang sets up a school with a teaching staff of "Erudites" (boshi)[13] | ||
| 1367 | October | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang's army under Zhu Liangzi takes Taizhou[14] |
| 1 October | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang takes Suzhou and Zhang Shicheng hangs himself;[15] 2,400 large and small cannons are deployed by the Ming army at the siege of Suzhou.[9] | |
| November | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Liangzi takes Wenzhou[14] | |
| 13 November | Red Turban Rebellion: Zhu Yuanzhang issues orders for Xu Da and Chang Yuchun to head north with 250,000 soldiers and Hu Mei, Tang He, and Liao Yongzhong to attack Fujian and Guangdong[16] | |
| December | Red Turban Rebellion: Fang Guozhen surrenders to Zhu Yuanzhang[17] | |
| 28 December | Red Turban Rebellion: Hu Mei's forces take Shaowu[16] | |
| Red Turban Rebellion: Xu Da and Chang Yuchun conquer Jinan[16] | ||
| Zhu Yuanzhang reestablishes the imperial examinations[18] | ||
| 1368 | 18 January | Red Turban Rebellion: Hu Mei captures Fuzhou[16] |
14th century
[edit]1360s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1368 | 23 January | Zhu Yuanzhang proclaims himself the Hongwu Emperor of the Ming dynasty (note that Ming and Qing use the era name rather than temple name)[18] |
| 17 February | Ming forces conquer Fujian and capture Chen Youding, who is executed[19] | |
| 1 March | Ming forces conquer Shandong[16] | |
| 16 April | Ming forces capture Kaifeng[16] | |
| 18 April | Ming forces reach Guangzhou and receive He Zhen's surrender[16] | |
| 25 April | Ming forces defeat Köke Temür and capture Luoyang[16] | |
| 26 May | Ming forces capture Wuzhou[16] | |
| July | Ming forces conquer Guangxi[16] | |
| 20 September | Ming forces capture Daidu (renamed Beiping) and the Yuan court flees to Inner Mongolia; so ends the Yuan dynasty[14] | |
| November | Ming forces capture Baoding[20] | |
| 26 December | Ming forces capture Zhaozhou[20] | |
| December | Ming forces capture Pingding[20] | |
| Crouching-tiger cannons are employed by the Ming army.[21] | ||
| The Guozijian is created[13] | ||
| 1369 | 9 January | Ming forces capture Taiyuan[20] |
| 3 March | Ming forces capture Datong[20] | |
| March | Song Lian and Wang Yi start compiling the History of Yuan[22] | |
| 18 April | Ming forces conquer Shanxi and Li Siqi flees to Lintao[23] | |
| 21 May | Li Siqi surrenders to Ming forces[23] | |
| 23 May | Ming forces capture Lanzhou[23] | |
| 8 June | Ming forces capture Pingliang[23] | |
| 20 July | Ming forces capture Shangdu[23] | |
| 22 September | Ming forces capture Qingyang[23] | |
| Construction of the Central Capital (Fengyang) begins[24] |
1370s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1370 | January | Köke Temür lays siege to Lanzhou but fails to take it[25] |
| Ming forces defeat Köke Temür at Gongchang but fail to capture him[26] | ||
| 5 June | The Hongwu Emperor authorizes the first Ming imperial examinations[27] | |
| 10 June | Ming forces capture Yingchang[28] | |
| June | The Hongwu Emperor bans White Lotus and Manichaean sects[29] | |
| Gunpowder is corned to strengthen the explosive power of land mines in the Ming dynasty.[30] | ||
| Cannon projectiles transition from stone to iron ammunition in the Ming dynasty.[31] | ||
| 1371 | 18 May | Ming forces capture Wenzhou[32] |
| July | Ming forces capture Hanzhou[33] | |
| 3 August | Ming Sheng surrenders Sichuan to the Ming dynasty[34] | |
| Registered students at the Guozijian reach 3,728[27] | ||
| 1372 | April | Ming forces defeat Köke Temür at the Tuul River[35] |
| Ming forces are routed at Karakorum[35] | ||
| Ming forces capture Yongchang and conquer Juyan[36] | ||
| Registered students at the Guozijian reach 10,000[27] | ||
| Cannons made specifically for naval usage appear in the Ming dynasty.[37] | ||
| 1373 | March | The Hongwu Emperor suspends imperial examinations[27] |
| 29 November | Ming forces defeat Köke Temür at Huairou[36] | |
| The Hongwu Emperor limits tribute missions from Goryeo to once every three years[38] | ||
| Ming officials draw up the first "house law" in Chinese history[39] | ||
| 1375 | Ming starts issuing a new note called the Da Ming Baochao[40] | |
| The Hongwu Emperor halts constructions at Fengyang due to expenses and waste; construction plans shift to Nanjing[24] | ||
| 1376 | March | Ming forces defeat Bayan Temür[41] |
| July | Ming forces defeat Bayan Temür again[41] | |
| 22 October | The Hongwu Emperor announces that he will accept straightforward criticism of his rule from officials[42] | |
| Ye Boju is starved to death in prison for criticising the emperor[42] | ||
| The Hongwu Emperor executes all officials connected to the "Case of the Pre-stamped Documents"[43] | ||
| 1377 | May | Ming forces invade Qinghai[41] |
| Palace construction in Nanjing is completed and the city is designated "Jingshi" (Capital)[44] | ||
| 1378 | Wu Mian rebellion: The Kam people rebel[45] | |
| 1379 | February | Ming forces defeat Tibetans in Gansu[46] |
| Champa sends tribute to Nanjing[47] |
1380s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1380 | Hu Weiyong plots to assassinate the Hongwu Emperor but gets arrested; the ensuing investigations lead to the execution of roughly 15,000 people[27] | |
| "Wasp nest" rocket launchers are manufactured for the Ming army.[48] | ||
| 1381 | December | Ming conquest of Yunnan: Ming forces take Qujing[49] |
| 1382 | April | Ming conquest of Yunnan: Ming forces conquer Yunnan[50] |
| 1384 | April | The Hongwu Emperor relocates government agencies from the palace to outside the city walls of Nanjing[51] |
| 1385 | Wu Mian rebellion: The Kam rebellion is defeated[52] | |
| The imperial examinations are reestablished[27] | ||
| Guo Huan is executed for embezzling 7 million piculs of grain[51] | ||
| 1386 | January | Ming–Mong Mao War: Si Lunfa of Mong Mao rebels[53] |
| 1387 | October | Ming campaign against the Uriankhai: Naghachu surrenders to Ming forces[54] |
| 1388 | May | Battle of Buir Lake: Ming forces defeat Uskhal Khan Tögüs Temür[55] |
| Ming–Mong Mao War:Mong Mao is defeated by the Ming artillery corps utilizing volley fire[56] | ||
| 1389 | January | Ming forces defeat Yi rebels in Yuezhou[57] |
| December | Ming–Mong Mao War: Si Lunfa surrenders to the Ming dynasty[57] |
1390s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1390 | April | Nayir Bukha and Yaozhu surrender to Ming forces[58] |
| 1391 | May | Ajashiri rebels and is suppressed[59] |
| Ming forces briefly occupy Hami and retreat[60] | ||
| 1392 | 5 August | Yi Songgye ousts Wang Yo and becomes Taejo of Joseon; so ends Goguryeo[38] |
| 1393 | Ming forces sack Hami[61] | |
| 1394 | Tributary relations between Ming and Joseon are normalized[62] | |
| 1396 | April | Ming forces defeat Bolin Temür[63] |
| 1397 | October | Lin Kuan rebellion: A Kam rebellion is defeated[64] |
| December | Ming–Mong Mao Intervention: Si Lunfa is deposed and requests Ming aid in restoring him to power[65] | |
| 1398 | January | Ming–Mong Mao Intervention: Si Lunfa is restored to power[66] |
| 24 May | The Hongwu Emperor becomes ill[67] | |
| 24 June | The Hongwu Emperor dies[68] | |
| 30 June | Zhu Yunwen becomes the Jianwen Emperor[67] | |
| The Jianwen Emperor eliminates the princedoms of Zhu Gui, Zhu Bo, Zhu Fu, and Zhu Pian[69] | ||
| Last recorded instance of human sacrifice in China[70] | ||
| 1399 | June | The Jianwen Emperor returns Zhu Di's sons[69] |
| July | A military official seizes two of Zhu Di's junior officials on the charge of sedition[71] | |
| 5 August | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di launches an offensive on neighboring counties[71] | |
| 25 September | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di defeats a 130,000 strong army sent by the Jianwen Emperor[72] | |
| 12 November | Jingnan Campaign: The Jianwen Emperor's forces lay siege to Beiping but are forced to retreat three weeks later[73] |
15th century
[edit]1400s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1400 | January | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di invades Shanxi[73] |
| 18 May | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di's forces deal heavy casualties upon the imperial army[73] | |
| 8 June | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di lays siege to Dezhou[73] | |
| 4 September | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di lifts the siege of Dezhou and returns to Beiping[73] | |
| 1401 | 9 January | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di's forces fall to explosives and suffer heavy casualties in Shandong, forcing their retreat[74] |
| 5 April | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di's forces deal a heavy defeat to the imperial army near Dezhou[74] | |
| August | Jingnan Campaign: The imperial army forces Zhu Di to retreat north to Beiping[74] | |
| August | The Jianwen Emperor restricts the size of Buddhist and Taoist landholdings[75] | |
| October | Jingnan Campaign: Imperial forces are expelled from the Beiping region[74] | |
| 1402 | January | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di conquers northwestern Shandong[76] |
| 3 March | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di takes Xuzhou[76] | |
| April | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di defeats imperial troops in Suzhou[76] | |
| 23 May | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di is repulsed by imperial troops in Anhui[76] | |
| 28 May | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di defeats imperial forces at Lingbi[76] | |
| 7 June | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di's forces cross the Huai River[76] | |
| 17 June | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di takes Yangzhou[76] | |
| 1 July | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Di is stopped at the Changjiang across from Nanjing[76] | |
| 3 July | Jingnan Campaign: Assistant chief commissioner Chen Xuan defects to Zhu Di and rebel forces cross the Changjiang[76] | |
| 13 July | Jingnan Campaign: Zhu Hui opens the Jinchuan Gate of Nanjing to lets Zhu Di in without a fight; the Jianwen Emperor disappears and his family is incarcerated[77] | |
| 17 July | Zhu Di ascends the throne as the Yongle Emperor[77] | |
| September | The Yongle Emperor commissions the Yongle Encyclopedia[78] | |
| 1403 | February | The Yongle Emperor designates Beiping the "Northern Capital", Beijing[79] |
| April | The Yongle Emperor settles loyal Uriankhai near Daning[80] | |
| 4 September | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued for the construction of 200 "seagoing transport ships"[81] | |
| December | The Yongle Emperor creates the Jianzhou Guard[82] | |
| Japanese missions to Ming China: Ashikaga Yoshimitsu sends an embassy to the Ming dynasty declaring himself "your subject, the King of Japan", and receives trading privileges[83] | ||
| 1404 | March | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued for the construction of 50 "seagoing ships"[84] |
| July | Engke Temiir of Kara Del receives the title of prince from the Ming court[85] | |
| October | Trần Thiêm Bình arrives in Nanjing and requests the Ming dynasty to restore him to the throne of the Trần dynasty[86] | |
| December | Tamerlane launches an invasion of the Ming dynasty but dies on the way[85] | |
| Empirewide imperial examinations are resumed[87] | ||
| 10,000 households from Shanxi are relocated to Beijing[79] | ||
| 1405 | 11 July | Treasure voyages: Zheng He and 27,800 men depart from Nanjing on 255 ships, of which 62 are treasure ships, "bearing imperial letters to the countries of the Western Ocean and with gifts to their kings of gold brocade, patterned silks, and colored silk gauze, according to their status."[88] |
| Construction of new palace buildings in Beijing begins[79] | ||
| 1406 | 4 April | Trần Thiêm Bình and his Ming escort are ambushed and killed while crossing into Lạng Sơn[86] |
| 19 November | Ming–Hồ War: Ming forces invade Đại Ngu[86] | |
| 13 December | Ming–Hồ War: Ming forces capture Đa Bang and Thăng Long[86] | |
| Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet visits Malacca and Java before heading up the Straits of Malacca to Aru, Samudera Pasai Sultanate, and Lambri, where the people are described as "very honest and genuine," and from there 3 days to the Andaman Islands, and then 8 more days to the west coast of Ceylon where the king reacts with hostility. The fleet departs for Calicut, which is described as "the Great country of the Western Ocean"[89] | ||
| 1407 | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet defeats Chen Zuyi's pirate fleet at Palembang and installs Shi Jinqing as "grand chieftain ruling over the native people of that place"[90] | |
| 13 March | Ming–Đại Ngu (Hồ dynasty) War: Hồ Quý Ly's counteroffensive against Ming forces fails[86] | |
| April | Deshin Shekpa, 5th Karmapa Lama arrives in Nanjing to perform religious ceremonies[91] | |
| 16 June | Ming–Đại Ngu (Hồ dynasty) War: Hồ Quý Ly and his son are captured and sent to Nanjing[86] | |
| 5 July | Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam: The Yongle Emperor announces the formal incorporation of Jiaozhi into the Ming dynasty[86] | |
| 2 October | Treasure voyages: Chinese Treasure fleet arrives back at Nanjing[92] | |
| 5 October | Treasure voyages: Wang Hao is ordered to refit 249 "sea transport ships" in "preparation for embassies to the countries of the Western Ocean"[93] | |
| 23 October | Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor issues orders for the second voyage and to confer formal investiture on the king of Calicut[94] | |
| Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor summons Javanese envoys to demand restitution for killing 710 Chinese and settles for 10,000 ounces of gold[95] | ||
| 30 October | Treasure voyages: A eunuch Grand Director departs with an imperial letter for the king of Champa[94] | |
| Treasure voyages: Zheng He departs with a fleet of 249 ships and takes a route similar to the first voyage with the addition of stops at Jiayile, Abobadan, Ganbali, Quilon, and Cochin[96] | ||
| December | The Yongle Encyclopedia is completed[97] | |
| Ironwood wadding is added to Ming cannons, increasing their effectiveness.[98] | ||
| 1408 | 14 February | Treasure voyages: Orders for the construction of 48 treasure ships are issued from the Ministry of Works in Nanjing[99] |
| 5 July | Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam: Ming troops seize 13,600,000 tons of rice; 235,900 cattles and livestock and vast amounts of materials in Vietnam[100] | |
| September | Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam: Trần Ngỗi rebels in Jiaozhi[86] | |
| 1409 | January | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued for the third voyage[101] |
| 15 February | Treasure voyages: The Galle Trilingual Inscription is produced[102] | |
| June | Oirats receives princely titles from the Ming court[85] | |
| summer | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet returns to China[96] | |
| 23 September | Battle of Kherlen: Ming forces are defeated by Öljei Temür Khan[103] | |
| October | Treasure voyages: Zheng He departs with 27,000 men, taking the usual route[102] | |
| December | Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam: Ming forces capture Trần Ngỗi but Trần Quý Khoáng becomes leader of the rebels[104] |
1410s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1410 | 15 June | First Mongol Campaign: The Yongle Emperor defeats Öljei Temür Khan on the banks of the Onon River[103] |
| July | First Mongol Campaign: Ming forces defeat Arughtai east of the Greater Khingan and withdraw to Nanjing[103] | |
| Ming–Kotte War: Treasure fleet lands at Galle in Ceylon and captures King Vijayabahu VI of the Kingdom of Gampola[102] | ||
| 1411 | July | Dredging and reconstruction of the Grand Canal begins[105] |
| 6 July | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet returns to Nanjing[106] | |
| The Yongle Emperor sends Yishiha to explore northern Manchuria[82] | ||
| Ashikaga Yoshimochi refuses the Yongle Emperor's request to suppress Japanese pirates[107] | ||
| 1412 | 18 December | Treasure voyages:The Yongle Emperor issues orders for the fourth voyage[108] |
| Shells are used as ammunition in the Ming dynasty.[109] | ||
| 1413 | autumn | Treasure voyages: Zheng He departs from Nanjingand takes the usual route with the addition of four new destinations: the Maldives, Bitra, Chetlat Island, and Hormuz, which is given the following description: "Foreign ships from every place, together with foreign merchants traveling by land, all come to this territory in order to gather together and buy and sell, and therefore the people of this country are all rich"[110] |
| Lopön Chenpo Gushri Lodrö Gyaltsen visits Nanjing[111] | ||
| Yongning Temple Stele: Ming dynasty sends Yishiha to the Nurgan Regional Military Commission to create postal stations and spread Buddhism[112] | ||
| 1414 | 30 March | Fourth Chinese domination of Vietnam: Trần Quý Khoáng is captured[104] |
| April | Second Mongol Campaign: Ming forces engage Oirats at the Tuul River, suffering heavy casualties, but ultimately prevail through the use of heavy cannon bombardments[113] | |
| Chöje Shakya Yeshe visits Nanjing[111] | ||
| 1415 | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet captures Sekandar, a rebel against Zain al-'Abidin, king of the Samudera Pasai Sultanate[114] | |
| June | The Grand Canal is reconstructed[115] | |
| 12 August | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet arrives back in Nanjing[116] | |
| 13 August | Treasure voyages: Zheng He's colleague is sent on a mission bearing gifts to Bengal[116] | |
| 1416 | 19 November | Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor bestows gifts upon ambassadors from 18 countries[117] |
| 19 December | Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor issues orders for the fifth voyage[118] | |
| 1417 | Lam Sơn uprising: Lê Lợi leads an insurrection against the Ming dynasty[104] | |
| autumn | Treasure voyages: Zheng He departs China taking the previous route to Hormuz, and then Aden, Mogadishu, Barawa, Zhubu, and Malindi[119] | |
| 1419 | 8 August | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet returns to China |
| 20 September | Treasure voyages: Ambassadors present exotic animals to the Ming court including a giraffe imported from Somalia by Bengalis[120] | |
| 2 October | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued for the construction of 41 Treasure ships[99] | |
| During the Lantern Festival, the Ming imperial palace puts on a display of pyrotechnics involving rockets running along wires which light up lanterns, illuminating the palace.[121] |
1420s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1420 | Forbidden City: Construction of the Altar of Heaven is completed[122] | |
| 28 October | Beijing officially becomes the capital of the Ming dynasty[122] | |
| 1421 | 3 March | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued for the sixth voyage and envoys from 16 countries including Hormuz are given gifts of paper and coin money, and ceremonial robes and linings[123] |
| 14 May | Treasure voyages: The Yongle Emperor orders the suspension of the Treasure voyages[124] | |
| 10 November | Treasure voyages: Orders are issued to Zheng He to provide Hong Bao and envoys from 16 countries passage back to their countries; the Treasure fleet takes its usual route to Ceylon where it splits up and heads for the Maldives, Hormuz, and the Arabian states of Djofar, Lasa, and Aden, and the two African states of Mogadishu and Barawa; Zheng He visits Ganbali[125] | |
| 1422 | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet regroups at Samudera Pasai Sultanate and visit Siam before heading back to China[125] | |
| April | Third Mongol Campaign: Ming forces are dispatched against Arughtai but fail to engage him in combat and return to Beijing[113] | |
| 3 September | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet returns to China bringing envoys from Siam, Samudera Pasai Sultanate, and Aden[126] | |
| 1423 | August | Fourth Mongol Campaign: The Yongle Emperor launches an offensive against Arughtai only to find out he had already been defeated by the Oirats[127] |
| 1424 | 27 February | Treasure voyages: Zheng He is sent on a diplomatic mission to Palembang to confer "a gauze cap, a ceremonial robe with floral gold woven into gold patterns in the silk, and a silver seal" on Shi Jinqing's son Shi Jisun[128] |
| April | Fifth Mongol Campaign: The Yongle Emperor leads an expedition against the remnants of Arughtai's horde but fails to find them[127] | |
| 12 August | The Yongle Emperor dies[129] | |
| 7 September | Treasure voyages: Zhu Gaozhi becomes the Hongxi Emperor and terminates the Treasure voyages[129] | |
| Metropolitan graduates fill posts down to the county magistrate[87] | ||
| 1425 | 29 May | The Hongxi Emperor dies[130] |
| 27 June | Zhu Zhanji becomes the Xuande Emperor[131] | |
| 2 September | Zhu Gaoxu rebels[132] | |
| 22 September | Zhu Gaoxu is defeated[133] | |
| 1426 | Ming dynasty sends Yishiha to the Wild Jurchens to construct shipyards and warehouses[112] | |
| 5 October | Lam Sơn uprising: Lê Lợi's forces inflict heavy casualties on Ming attacks in Battle of Tốt Động – Chúc Động[134] | |
| winter | Lam Sơn uprising: Lam Sơn forces drive out the Ming army from most of the Red River Delta and Northern Vietnam[135] | |
| 1427 | 10 October | Lam Sơn uprising: Ming reinforcements are encircled and defeated in Lạng Sơn[136][134] |
| 14 December | Lam Sơn uprising: Ming forces are withdrawn from Jiaozhi[104] | |
| 1428 | 25 March | Treasure voyages: The Xuande Emperor orders Zheng He to supervise the reconstruction of the Great Baoen Temple[137] |
| 29 April | Lê Lợi reestablished the kingdom of Đại Việt under Later Lê dynasty | |
| October | Uriankhai raid Ming borders and the Xuande Emperor personally leads troops to repel them[138] | |
| 1429 | The Xuande Emperor conducts a major military review on the outskirts of Beijing[139] | |
| Mounted infantry carrying hand cannons are employed by the Ming army.[140] |
1430s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1430 | May | The Xuande Emperor orders a tax reduction on all imperial lands[141] |
| 29 June | Treasure voyages: The Xuande Emperor issues orders for the seventh voyage[142] | |
| 1431 | 19 January | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet departs from Nanjing[143] |
| 14 March | Treasure voyages: Liujiagang Inscription is erected[144] | |
| 12 June | Vietnamese emperor Lê Thái Tổ of the Lê dynasty offers a nominate tributary relation with Ming China and was titled King of Annam by the Ming emperor.[145] | |
| December | Treasure voyages: The Changle Inscription is erected and the fleet departs from Changle[144] | |
| 1432 | 12 September | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet arrives at Samudera Pasai Sultanate and Hong Bao and Ma Huan detach from the fleet to visit Bengal[146][147] |
| Ming dynasty sends Yishiha to present seals to Ming-allied Jurchens and to repair the Yongning Temple[112] | ||
| 1433 | Treasure voyages: Zheng He dies[148] | |
| Treasure voyages: Hong Bao and Ma Huan arrive in Calicut and send seven men to Mecca while Hong Bao visits Djofar, Lasa, Aden, Mogadishu, and Barawa before heading back to China[149] | ||
| 9 March | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet departs from Hormuz and heads back to China[150] | |
| June | Japanese missions to Ming China: Relations between Ming and Japan are renewed[151] | |
| 7 July | Treasure voyages: Treasure fleet arrives back in China[152] | |
| 14 September | Treasure voyages: Envoys from Samudera Pasai Sultanate, Calicut, Cochin, Ceylon, Djofar, Aden, Coimbatore, Hormuz, Kayal, and Mecca present tribute[153] | |
| Treasure voyages: Ma Huan publishes his Yingya Shenglan[154] | ||
| 1434 | Treasure voyages: Gong Zhen publishes his Xiyang Fanguo Zhi[154] | |
| 1435 | 31 January | The Xuande Emperor dies and Empress Zhang (Hongxi) becomes regent for the Zhengtong Emperor[155] |
| The Northern China Plain and Shandong suffer from drought and plagues[156] | ||
| 1436 | Treasure voyages: Ming dynasty bans building seagoing ships[157] | |
| Treasure voyages: Fei Xin publishes his Xingcha Shenglan[157] | ||
| Flooding strikes northern Jiangsu, the Northern China Plain and Shandong[156] | ||
| 1437 | Shanxi and Shaanxi experience drought[156] | |
| Flooding strikes northern Jiangsu[156] | ||
| 1438 | 8 December | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Ming carries out a punitive expedition against Si Renfa of Mong Mao for attacking neighboring tusi, but fails to defeat him[158] |
| 1439 | Flooding strikes the northern China Plain and Shandong[156] |
1440s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1440 | Flooding strikes Suzhou, Jiangnan, the northern China Plain and Shandong[156] | |
| Famine strikes Zhejiang[156] | ||
| 1441 | 27 February | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Ming forces attack Mong Mao[159] |
| Flooding strikes the northern China Plain and Shandong[156] | ||
| Famine strikes Zhejiang[156] | ||
| 1442 | January | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Mong Mao is defeated but Si Renfa escapes to Ava[160] |
| 20 November | Empress Zhang (Hongxi) dies[161] | |
| 1443 | March | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Ming forces defeat Si Jifa but fail to capture him[162] |
| 1444 | Famine strikes Shanxi and Shaanxi[156] | |
| Flooding strikes northern Jiangsu[156] | ||
| 1445 | August | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Ava hands over Si Renfa to Ming in return for their support in attacking Hsenwi[163] |
| Drought and a plague epidemic strike Zhejiang[156] | ||
| 1446 | January | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Si Renfa is executed.[163] |
| Floods strike Jiangnan[156] | ||
| 1447 | Ye Zongliu rebels with a group of silver miners in Zhejiang[164] | |
| Famine strikes northern Jiangsu[156] | ||
| 1448 | March | Deng Maoqi rebels with a group of tenant farmers northwest of the Fujian and Jiangxi border[164] |
| December | Ming forces kill Ye Zongliu, but his rebels remain intact and retreat further south to siege Chuzhou[165] | |
| 1448 Yellow River flood: Yellow River dikes burst[164] | ||
| Drought and locust plague strike northwest China[156] | ||
| Drought strikes Jiangnan[156] | ||
| 1449 | March | Luchuan–Pingmian campaigns: Ming forces invade Mong Yang for harboring Si Jifa, but he manages to escape again[166] |
| May | Deng Maoqi's rebels are defeated[165] | |
| July | Tumu Crisis: Esen Taishi of the Oirats and de facto ruler of the Northern Yuan launches an invasion of the Ming dynasty[167] | |
| 4 August | Tumu Crisis: The Zhengtong Emperor departs from Beijing to personally confront Esen Taishi[168] | |
| 30 August | Tumu Crisis: The Ming rearguard is defeated[169] | |
| August | Ye Zongliu's rebels are defeated[165] | |
| 1 September | Tumu Crisis: The Ming army is annihilated and the Zhengtong Emperor is captured by Esen Taishi[170] | |
| 23 September | Zhu Qiyu becomes the Jingtai Emperor[171] | |
| 27 October | Esen Taishi lays siege to Beijing but fails to take it and withdraws after 5 days[172] | |
| Yellow River dikes burst again causing the river to change course slightly[164] |
1450s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1450 | 19 September | The Zhengtong Emperor is released and arrives back in Beijing, where he is kept under house arrest by the Jingtai Emperor[173] |
| Yao and Miao people rebel in Guizhou and Huguang[174] | ||
| Famine strikes Shandong[174] | ||
| 1452 | 1452 Yellow River floods: Yellow River dikes burst[175] | |
| Yao and Miao rebels are suppressed[174] | ||
| Northern China experiences flooding[174] | ||
| 1454 | Unusually heavy snowfall causes starvation in Suzhou and Hanzhou[176] | |
| 1455 | Xu Youzhen finishes repairs on the Yellow Riverdikes[175] | |
| Widespread drought affects Central China[176] | ||
| 1456 | Miao people in Huguang rebel and are suppressed[174] | |
| 1457 | 11 February | The former emperor is reinstated by the military and becomes the Tianshun Emperor[177] |
1460s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1461 | 7 August | Rebellion of Cao Qin: Cao Qin rebels and tries to storm Beijing but gets arrested and is forced to commit suicide[178] |
| 1464 | 23 February | The Tianshun Emperor dies and Zhu Qianshen becomes the Chenghua Emperor[179] |
| Hou Dagou of the Yao people rebels in Guangxi[180] | ||
| Treasure voyages: Documents of the treasure voyages are removed from the archives of the Ministry of War and destroyed by Liu Daxia on the basis that they were "deceitful exaggerations of bizarre things far removed from the testimony of people's ears and eyes," and that "the expeditions of Sanbao to the Western Ocean wasted tens of myriads of money and grain, and moreover the people who met their deaths [on these expeditions] may be counted in the myriads. Although he returned with wonderful precious things, what benefit was it to the state? This was merely an action of bad government of which ministers should severely disapprove. Even if the old archives were still preserved they should be destroyed in order to suppress [a repetition of these things] at the root."[181] | ||
| 1466 | January | Ming forces defeat and capture Hou Dagou but the rebellion continues anyway[180] |
| The Ming execute Dongshan of the Left Jianzhou Guard[182] | ||
| Miao people rebel in Hunan as well as the Sichuan-Guizhou border and are suppressed[183] | ||
| Liu Tong rebels near Xiangyang and is defeated[184] | ||
| 1467 | A Ming-Joseon expedition defeats the Jianzhou Jurchens and kill Li Manzhu[182] | |
| 1468 | May | Mongols rebel at Guyuan[185] |
| 12 May | 1,000 Vietnamese troops occupy the border town Pingxiang, Guangxi[186] | |
| 1469 | The Mongol rebellion at Guyuan is suppressed[185] |
1470s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1470 | The governor of Liaodong, Chen Yue, attacks the Jurchens and demands bribes from Jurchen embassies[182] | |
| Remnants of Liu Tong's rebels rebel again[184] | ||
| 1471 | Liu Tong's rebels are defeated[184] | |
| 1473 | Ming forces launch an attack on Hami in conjunction with Mongol allies but retreat when the Mongols abandon them[187] | |
| 1474 | Yu Zijun directs the reconstruction and extension of the Great Wall of China to seal off Ordos from the south[188] | |
| 1475 | Miao people rebel in Hunan and are suppressed[183] | |
| 1476 | June | Vagrant population around Xiangyang rebel until the government allows them to claim lands with reduced taxes[189] |
| 1479 | Miao people rebel in Sichuan[190] | |
| 28 April | Vietnamese emperor Lê Hạo of the Lê dynasty sends gold, silver utensils, local silk products to the Chinese court as gifts[191] |
1480s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1485 | Number of eunuchs passes 10,000[192] | |
| 1487 | 1 September | The Chenghua Emperor falls ill[193] |
| 9 September | The Chenghua Emperor dies[193] | |
| 17 September | Zhu Youtang becomes the Hongzhi Emperor[193] |
1490s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1492 | Europe reaches parity with China in health, fertility rate, life expectancy, and human capital[194] | |
| 1494 | 1494 Yellow River flood: Yellow River floods but Liu Daxia successfully directs the river to flow south of Shandong, stabilizing the course of the Yellow River until the 19th century[195] | |
| National military reforms switch to recruiting volunteers for local units[196] | ||
| 1495 | Ming forces briefly occupy Hami before reinforcements from Turpan force them to retreat[197] | |
| 1496 | Japanese missions to Ming China: Japanese envoys kill several people on their return trip from Beijing[198] | |
| 1499 | A trade embargo on Turpan forces them to return Hami to Uyghur control[197] | |
| Yi people rebel in Guizhou[199] |
16th century
[edit]1500s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1500 | Li people rebel on Hainan[200] | |
| 1502 | Yi rebels in Guizhou are suppressed[199] | |
| 1503 | Li rebels are suppressed[200] | |
| 1504 | Datong is raided by Mongols[201] | |
| 1505 | 8 June | The Hongzhi Emperor dies[202] |
| 19 June | Zhu Houzhao becomes the Zhengde Emperor[202] | |
| The Zhengde Emperor starts using eunuchs as military and fiscal intendants[203] | ||
| 1506 | May | The Ministry of Revenue is ordered to investigate the lack of revenue[203] |
| July | The Minister of Revenue, Han Wen, complains about the emperor's expenditures using the ministerial treasuries[204] | |
| 28 October | The Minister of Revenue petitions the emperor to execute all the eunuchs in his personal employ, but the emperor refuses, and as a result all the grand secretaries resign[205] | |
| The Zhengde Emperor takes to wandering the streets of Beijing in disguise[203] | ||
| 1507 | September | 350,000 ounces of silver are spent on lanterns for the Lantern Festival[205] |
| 1509 | August | Two garrisons in Liaodong revolt and are quelled after 2,500 ounces of silver are distributed among them[206] |
1510s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1510 | 12 May | Prince of Anhua rebellion: Zhu Zhifan rebels in Shanxi[207] |
| 30 May | Prince of Anhua rebellion: Zhu Zhifan is captured[207] | |
| Dayan Khan conquers the Ordos Loop[208] | ||
| 1511 | February | Bandits around Beijing revolt[209] |
| October | Bandits burn imperial grain carriages around Beijing[209] | |
| Capture of Malacca (1511): The Malacca Sultanate sends a plea for help against the Portuguese[210] | ||
| 1512 | January | Bandits attack Bazhou[209] |
| 7 September | The bandit armies are defeated[209] | |
| 1514 | 10 February | Gunpowder tents in the palace courtyard catch fire and destroy the residential palaces[211] |
| September | The Zhengde Emperor is badly mauled by a tiger[212] | |
| 1515 | summer | 30,000 troops from the capital garrisons and Imperial Bodyguard are dispatched to rebuild the palaces[213] |
| 1517 | 16 October | Dayan Khan raids the Ming dynasty[214] |
| 20 October | The Zhengde Emperor repels Dayan Khan's raiding party[215] | |
| Tomé Pires arrives at Guangzhou[210] | ||
| 1518 | January | The Zhengde Emperor imprisons the court at Beijingfor not giving him enough money[214] |
| 1519 | 9 July | Prince of Ning rebellion: Zhu Chenhao rebels in Jiangxi[216] |
| 13 July | Prince of Ning rebellion: Rebel forces capture Jiujiang[217] | |
| 23 July | Prince of Ning rebellion: Rebel forces lay siege to Anqing[217] | |
| 9 August | Prince of Ning rebellion: Rebel forces lift the siege on Anqing[218] | |
| 13 August | Prince of Ning rebellion: Imperial forces capture Nanchang[218] | |
| 15 August | Prince of Ning rebellion: Zhu Chenhao's army is defeated[218] | |
| 20 August | Prince of Ning rebellion: Zhu Chenhao flees from his fleet and is captured[218] |
1520s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1520 | January | The Zhengde Emperor forbids the slaughtering of pigs[219] |
| May | The Portuguese bribe a eunuch official in Guangzhou to let them through and Tomé Pires' party arrive at Nanjing[220] | |
| 1521 | 20 April | The Zhengde Emperor dies[220] |
| 21 April | Tomé Pires' party is expelled from Beijing[220] | |
| 27 April | Zhu Houcong becomes the Jiajing Emperor[221] | |
| May | Battle of Tunmen: Ming forces expel a Portuguese fleet from Tunmen when they refuse to leave[222] | |
| Palace reconstruction is completed[211] | ||
| 1522 | Portuguese are forbidden from trading in Guangzhou[198] | |
| Battle of Shancaowan: A Portuguese fleet runs a Ming blockade near Lantau Island and manages to leave with heavy casualties[223] | ||
| 1523 | May | Ningbo incident: The Hosokawa trade mission attacks the Ouchi trade mission and loots Ningbo, seizes ships, and kills a Ming commander before setting sail; the Chinese tributary system loses maritime trade value[224] |
| The Ming dynasty produces breech-loading swivel guns based on Portuguese designs.[225] | ||
| 1524 | August | The garrison of Datong rebels[226] |
| Ming–Turpan conflict: Turpan attacks Ganzhou and is repelled[227] | ||
| 1525 | April | The Datong rebels are defeated[228] |
| Jiajing wokou raids: Shuangyu becomes a trading enclave[198] | ||
| Some merchants from Fujian are able to speak Formosan languages[229] | ||
| 1526 | Famine strikes Beijing[230] | |
| 1527 | Floods sweep through Huguang[230] | |
| 1528 | Ming–Turpan conflict: Turpan's trading privileges are restored[231] | |
| 1529 | Jiajing wokou raids: Several commanders at Wenzhou are exiled for consorting with pirates[232] | |
| An inauspicious comet is sighted[230] |
1530s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1531 | Datong comes under raid by Mongols[233] | |
| An inauspicious comet is sighted[230] | ||
| 1532 | Jiajing wokou raids: The governor of Guangzhou is recalled for failing to eradicate pirates[232] | |
| A really inauspicious comet is sighted[230] | ||
| 1533 | 24 October | The Datong garrison rebels and is suppressed[228] |
| 1534 | Jiajing wokou raids: A pirate with over 50 large ships under his command is captured[232] | |
| The Jiajing Emperor stops attending routine court audiences[234] | ||
| 1535 | The garrisons at Liaodong and Guangning revolt and are suppressed[235] | |
| 1536 | Mongols raid Shanxi but are repelled[236] | |
| 1537 | Mongols raid Datong[236] | |
| 1539 | Japanese missions to Ming China: Japanese envoys are apprehended and forbidden from trading upon reaching China[237] | |
| The garrison at Liaodong rebels and is suppressed[238] |
1540s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1540 | September | The Jiajing Emperor announces his intention to seclude himself for several years to pursue immortality; a court official says this is nonsense and gets tortured to death[239] |
| 1541 | 30 April | A fire destroys the Imperial Ancestral Temple compound.[240] |
| October | Altan Khan raids Shaanxi.[241] | |
| Gunpowder is used for hydraulic engineering in the Ming dynasty.[242] | ||
| 1542 | July | Altan Khan raids Shaanxi again.[241] |
| 4 August | Ming forces are defeated by Altan Khan at Guangwu.[241] | |
| 8 August | Altan Khan pillages the suburbs of Taiyuan.[241] | |
| Renyin palace rebellion: Consort Fang prevents an assassination on the Jiajing Emperor.[243] | ||
| The Jiajing Emperor withdraws from his formal duties completely and spends the remainder of his life in the Palace of Everlasting Longevity obsessed with physical immortality through drugs, rituals, and esoteric physical regimens.[234] | ||
| 1543 | December | Construction on a new Imperial Ancestral Temple begins.[240] |
| Famine strikes Zhejiang.[244] | ||
| 1544 | Japanese missions to Ming China: Ming officials refuse to meet with Japanese envoys.[237] | |
| Famine strikes Zhejiang again.[244] | ||
| 1545 | January | An outbreak of pestilence occurs in Beijing.[241] |
| April | Dust storms destroy winter wheat and barley crops.[241] | |
| July | The new Imperial Ancestral Temple is completed.[240] | |
| Datong rebels and is suppressed.[228] | ||
| Japanese missions to Ming China: Wang Zhi returns to Japan with the Japanese mission and leads a trade mission to Shuangyu.[237] | ||
| 1547 | Jiajing wokou raids: A censor reports that piracy on the southeast coast is out of control.[245] | |
| 1548 | February | Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates raid Ningbo and Taizhou.[245] |
| April | Jiajing wokou raids: Ming forces attack Shuangyu but many of the ships in the harbor escape.[245] | |
| June | Mongols defeat Ming forces at Xuanfu.[246] | |
| October | Mongols raid Huailai.[246] | |
| The Ming army starts fielding matchlocks.[247] | ||
| 1549 | March | Altan Khan defeats Ming forces at Xuanfu but suffers heavy casualties.[246] |
| Jiajing wokou raids: Ming forces attack a large merchant fleet anchored off the coast of southern Fujian.[248] |
1550s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1550 | 1 October | Altan Khan pillages the suburbs of Beijing[246] |
| 6 October | Ming forces are defeated by Mongols[249] | |
| Towns and villages in Zhejiang erect palisades in response to brigands[244] | ||
| 1551 | Fishing boats are forbidden from going out to sea[248] | |
| 1552 | April | Ming forces are defeated by Mongols north of Datong[250] |
| Jiajing wokou raids: Raiding parties attack the coast of Zhejiang[244] | ||
| The Jiajing Emperor selects 800 girls between the ages of 8 and 14 for palace service[251] | ||
| 1553 | Jiajing wokou raids: Wang Zhi raids the coast of Zhejiang north of Taizhou[244] | |
| 1554 | spring | Serious epidemics break out in Beijing[252] |
| March | Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates kill the magistrate of Songjiang and occupy Chongming Island[244] | |
| Luso-Chinese agreement (1554): Leonel de Sousa bribes the vice-commissioner of maritime defense into letting the Portuguese stay at Macau for an annual payment of 500 taels and 20 percent imperial duty on half their products[253] | ||
| 1555 | Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates attack Hangzhou[254] | |
| May | Jiajing wokou raids: Ming forces defeat a large raiding party north of Jiaxing[254] | |
| The Jiajing Emperor selects 180 girls under the age of 10 for palace service[251] | ||
| 1556 | January | 1556 Shaanxi earthquake: An earthquake devastates Shaanxi, with over 800,000 reported dead[255] |
| Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates raid the entire coastline from Nanjing to Hangzhou[244] | ||
| The Jiajing Emperor asks the Ministry of Rites to find some magical plants to make him immortal[251] | ||
| 1557 | May | The three main audience halls in the Forbidden City are destroyed in a fire[255] |
| winter | Sengge, son of Altan Khan, lays siege to a garrison near Datong[255] | |
| 1558 | April | Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates raid Zhejiang and northern Fujian[256] |
| Sengge retreats upon the arrival of reinforcements[255] | ||
| The Ministry of Rites presents 1,860 magical plants to the Jiajing Emperor[257] | ||
| Imperial treasuries fall to less than 200,000 ounces of silver[255] | ||
| 1559 | summer | Qi Jiguang begins applying his tactical reforms on newly recruited soldiers[258] |
| A drought causes starvation in the Changjiang River Delta[259] | ||
| December | The Suzhou garrison mutinies[259] | |
| Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates take over Kinmen Island (Quemoy) and launch raids into Fujian and Guangdong[259] |
1560s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1560 | March | The Nanjing garrison rebels in response to cuts in rations until they're given 40,000 ounces of silver[260] |
| The Jiajing Emperor suffers from insomnia[261] | ||
| Qi Jiguang publishes his Jixiao Xinshu describing the musket volley fire technique and his experience training the Ming army in its use.[262] | ||
| 1561 | December | The Forbidden City 's residential palace is destroyed in a fire[263] |
| The Ming dynasty starts producing portable breech-loading firearms.[264][265] | ||
| 1562 | June | The Forbidden City 's residential palace is rebuilt[263] |
| December | Jiajing wokou raids: Pirates capture Xinghua[259] | |
| 1563 | May | Jiajing wokou raids: Ming forces retake Xinghua and destroy pirate bases in Fujian[259] |
| Pirate Lin Daoqian retreats to southwestern Taiwan after being chased by Ming naval forces[266] | ||
| A walled town is built in Penghu on the orders of a Ming general[267] | ||
| 1564 | Eunuchs drop peaches into the Jiajing Emperor's bed and tell him they fell from heaven[268] | |
| The Jiajing Emperor reduces all imperial clansmen to commoner status in response to their demand for stipends[260] | ||
| 1565 | The Jiajing Emperor becomes ill[268] | |
| 1566 | Jiajing wokou raids: Ming forces eradicate pirates in Jiangxi and Guangdong[259] | |
| 1567 | 23 January | The Jiajing Emperor dies[268] |
| 4 February | Zhu Zaihou becomes the Longqing Emperor[269] | |
| The ban on overseas trading is lifted[259] |
1570s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1570 | Wang Gao of the Jianzhou Guard raids Ming settlements[270] | |
| 1572 | 5 July | The Longqing Emperor dies[271] |
| 19 July | Zhu Yijun becomes the Wanli Emperor[271] | |
| 1573 | Spanish trade with China begins in Yuegang[272] | |
| 1574 | Li Chengliang kills Wang Gao with the help of Giocangga and Taksi[270] | |
| A wall is erected around Macau[273] | ||
| 1575 | Wang Wanggao, a Ming naval officer, arrives at Luzon and returns with a Spanish embassy headed by Martín de Rada; the embassy fails due to the Spanish inability to capture Lin Feng, a Chinese pirate[274] | |
| 1576 | The China-America trade is established[272] | |
| 1578 | Portuguese are allowed to travel to Guangzhou[273] | |
| 1579 | Donglin movement: All private Donglin Academies are shut down[275] |
1580s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1580 | Single whip law: Tax laws are simplified[276] | |
| Officials criticize the Wanli Emperor for negligence and the questionable propriety of his personal life[277] | ||
| 1582 | Ming forces defeat Atai of the Jianzhou Jurchens, and accidentally kill Giocangga and Taksi, grandfather and father of Nurhaci[278] | |
| The Taicang Treasury accumulates over 6 million taels of silver[279] | ||
| A Gregorian calendar more accurate than the Chinese calendar is produced in Europe[280] | ||
| 1583 | Matteo Ricci sets up a church in Zhaoqing[281] | |
| 1589 | Bozhou rebellion: Miao people rebel in Bozhou[282] |
1590s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1590 | Chinese from Fujian start settling in southwestern Taiwan[283] | |
| 1592 | March | Ordos Campaign: Liu Dongyang and Pubei rebel in Ningxia[284] |
| 14 July | Ordos Campaign: Ye Mengxiong brings cannons and additional Miao troops to the siege of Ningxia[285] | |
| 23 August | Ordos Campaign: Dikes around Ningxia are completed[286] | |
| 6 September | Ordos Campaign: Ningxia is flooded[287] | |
| 25 September | Ordos Campaign: Rebels make one last attempt to break out of Ningxia[287] | |
| 12 October | Ordos Campaign: The north wall collapses and the rebellion is defeated[288] | |
| Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98): Ming forces mobilize to intervene in the Japanese invasion of Joseon[289] | ||
| Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98): Nurhaci offers to fight the Japanese but is refused; Ming reacts with alarm to the size and quality of Nurhaci's troops[290] | ||
| 1593 | 8 January | Siege of Pyongyang (1593): Ming and Joseon forces evict Japanese troops from Pyeongyang[289] |
| 27 January | Battle of Byeokjegwan: An advance Ming scout party is defeated by Japanese forces[291] | |
| Expansion of the Jia Canal begins[292] | ||
| Middle and junior grade assignments are assigned by drawing lots[293] | ||
| Ming officials issue ten licenses each year for Chinese junks to trade in northern Taiwan[294] | ||
| 1594 | Bozhou rebellion: Ming forces are defeated in Sichuan[295] | |
| 1596 | The Wanli Emperor dispatches eunuchs as tax collectors and mining intendants[296] | |
| 1597 | 17 October | Battle of Jiksan: The Japanese advance towards Hanseong is halted by Ming forces[297] |
| 1598 | 4 January | Siege of Ulsan: Ming and Joseon forces fail to evict the Japanese from Ulsan Castle[298] |
| October | Battle of Sacheon (1598): Ming and Joseon forces fail to evict the Japanese from Sacheon[298] | |
| 7 October | Siege of Suncheon: Ming and Joseon forces fail to evict the Japanese from Suncheon Castle[298] | |
| 16 December | Battle of Noryang: Ming and Joseon naval forces defeat the Japanese fleet[298] | |
| 24 December | Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98): Japanese forces withdraw from Korea[299] | |
| Bozhou rebellion: The Miao rebellion is suppressed[295] | ||
| Mongols kill Li Rusong, the Ming commander-in-chief[300] | ||
| Ming cavalry experiments with firing a three-barreled matchlock before using it as a shield while they attack with a saber using their other hand.[301] | ||
| Cantonese officials give permission to the Spanish to trade in El Piñal[302] | ||
| 1599 | All major ports have senior eunuchs in residence[303] |
17th century
[edit]1600s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1600 | January 17 | The Portuguese in Macau attack the Spanish in Lampacau. The Spanish abandons El Piñal.[304] |
| The size of European book collections surpass that of China[305] | ||
| 1602 | Matteo Ricci settles in Beijing to preach Christianity[281] | |
| 1603 | October | Sangley Rebellion: The Spanish, Japanese, and Filipinos massacre the Chinese population in Manila; the Wanli Emperor blames a eunuch for aggravating the Spanish by asking if they could mine in Cavite[306] |
| Nurhaci and Ming generals agree to delineate the boundary between their territories[291] | ||
| Chinese scholar Chen Di spends some time at the Bay of Tayouan (which Taiwan takes its name from) during a Ming dynasty anti-pirate mission and provides the first significant description of Taiwanese aborigines[307] | ||
| 1604 | Donglin movement: The Donglin Academy is founded[308] | |
| 1605 | June | A thunderbolt knocks down the flagpole at the Altar of Heaven, which is very inauspicious, causing some officials to resign[309] |
| 1606 | Army officers in Yunnan riot and kill Yang Rong, a eunuch superintendent of mining[303] | |
| Ming muskets are attached with plug bayonets.[310] | ||
| 1607 | The first six books of Euclid's Elements are translated into Chinese[311] | |
| 1609 | The Jia Canal is completed[312] |
1610s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1610 | Joseph Needham estimates that European civilization surpassed China in astronomy and physics around this time[280] | |
| 1615 | Nurhaci sends his last tributary emissary to Beijing[313] | |
| 1616 | Nurhaci declares the Later Jin, also known as the Amaga Aisin Gurun[314] | |
| 1618 | 9 May | Battle of Fushun: Later Jin seizes Fushun[315] |
| summer | Battle of Qinghe: Later Jin takes Qinghe[316] | |
| 1619 | 18 April | Battle of Sarhū: Ming forces are annihilated by Later Jin[317] |
| 26 July | Battle of Kaiyuan: Later Jin takes Kaiyuan[318] | |
| 3 September | Battle of Tieling: Later Jin takes Tieling[318] | |
| September | The first Russian envoy, Ivan Petlin, reaches Beijing[319] |
1620s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1620 | 18 August | The Wanli Emperor dies[320] |
| 28 August | Zhu Changluo becomes the Taichang Emperor[320] | |
| 6 September | The Taichang Emperor becomes ill[321] | |
| 26 September | The Taichang Emperor dies[321] | |
| 1 October | Zhu Youjiao becomes the Tianqi Emperor[322] | |
| Ming foundries start producing Hongyipao.[323] | ||
| 1621 | 4 May | Battle of Shen-Liao: Later Jinseizes Shenyang[324] |
| fall | She-An Rebellion: Yi people rebel in Sichuan and Guizhou[325] | |
| December | Battle of Fort Zhenjiang: Ming raids into Later Jin are repulsed[326] | |
| 1622 | 11 March | Battle of Guangning: Later Jin seizes Guangning[326] |
| 24 June | Battle of Macau: A Dutch attack on Macau is repelled by the Portuguese[327] | |
| June | White Lotus rebels appear in Shandong[328] | |
| August | White Lotus rebels block the Grand Canal[329] | |
| The Dutch start building a fort at Penghu[330] | ||
| October | Sino-Dutch conflicts: Dutch vessels start raiding Ming trading ships[327] | |
| November | White Lotus rebels are defeated[329] | |
| An earthquake strikes Gansu, killing 12,000[328] | ||
| 1623 | October | Sino-Dutch conflicts: A Dutch raid on Xiamen is repulsed[327] |
| She-An Rebellion: Ming forces are defeated[325] | ||
| The Yellow River bursts its dikes and flood Xuzhou[328] | ||
| 1624 | 26 August | Sino-Dutch conflicts: Ming forces evict the Dutch from Penghu and they retreat to Taiwan, settling near the Bay of Tayouan next to a pirate village[327] |
| She-An Rebellion: Ming forces defeat rebels but are unable to decisively quell the rebellion[325] | ||
| 1625 | The Donglin movement is purged[331] | |
| 1626 | 10 February | Battle of Ningyuan: A Later Jin attack on Ningyuan is repulsed and Nurhaci is wounded and dies[332] |
| 1627 | spring | Battle of Ning-Jin: Later Jin forces under Hong Taiji attack Jinzhou but are repelled |
| 30 September | The Tianqi Emperor dies[333] | |
| 2 October | Zhu Youjian becomes the Chongzhen Emperor[334] | |
| 1628 | spring | Drought hits Shanxi[335] |
| August | Pirate lord Zheng Zhilong surrenders to the Ming[336] | |
| 1629 | winter | Jisi Incident: Later Jin forces break through the Great Wall and loot the region around Beijing[337] |
| The Chongzhen Emperor cuts funding for the imperial post service, causing out of work postal workers to rebel in Shanxi[335] | ||
| She-An Rebellion: The rebels are defeated[325] |
1630s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1630 | summer | Jisi Incident: Later Jin forces retreat[337] |
| 1631 | April | Rebels capture Pingdu[338] |
| 21 November | Battle of Dalinghe: Later Jin seizes Dalinghe[339] | |
| 1632 | 22 February | Wuqiao Mutiny: Troops from Shandong mutiny and capture Dengzhou[338] |
| Spanish Manila trade with China reaches 2 million pesos per year[335] | ||
| Ming defensive planners build some star forts but they don't catch on in China.[340] | ||
| 1633 | April | Wuqiao Mutiny: Shandong rebels defect to Later Jin[338] |
| 7 July | Battle of Liaoluo Bay: Ming dockyards start construction of multidecked broadside sailing ships capable of holding large cannons under the supervision of Zheng Zhilong; they get blown up by a Dutch surprise attack[341] | |
| summer | Siege of Lüshun: Later Jin seizes Lüshun[342] | |
| 22 October | Battle of Liaoluo Bay: Ming forces defeat a Dutch pirate fleet near Kinmen Island (Quemoy)[343] | |
| 27 December | Rebels take Mianzhi[344] | |
| 1634 | 14 September | Rebellion breaks out at Tongcheng[345] |
| 1635 | March | Rebels take Fengyang[346] |
| August | Ming forces are defeated by rebels in Gansu[346] | |
| September | Li Zicheng rebels in Shanxi[345] | |
| Telescopes are used for aiming artillery in the Ming dynasty.[347] | ||
| 1636 | Hong Taiji proclaims the Qing dynasty[348] | |
| 1638 | Qing dynasty conquers Shandong[349] | |
| Ming forces are defeated on the Shanxi-Henan border[349] | ||
| 1639 | The Spanish and Filipinos massacre 20,000 Chinese in Luzon[350] | |
| Portuguese merchants from Macau are banned from Nagasaki[350] | ||
| Zhejiang experiences drought[351] |
1640s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1640 | summer | Rebels enter Sichuan[349] |
| 1641 | Li Zicheng enters Henan[350] | |
| March | Li Zicheng takes Luoyang[350] | |
| Rebel leader Zhang Xianzhong takes Xiangyang[350] | ||
| 15 July | Zhang Xianzhong takes Wuchang[352] | |
| October | Zhang Xianzhong takes Changsha and Hengzhou[353] | |
| Li Zicheng takes Kaifeng[353] | ||
| Locusts attack Zhejiang[351] | ||
| 1642 | 8 April | Battle of Song-Jin: Qing dynasty takes Jinzhou[354] |
| Floods strike Zhejiang[351] | ||
| Composite metal cannons are produced in the Ming dynasty.[323][355][356] | ||
| Li Zicheng's rebels manage to create a two zhang breach in Ming fortifications using cannons.[357] | ||
| 1643 | January | Li Zicheng takes Xiangyang[353] |
| November | Li Zicheng takes Xi'an[354] | |
| Zhang Xianzhong declares the Xi dynasty in Huguang[358] | ||
| 1644 | 8 February | Li Zicheng proclaims his Shun dynasty in Xi'an[359] |
| 25 April | Li Zicheng takes Beijing and the Chongzhen Emperor hangs himself[360] | |
| 27 May | Battle of Shanhai Pass: Wu Sangui lets the Qing forces through the Great Wall and their forces defeat Li Zicheng in battle, after which Li retreats to Beijing[361] | |
| 5 June | Qing dynasty takes Beijing and Li Zicheng flees[361] | |
| 19 June | Zhu Yousong becomes the Hongguang Emperor of Southern Ming in Nanjing[362] | |
| Zhang Xianzhong relocates to Chengdu and proceeds to massacre the Sichuanpopulation[358] | ||
| 1645 | January | Qing forces capture Luoyang[363] |
| 20 May | Qing forces capture Yangzhou[363] | |
| 16 June | Qing forces capture Nanjing and the Hongguang Emperor[364] | |
| June | Li Zicheng dies[365] | |
| 6 July | Qing forces capture Hangzhou[364] | |
| 21 July | All nonclerical adult male citizens are ordered to adopt the Manchu queue to show their allegiance to the Qing dynasty[366] | |
| 18 August | Zhu Yujian becomes the Longwu Emperor at Fuzhou[367] | |
| August | Zhu Yihai becomes regent of Ming at Shaoxing, taking control of Ming loyalists at Yuyao and Taizhou[367] | |
| 1646 | February | Ming forces are defeated in Jiangnan[368] |
| 10 July | Qing forces defeat the Ming army at Tonglu[369] | |
| 30 September | Qing forces capture Yanping[370] | |
| 6 October | The Longwu Emperor is killed by Qing forces[370] | |
| 17 October | Qing forces take Fuzhou[370] | |
| 12 December | Zhu Yuyue becomes the Shaowu Emperor in Guangzhou[371] | |
| 24 December | Zhu Youlang becomes the Yongli Emperor in Zhaoqing[371] | |
| 1647 | 2 January | Zhang Xianzhong is killed by Qing forces but his army occupies Chongqing and then occupies Sichuan under the leadership of Sun Kewang[372] |
| 20 January | Qing forces capture Guangzhou and the Shaowu Emperor[373] | |
| 5 March | Qing forces conquer Guangdong, half of Guangxi, and Hainan[373] | |
| March | Qing forces take Changsha[374] | |
| spring | Qing forces raid Anping[375] | |
| 23 September | Qing forces take Wugang[376] | |
| Zhu Yihai conducts raids on the coast of Fujian from island bases[377] | ||
| 1648 | 20 February | Ming loyalists rebel at Nanchang and Nanning[378] |
| 14 April | Qing forces fail to take Guilin[376] | |
| 1649 | 15 January | Ming loyalists rebel at Datong[379] |
| 1 March | Qing forces take Nanchang[380] | |
| 4 October | Ming loyalists at Datong are defeated[379] | |
| summer | Qing forces conquer southern Huguang[381] | |
| 24 November | Qing forces slaughter the population of Guangzhou[382] | |
| 27 November | Qing forces capture Guilin[382] | |
| 2 December | Qing forces capture Zhaoqing and the Yongli Emperor flees[382] |
1650s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1651 | 15 October | Qing forces capture Zhoushan and Zhu Yihai flees[383] |
| 1652 | 7 August | Rebel general Li Dingguo takes Guilin[384] |
| winter | Sun Kewang's army is routed by Qing forces[384] | |
| Zhu Yihai settles on Kinmen Island (Quemoy) with the help of Zheng Chenggong and renounces his title as Regent of Ming[385] | ||
| 1653 | Li Dingguo retreats to Guangdong[384] | |
| 1655 | Li Dingguo 's army is routed by Qingforces[384] | |
| Ming loyalist Zheng Chenggong establishes Xiamen as his base[386] | ||
| 1656 | March | The Yongli Emperor arrives in Yunnan[387] |
| 9 May | Qing forces try to invade Kinmen Island (Quemoy) but their fleet is destroyed in a storm[388] | |
| 1657 | February | Ming forces defeat a Qing army near the Changjiang River Delta[388] |
| October | Sun Kewang's forces are defeated by Li Dingguo in eastern Yunnan and he retreats to Guizhou[387] | |
| December | Sun Kewang surrenders to the Qing dynasty[387] | |
| 1658 | June | Zheng Chenggong occupies Wenzhou[389] |
| 1659 | 7 January | Qing forces advance into Yunnan and the Yongli Emperor flees to Toungoo dynasty[390] |
| 10 March | Qing forces capture Yongchang and defeat Li Dingguo 's army, securing Yunnan[390] | |
| June | The Yongli Emperor reaches Inwa[391] | |
| 10 August | Zheng Chenggong takes Zhenjiang[392] | |
| 24 August | Zheng Chenggong lays siege to Nanjing[392] | |
| 9 September | Zheng Chenggong's army is annihilated and he retreats to Xiamen[393] |
1660s
[edit]| Year | Date | Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1660 | February | Qing forces launch an attack on Kinmen Island(Quemoy) and Xiamen but fail[393] |
| 1661 | 21 April | Zheng Chenggong departs from Kinmen Island (Quemoy) for Taiwan[394] |
| 30 April | Zheng Chenggong arrives on the shores of Dutch Formosa[394] | |
| 1 May | Fort Provintia surrenders to Zheng Chenggong[395] | |
| June | Pye Min massacres most of the Yongli Emperor's entourage[396] | |
| 1662 | 20 January | Qing forces advance towards Inwa and force the return of the Yongli Emperor [396] |
| 1 February | Siege of Fort Zeelandia: Fort Zeelandia surrenders to Zheng Chenggong[395] | |
| May | The Yongli Emperor is executed in Yunnan; so ends the Southern Ming resistance on the mainland[396] | |
| 23 June | Zheng Chenggong dies and is succeeded by his son Zheng Jing[397] | |
| 23 December | Zhu Yihai dies[397] | |
| 1664 | The Qing dynasty conquers Fujian and Zheng Jing retreats to Taiwan[398] |
Gallery
[edit]-
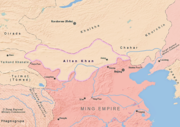
Red Turban Rebellion (1351–1368)
-
Yellow River course change in 1358
-
Moghulistan in 1372
-
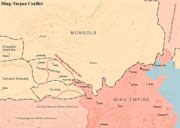
Jingnan Campaign (1399–1402)
-
Zheng He's treasure ships (1405–1433)
-
Yishiha's voyages in the context of military and diplomatic activities in the Yongle era of the Ming dynasty. Yishiha's route is in blue, along with those of Zheng He (in black) and Chen Cheng (in green).
-
The Yongle Emperor's campaigns against the Mongols, (1410–1424)
-
Region suffering from Miao rebellions during the Ming dynasty
-
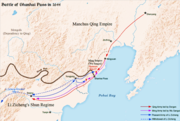
Tumu Crisis in 1449
-
Moghulistan in 1490
-
14th and 16th century wokou raids
-
Yarkent Khanate and Mansur Khan's Turpan Khanate in 1517
-
Realm of Altan Khan in 1571
-
Yarkent Khanate in 1572
-
Xu Xiake's (1587–1641) travels
-
Ming–Turpan conflict, 15th to 16th centuries
-
Battle of Ningyuan in 1626
-
Late Ming peasant rebellions 1628–1636
-
Li Zicheng's rebellion 1637–1644
-
Battle of Shanhai Pass in 1644
-
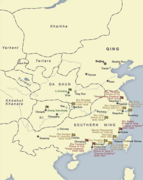
Southern Ming in November 1644
-
The flight of the Yongli Emperor—the last sovereign of the Southern Ming dynasty—from 1647 to 1661. The provincial and national boundaries are those of the People's Republic of China.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 11.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 44.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 45.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 46.
- ^ Twitchett 1994, p. 583.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 47.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 32.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 33.
- ^ a b Andrade 2016, p. 66.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 41.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 51.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 34.
- ^ a b Mote 2003, p. 571.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 96.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 34-35.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Twitchett 1998, p. 97.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 37.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 57.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 24.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 115.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 313.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 116.
- ^ a b c d e f Twitchett 1998, p. 117.
- ^ a b Mote 2003, p. 567.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 118.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 119.
- ^ a b c d e f Mote 2003, p. 572.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 120.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 122.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 110.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 105.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 125.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 126.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 540.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 128.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 129.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 296.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 166.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 565.
- ^ Tsien 1985, p. 100.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 130.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 136.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 573.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 568.
- ^ Geary 2003, p. 8.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 139.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 140.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 514.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 144.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 557.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 151.
- ^ Geary 2003, p. 10.
- ^ Ming 1996, p. 163-164.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 158.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 159.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 158.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 160.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 162.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 165.
- ^ Twitchett 1998b, p. 247.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 257.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 168.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 178.
- ^ Geary 2003, p. 12.
- ^ Fernquest 2006, p. 47.
- ^ Fernquest 2006, p. 47-8.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 181.
- ^ Mote 2003, p. 583.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 194.
- ^ Twitchett 2008, p. 32.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 195.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 196.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 198.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 199.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 190-191.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Twitchett 1998, p. 200.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 201.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 220.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 238.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 222.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 104-105.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 267.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 269.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 105.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 223.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Twitchett 1998, p. 230.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 212.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 51-52.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 53.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 57.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 262.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 55.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 62-63.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 59.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 63.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 64.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 221.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 311.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 104.
- ^ Yong-le: Year 6, Month 6, Day 12
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 65.
- ^ a b c Dreyer 2007, p. 66.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 226.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 231.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 252.
- ^ Duyvendak 1938, p. 361.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 270.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 75.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 264.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 77-78.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 263.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998b, p. 264.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 227.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 79.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 239.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 81.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 82.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 76.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 83.
- ^ Duyvendak 1938, p. 402.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 516.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 241.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 91.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 138.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 93.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 94.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 228.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 57-58.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 137.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 140.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 135.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 288.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 289.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 290.
- ^ Xuan-de: Year 1, Month 12, Day 2
- ^ Year 2, Month 11, Day 1
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 142.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 299.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 294.
- ^ Chase 2003, p. 68.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 296.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 144.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 151.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 145.
- ^ Xuan-de: Year 6, Month 5, Day 3
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 153.
- ^ Mills 1970, p. 35.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 165.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 158.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 160.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 300.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 161.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 162-163.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 219.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 303.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Twitchett 1998, p. 310.
- ^ a b Dreyer 2007, p. 171.
- ^ Liew 1996, p. 174-175.
- ^ Liew 1996, p. 178.
- ^ Liew 1996, p. 181-2.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 307.
- ^ Liew 1996, p. 184.
- ^ a b Liew 1996, p. 185.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 312.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 313.
- ^ Liew 1996, p. 192.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 322.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 323.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 324.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 325.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 327.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 328.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 330.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 336.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 335.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 337.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 339.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 341.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 343.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 377.
- ^ Dreyer 2007, p. 173.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998b, p. 269.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 380.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 387.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 399.
- ^ Cheng-hua: Year 4, Month 4, Day 21
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 394.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 401.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 388.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 383.
- ^ Cheng-hua: Year 15, Month 4, Day 7
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 365.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 351.
- ^ Jin 2016, p. 31.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 357.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 374.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 395.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 491.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 381.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 382.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 371.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 403.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 404.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 405.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 407.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 409.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 410.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 467.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 413.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 433.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 416.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 415.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 417.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 420.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 421.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 428.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 429.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 430.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 432.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 434.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 443.
- ^ Hao 2011, p. 12.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 130.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 492.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 141.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 451.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 453.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 452.
- ^ Andrade 2008f.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 479.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 456.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 490.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 468.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 465.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 469.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 472.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 493.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 470.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 480.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 460.
- ^ a b c d e f Twitchett 1998, p. 473.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 543.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 462.
- ^ a b c d e f g Twitchett 1998, p. 496.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 494.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 475.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 171.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 495.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 476.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 477.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 481.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 487.
- ^ Wills 2011, p. 38.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 498.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 478.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 502.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 482.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 503.
- ^ a b c d e f g Twitchett 1998, p. 504.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 489.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 507.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 173.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 506.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 33.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 380.
- ^ Knapp 1980, p. 9.
- ^ Knapp 1980, p. 117.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 508.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 512.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998b, p. 270.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 514.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 505.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 559.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 560.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 532.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 525.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 515.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 575.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 522.
- ^ a b Jin 2016, p. 30.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 562.
- ^ Lewis 2015, p. 209.
- ^ Knapp 1980, p. 10.
- ^ Lewis 2015, p. 239.
- ^ Swope 2009, p. 30.
- ^ Swope 2009, p. 31-32.
- ^ a b Swope 2009, p. 32-33.
- ^ Swope 2009, p. 33.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 568.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 576.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 570.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 552.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 539.
- ^ Andrade 2008d.
- ^ a b Dardess 2012, p. 9.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 530.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 572.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 573.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 574.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 557.
- ^ Chase 2003, p. 148.
- ^ Sousa Pinto 2008, p. 22.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 531.
- ^ Sousa Pinto 2008, pp. 33, 39.
- ^ Wilkinson 2012, p. 934.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 561.
- ^ Andrade 2008a.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 540.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 541.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 456.
- ^ Jin 2016, p. 24.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 553.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 558.
- ^ Twitchett 1998b, p. 271.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 577.
- ^ Swope 2014, p. 14.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 579.
- ^ a b Wakeman 1985, p. 63.
- ^ Dmytryshyn 1985, p. 90.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 591.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 593.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 595.
- ^ a b Andrade 2016, p. 201.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 600.
- ^ a b c d Dardess 2012, p. 10.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 601.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 603.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 604.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 605.
- ^ Knapp 1980, p. 12.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 610.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 602.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 611.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 612.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 615.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 614.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 616.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 618.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 617.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 212.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 204.
- ^ Swope 2014, p. 102.
- ^ Andrade 2016, p. 208.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 621.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 623.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 622.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 412.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 629.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 630.
- ^ a b c d e Twitchett 1998, p. 631.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 632.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 634.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 635.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 636.
- ^ Needham 1986, p. 334.
- ^ "The Rise and Fall of Distinctive Composite-Metal Cannons Cast During the Ming-Qing Period". Retrieved 19 December 2016.
- ^ Swope 2014.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 701.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 638.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 637.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 639.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 644.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 656.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 660.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 658.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 662.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 665.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 673.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 675.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 676.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 678.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 702.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 679.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 682.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 712.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 683.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 695.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 684.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 691.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 686.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 690.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 692.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 698.
- ^ a b c d Twitchett 1998, p. 704.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 699.
- ^ Andrade 2008j.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 706.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 718.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 719.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 707.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 708.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 720.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 721.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 722.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 723.
- ^ a b c Twitchett 1998, p. 710.
- ^ a b Twitchett 1998, p. 724.
- ^ Twitchett 1998, p. 725.
Bibliography
[edit]- Andrade, Tonio (2008a), "Chapter 1: Taiwan on the Eve of Colonization", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008b), "Chapter 2: A Scramble for Influence", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008c), "Chapter 3: Pax Hollandica", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008d), "Chapter 4: La Isla Hermosa: The Rise of the Spanish Colony in Northern Taiwan", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008e), "Chapter 5: The Fall of Spanish Taiwan", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008f), "Chapter 6: The Birth of Co-colonization", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008g), "Chapter 7: The Challenges of a Chinese Frontier", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008h), "Chapter 8: "The Only Bees on Formosa That Give Honey"", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008i), "Chapter 9: Lord and Vassal: Company Rule over the Aborigines", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008j), "Chapter 10: The Beginning of the End", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008k), "Chapter 11: The Fall of Dutch Taiwan", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2008l), "Conclusion", How Taiwan Became Chinese: Dutch, Spanish, and Han Colonization in the Seventeenth Century, Columbia University Press
- Andrade, Tonio (2016), The Gunpowder Age: China, Military Innovation, and the Rise of the West in World History, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-13597-7.
- Asimov, M.S. (1998), History of civilizations of Central Asia Volume IV The age of achievement: A.D. 750 to the end of the fifteenth century Part One The historical, social and economic setting, UNESCO Publishing
- Atwood, Christopher P. (2004), Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire, Facts On File
- Barfield, Thomas (1989), The Perilous Frontier: Nomadic Empires and China, Basil Blackwell
- Barrett, Timothy Hugh (2008), The Woman Who Discovered Printing, Great Britain: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-12728-7 (alk. paper)
- Beckwith, Christopher I. (2009), Empires of the Silk Road: A History of Central Eurasia from the Bronze Age to the Present, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-13589-2
- Beckwith, Christopher I (1987), The Tibetan Empire in Central Asia: A History of the Struggle for Great Power among Tibetans, Turks, Arabs, and Chinese during the Early Middle Ages, Princeton University Press
- Biran, Michal (2005), The Empire of the Qara Khitai in Eurasian History: Between China and the Islamic World, Cambridge Studies in Islamic Civilization, Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521842263
- Bregel, Yuri (2003), An Historical Atlas of Central Asia, Brill
- Chase, Kenneth (2003), Firearms: A Global History to 1700, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-82274-2.
- Dardess, John (2012), Ming China 1368-1644 A Concise History of A Resilient Empire, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.
- Dmytryshyn, Basil (1985), Russia's Conquest of Siberia, Western Imprints, The Press of the Oregon Historical Society
- Dreyer, Edward L. (2007), Zheng He: China and the Oceans in the Early Ming Dynasty, 1405-1433, Pearson Longman
- Drompp, Michael Robert (2005), Tang China And The Collapse Of The Uighur Empire: A Documentary History, Brill
- Duyvendak, J.J.L. (1938), "The True Dates of the Chinese Maritime Expeditions in the Early Fifteenth Century", T'oung Pao, 34 (5): 341–413, doi:10.1163/156853238X00171
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley (1999), The Cambridge Illustrated History of China, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-66991-X (paperback).
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley; Walthall, Anne; Palais, James B. (2006), East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History, Boston: Houghton Mifflin, ISBN 0-618-13384-4
- Fernquest, John (2006), Crucible of War: Burma and the Ming in the Tai Frontier Zone (1382-1454)
- Geary, Norman (2003), The Kam People of China, RoutledgeCurzon
- Golden, Peter B. (1992), An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples: Ethnogenesis and State-Formation in Medieval and Early Modern Eurasia and the Middle East, OTTO HARRASSOWITZ · WIESBADEN
- Graff, David A. (2002), Medieval Chinese Warfare, 300-900, Warfare and History, London: Routledge, ISBN 0415239559
- Graff, David Andrew (2016), The Eurasian Way of War Military Practice in Seventh-Century China and Byzantium, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-46034-7.
- Hao, Zhidong (2011), Macau History and Society, HKU Press, ISBN 9789888028542.
- Haywood, John (1998), Historical Atlas of the Medieval World, AD 600-1492, Barnes & Noble
- Jin, Dengjian (2016), The Great Knowledge Transcendence, Palgrave Macmillan
- Knapp, Ronald G. (1980), China's Island Frontier: Studies in the Historical Geography of Taiwan, The University of Hawaii
- Latourette, Kenneth Scott (1964), The Chinese, their history and culture, Volumes 1-2, Macmillan
- Lewis, James (2015), The East Asian War, 1592-1598: International Relations, Violence and Memory, Routledge
- Liew, Foon Ming (1996), The Luchuan-Pingmian Campaigns (1436-1449) in the Light of Official Chinese Historiography
- Lorge, Peter A. (2008), The Asian Military Revolution: from Gunpowder to the Bomb, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-60954-8
- Luttwak, Edward N. (2009), The Grand Strategy of the Byzantine Empire, The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press
- Mills, J.V.G. (1970), Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' [1433], Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Millward, James (2009), Eurasian Crossroads: A History of Xinjiang, Columbia University Press
- Ming, Liew Foon (1996), The Luchuan-Pingmian Campaigns (1436-1449) in the Light of Official Chinese Historiography
- Mote, F. W. (2003), Imperial China: 900–1800, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0674012127
- Narangoa, Li (2014), Historical Atlas of Northeast Asia, 1590-2010: Korea, Manchuria, Mongolia, Eastern Siberia, New York: Columbia University Press, ISBN 9780231160704
- Needham, Joseph (1986), Science & Civilisation in China, vol. V:7: The Gunpowder Epic, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-30358-3
- Rong, Xinjiang (2013), Eighteen Lectures on Dunhuang, Brill
- Rubinstein, Murray A. (1999), Taiwan: A New History, East Gate Books
- Schafer, Edward H. (1985), The Golden Peaches of Samarkand: A study of T'ang Exotics, University of California Press
- Shaban, M. A. (1979), The ʿAbbāsid Revolution, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-29534-3
- Sinor, Denis (1990), The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia, Volume 1, Cambridge University Press
- Sima, Guang (2015), Bóyángbǎn Zīzhìtōngjiàn 54 huánghòu shīzōng 柏楊版資治通鑑54皇后失蹤, Yuǎnliú chūbǎnshìyè gǔfèn yǒuxiàn gōngsī, ISBN 978-957-32-0876-1
- Skaff, Jonathan Karam (2012), Sui-Tang China and Its Turko-Mongol Neighbors: Culture, Power, and Connections, 580-800 (Oxford Studies in Early Empires), Oxford University Press
- Sousa Pinto, Paulo Jorge de (2008). "Enemy at the Gates - Macao, Manila and the "Pinhal Episode" (end of the 16th Century)". Bulletin of Portuguese - Japanese Studies. 16: 11–43.
- Standen, Naomi (2007), Unbounded Loyalty Frontier Crossings in Liao China, University of Hawai'i Press
- Steinhardt, Nancy Shatzman (1997), Liao Architecture, University of Hawaii Press
- Swope, Kenneth M. (2009), A Dragon's Head and a Serpent's Tail: Ming China and the First Great East Asian War, 1592-1598, University of Oklahoma Press.
- Swope, Kenneth (2014), The Military Collapse of China's Ming Dynasty, Routledge
- Tsien Tsuen-Hsuin (1985). Needham, Joseph (ed.). Science and Civilisation in China: Volume 5, Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Part 1, Paper and Printing. Taipei: Caves Books. ISBN 978-0-521-08690-5.
- Twitchett, Denis C. (1979), The Cambridge History of China, Vol. 3, Sui and T'ang China, 589–906, Cambridge University Press
- Twitchett, Denis (1994), "The Liao", The Cambridge History of China, Volume 6, Alien Regime and Border States, 907-1368, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 43–153, ISBN 0521243319
- Twitchett, Denis (1998), The Cambridge History of China Volume 7 The Ming Dynasty, 1368—1644, Part I, Cambridge University Press
- Twitchett, Denis (1998b), The Cambridge History of China Volume 8 The Ming Dynasty, 1368—1644, Part 2, Cambridge University Press
- Twitchett, Denis (2008), The Cambridge History of China 1, Cambridge University Press
- Twitchett, Denis (2009), The Cambridge History of China Volume 5 The Sung dynasty and its Predecessors, 907-1279, Cambridge University Press
- Wakeman, Frederic (1985), The Great Enterprise: The Manchu Reconstruction of Imperial Order in Seventeenth-Century China, vol. 1, University of California Press
- Wang, Zhenping (2013), Tang China in Multi-Polar Asia: A History of Diplomacy and War, University of Hawaii Press
- Wilkinson, Endymion (2012), Chinese History: A New Manual, Harvard University Asia Center for the Harvard-Yenching Institute
- Wilkinson, Endymion (2015). Chinese History: A New Manual, 4th edition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Asia Center distributed by Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674088467.
- Wills, John E. (2011), China and Maritime Europe, 1500–1800: Trade, Settlement, Diplomacy, and Missions, Cambridge University Press.
- Xiong, Victor Cunrui (2000), Sui-Tang Chang'an: A Study in the Urban History of Late Medieval China (Michigan Monographs in Chinese Studies), U OF M CENTER FOR CHINESE STUDIES, ISBN 0892641371
- Xiong, Victor Cunrui (2009), Historical Dictionary of Medieval China, United States of America: Scarecrow Press, Inc., ISBN 978-0810860537
- Xu, Elina-Qian (2005), HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE PRE-DYNASTIC KHITAN, Institute for Asian and African Studies 7
- Xue, Zongzheng (1992), Turkic peoples, 中国社会科学出版社
- Yuan, Shu (2001), Bóyángbǎn Tōngjiàn jìshìběnmò 28 dìèrcìhuànguánshídài 柏楊版通鑑記事本末28第二次宦官時代, Yuǎnliú chūbǎnshìyè gǔfèn yǒuxiàn gōngsī, ISBN 957-32-4273-7
- Yule, Henry (1915), Cathay and the Way Thither: Being a Collection of Medieval Notices of China, Vol I: Preliminary Essay on the Intercourse Between China and the Western Nations Previous to the Discovery of the Cape Route, Hakluyt Society
Categories:
- Timelines of Chinese dynasties
- Ming dynasty
- 14th century in China
- 15th century in China
- 16th century in China
- 17th century in China
- States and territories established in 1368
- States and territories disestablished in 1644
- 1368 establishments in Asia
- 14th-century establishments in China
- 1644 disestablishments in Asia
- 1640s disestablishments in China