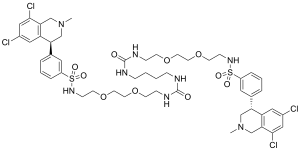
Tenapanor
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ibsrela, Xphozah, others |
| Other names | Tenapanor hydrochloride |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | NHE3 inhibitors |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.243.471 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C50H66Cl4N8O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 1145.04 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Tenapanor, sold under the brand name Ibsrela among others, is a medication used for the treatment of adults with a disease of the gut called irritable bowel syndrome with constipation commonly referred to as IBS-C.[3][5] It is used in form of tenapanor hydrochloride.[3] It is also used in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia associated with chronic kidney disease.[4] Tenapanor is a sodium hydrogen exchanger 3 (NHE3) inhibitor.[4]
Tenapanor is a drug developed by Ardelyx, which acts as an inhibitor of the sodium-proton exchanger NHE3. This antiporter protein is found in the kidney and intestines, and normally acts to regulate the levels of sodium absorbed and secreted by the body. When administered orally, tenapanor selectively inhibits sodium uptake in the intestines, limiting the amount absorbed from food, and thereby reduces levels of sodium in the body.[6] This may make it useful in the treatment of chronic kidney disease and hypertension, both of which are exacerbated by excess sodium in the diet.[7]
It was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2019.[3][8][5][9] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[10] In October 2023, tenapanor was approved by the FDA for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia.[11]
References
[edit]- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Ibsrela". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 30 May 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Regulatory Decision Summary - Ibsrela". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 13 November 2021. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d "Ibsrela- tenapanor hydrochloride tablet". DailyMed. 14 April 2022. Archived from the original on 19 October 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- ^ a b c "Xphozah 10 MG- tenapanor tablet, film coated; Xphozah 20 MG- tenapanor tablet, film coated; Xphozah 30 MG- tenapanor tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 17 October 2023. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- ^ a b "Drug Trials Snapshots: Ibsrela". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 September 2019. Archived from the original on 19 November 2019. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Spencer AG, Labonte ED, Rosenbaum DP, Plato CF, Carreras CW, Leadbetter MR, et al. (2014). "Intestinal inhibition of the na+/h+ exchanger 3 prevents cardiorenal damage in rats and inhibits na+ uptake in humans". Sci Transl Med. 6 (227): 227ra36. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007790. PMID 24622516. S2CID 10741924.
- ^ Spencer AG, Labonte ED, Rosenbaum DP, Plato CF, Carreras CW, Leadbetter MR, et al. (March 2014). "Intestinal inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchanger 3 prevents cardiorenal damage in rats and inhibits Na+ uptake in humans". Sci Transl Med. 6 (227): 227ra36. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007790. PMID 24622516. S2CID 10741924.
- ^ "Ibsrela (tenapanor) FDA Approval History". Drugs.com. 12 September 2019. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 19 November 2019.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Ibsrela". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 19 November 2019. Archived from the original on 19 November 2019. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ^ "New Drug Therapy Approvals 2019". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 16 September 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ "US FDA approves Ardelyx's kidney disease-related drug". Reuters. 18 October 2023. Archived from the original on 24 October 2023. Retrieved 24 October 2023.
External links
[edit]- Clinical trial number NCT02686138 for "A 26-Week Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Tenapanor in IBS-C (T3MPO-2)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT02621892 for "A 12-Week Study With a 4-Week Randomized Withdrawal Period to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Tenapanor for the Treatment of IBS-C (T3MPO-1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT02675998 for "An 8-Week Study to Evaluate Tenapanor in the Treatment of Hyperphosphatemia in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients on Hemodialysis (ESRD-HD)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03427125 for "A Phase 3 Study of Tenapanor to Treat Hyperphosphatemia in ESRD Patients on Dialysis" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03824587 for "Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of Tenapanor as Adjunctive Therapy to Phosphate Binder Therapy" at ClinicalTrials.gov
