Taxation in the United Kingdom
| Taxation in the United Kingdom |
|---|
 |
| UK Government Departments |
| UK Government |
|
| Scottish Government |
| Welsh Government |
| Local Government |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Politics of the United Kingdom |
|---|
 |
|
|
In the United Kingdom, taxation may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government (HM Revenue and Customs), devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2023–24, total government revenue was forecast to be £1,139.1 billion, or 40.9 per cent of GDP, with income taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at around £470 billion[1].
History
[edit]A uniform Land Tax, originally introduced in England during the late 17th century, formed the main source of government revenue throughout the 18th century and the early 19th century.[2]
Napoleonic wars
[edit]Income tax was announced in Britain by William Pitt the Younger in his budget of December 1798 and introduced in 1799, to pay for weapons and equipment in preparation for the Napoleonic Wars. Pitt's new graduated (progressive) income tax began at a levy of 2 old pence in the pound (1⁄120th) on annual incomes over £60 (equivalent to £7,978 as of 2023),[3] and increased up to a maximum of 2 shillings (10 per cent) on annual incomes of over £200. Pitt hoped that the new income tax would raise £10 million, but receipts for 1799 totalled just over £6 million.[4]
Income tax was levied under five schedules. Income not falling within those schedules was not taxed. The schedules were:
- Schedule A (tax on income from United Kingdom land)
- Schedule B (tax on commercial occupation of land)
- Schedule C (tax on income from public securities)
- Schedule D (tax on trading income, income from professions and vocations, interest, overseas income and casual income)
- Schedule E (tax on employment income)
Later, Schedule F (tax on United Kingdom dividend income) was added.
Pitt's income tax was levied from 1799 to 1802, when it was abolished by Henry Addington during the Peace of Amiens. Addington had taken over as prime minister in 1801. The income tax was reintroduced by Addington in 1803 when hostilities recommenced, but it was again abolished in 1816, one year after the Battle of Waterloo.
Considerable controversy was aroused by the malt, house, windows and income taxes. The malt tax was easy to collect from brewers; even after it was reduced in 1822, it produced over 10 per cent of government's annual revenues through the 1840s. The house tax mostly hit London town houses; the windows tax mostly hit country manors.[5]
Peel's income tax
[edit]The income tax was reintroduced by Sir Robert Peel in the Income Tax Act 1842. Peel, as a Conservative, had opposed income tax in the 1841 general election, but a growing budget deficit required a new source of funds. The new income tax of 7d in the pound (about 2.9%), based on Addington's model, was imposed on annual incomes above £150 (equivalent to £17,836 as of 2023).[3][6]
First World War
[edit]The war (1914–1918) was financed by borrowing large sums at home and abroad, by new taxes, and by inflation. It was implicitly financed by postponing maintenance and repair, and canceling capital expenditure. The government avoided indirect taxes because they raised the cost of living, and caused discontent among the working class. There was a strong emphasis on being "fair" and being "scientific". The public generally supported the heavy new taxes, with minimal complaints. The Treasury rejected proposals for a stiff capital levy, which the Labour Party wanted to use to weaken the capitalists. Instead, there was an excess profits tax, of 50% on profits above the normal pre-war level; the rate was raised to 80% in 1917. Excise taxes were added on luxury imports such as automobiles, clocks and watches. There was no sales tax or value added tax. The main increase in revenue came from the income tax, which in 1915 went up to 3s. 6d in the pound (17.5%), and individual exemptions were lowered. The income tax rate increased to 5s. (25%) in 1916, and 6s. (30%) in 1918. Altogether, taxes provided at most 30% of national expenditure, with the rest from borrowing. The national debt soared from £625 million to £7,800 million. Government bonds typically paid 5% p.a. Inflation escalated so that the pound in 1919 purchased only a third of the basket it had purchased in 1914. Wages were laggard, and the poor and retired were especially hard hit.[7][8]
Modern rules
[edit]Business rates were introduced in England and Wales in 1990 and are a modernised version of a system of rating that dates back to the Poor Relief Act 1601. As such, business rates retain many previous features from, and follow some case law of, older forms of rating. The Finance Act 2004 introduced an income tax regime known as "pre-owned asset tax" which aims to reduce the use of common methods of inheritance tax avoidance.
Britain's income tax has changed over the years. Originally it taxed a person's income regardless of who was beneficially entitled to that income, but now tax is paid on income to which the taxpayer is beneficially entitled. Most companies were taken out of the income tax net in 1965 when corporation tax was introduced. These changes were consolidated by the Income and Corporation Taxes Act 1970. Also the schedules under which tax is levied have changed. Schedule B was abolished in 1988, Schedule C in 1996 and Schedule E in 2003. For income tax purposes, the remaining schedules were superseded by the Income Tax (Trading and Other Income) Act 2005, which also repealed Schedule F. For corporation tax purposes, the Schedular system was repealed and superseded by the Corporation Tax Acts of 2009 and 2010. The highest rate of income tax peaked in the Second World War at 99.25%. This was slightly reduced after the war and was around 97.5 per cent (nineteen shillings and sixpence in the pound) through the 1950s and 1960s.[9]

In 1971, the top rate of income tax on earned income was cut to 75%. A surcharge of 15% on investment income kept the overall top rate on that income at 90%. In 1974 the top tax rate on earned income was again raised, to 83%. With the investment income surcharge this raised the overall top rate on investment income to 98%, the highest permanent rate since the war. This applied to incomes over £20,000 (equivalent to £263,269 in 2023 terms).[3] In 1974, as many as 750,000 people were liable to pay the top rate of income tax.[10]
Margaret Thatcher, who favoured indirect taxation, reduced personal income tax rates during the 1980s.[11] In the first budget after her election victory in 1979, the top rate was reduced from 83% to 60% and the basic rate from 33% to 30%.[12] The basic rate was further cut in three subsequent budgets, to 29% in 1986 budget, 27% in 1987 and 25% in 1988.[13] The top rate of income tax was cut to 40% in the 1988 budget. The investment income surcharge was abolished in 1985.
Subsequent governments reduced the basic rate further, to the present level of 20% in 2007. Since 1976 (when it stood at 35%), the basic rate has been reduced by 15%, but this reduction has been largely offset by increases in national insurance contributions and value added tax.
In 2010 a new top rate of 50% was introduced on income over £150,000. The then opposition Conservative party claimed that this policy actually caused a decrease in revenue to the Exchequer, by incentivizing tax-avoidance or emigration/offshoring.[14] In the 2012 budget this rate was cut to 45% for 2013–14; this was followed by an increase in the tax paid by additional rate taxpayers from £38 billion to £46 billion. Chancellor George Osborne said that the lower, more competitive tax rate had caused the increase.[15] Both the initial claim that the raised 50% rate in 2010 caused a decreased effective tax take, and that its lowering in 2012 an increase, have been contested by the OBR[16] which described complications from "forestalling" and "income-shifting" (as both rate changes were pre-announced, high earners were first able to bring forward earnings to before the rate increase came into effect, under the outgoing Labour government, and then again to delay them to occur after the rate decrease under the new Lib-Con Coalition Government). In contrast to the chancellor's public statements, the government's own policy documents showed that the rate cut would be a net cost to the treasury of around 100 million per year[17][18] (a small cost proportionally, but a cost nonetheless).
In September 2022 the new Chancellor, Kwazi Kwarteng, announced that from April 2023 the top rate of tax would be further reduced from 45% to 40% and the basic rate reduced from 20% to 19%,[19] as part of what was referred to as a "Growth Plan".[20] After the collapse of the Truss government, the abolition of the 45% additional rate of tax was cancelled.[21]
HM Revenue and Customs[22] has published online a comprehensive set of manuals about the UK tax system.[23]
- ^ "A brief history of income tax".
- ^ Commissioners for Revenue and Customs Act 2005
- ^ Land Tax Act 1834
- ^ managed by Board of Customs and Excise
- ^ Managed by Board of Inland Revenue
- ^ Stamp Act 1694 (5 & 6 Will. & Mar. c. 21)
- ^ Inland Revenue Board Act 1849
- ^ replacing Purchase Tax, managed by Board of Customs and Excise
- ^ "A brief history of HM Customs and Excise".
Overview
[edit]Income tax forms the single largest source of revenues collected by the government. The second largest source of government revenue is National Insurance Contributions. The third largest source of government revenues is value added tax (VAT), and the fourth-largest is corporation tax.
Residence and domicile
[edit]
United Kingdom source income is generally subject to UK taxation whatever the citizenship and place of residence of an individual, or the place of registration of a company. This means that the UK income tax liability of an individual who is neither resident nor ordinarily resident in the United Kingdom is limited to any tax deducted at source on UK income, together with tax on income from a trade or profession carried on through a permanent establishment in the UK and tax on rental income from UK real estate.
People who are both resident and domiciled in the United Kingdom are additionally liable to taxation on their worldwide income and gains. For people resident but not domiciled in the United Kingdom (referred to as "non-domiciled", or "non-dom"), foreign income and gains have historically been taxed on the remittance basis, that is to say, only income and gains remitted to the United Kingdom are taxed (for such people the United Kingdom is sometimes called a tax haven). From 6 April 2008, a long-term non-dom (defined as resident in 7 of the previous 9 years) wishing to retain the remittance basis is required to pay an annual tax of £30,000.[24] Since 6 April 2017, non-domiciled individuals who have been resident in the UK for 15 out of the last 20 tax years lose their non-domiciled status[25] and become liable for tax on worldwide income and capital gains, and their worldwide assets become subject to inheritance tax on death.[26][27]
UK-domiciled individuals who are not resident for three consecutive tax years are not liable for UK tax on their worldwide income, and those who are not resident for five consecutive tax years are not liable for UK tax on their worldwide capital gains. Anyone physically present in the UK for 183 or more days in a tax year is classed as resident for that year.
Domicile is a term with a technical meaning. Essentially an individual is domiciled in the United Kingdom if the UK is deemed to be their permanent home. A British citizen may be accepted by the tax authorities as non-domiciled in the UK, but being born in another country, or in Britain to a non-domiciled father, facilitates non-dom status.
A company is resident in the United Kingdom if it is incorporated there or if its central management and control are there (although in the former case a company could be resident in another jurisdiction in certain circumstances where a tax treaty applies).
Double taxation of income and capital gains may be avoided by an applicable double tax treaty; the United Kingdom has one of the largest networks of treaties of any country.[28][29]
Non-domiciled status
[edit]UK residents whose permanent home is outside the UK may be entitled to non-domiciled status. A non-domiciled UK resident earning less than £2,000 in a year outside the UK does not pay tax on this unless it is transferred to the UK. This would apply to the typical person taking up a temporary job in the UK, being paid, and paying tax on it, in the UK, with possible additional small earnings in the home country. For a person with larger foreign income the rules are rather complex, but, for example, earnings may not be taxed at all in the UK if not brought into the UK, subject to the person paying an annual charge of £30,000. Details are explained on the UK government website,[30] and there is a simpler explanation in the context of a particular non-domiciled person on the BBC website.[31]
The majority of people making use of the non-domiciled tax exemption are wealthy individuals with substantial income from outside of the United Kingdom. Typical non-domiciled UK residents include senior company executives, bankers, lawyers, business owners and international recording artists; see list of people with non-domiciled status in the UK.
The tax year
[edit]The tax year is sometimes also called the "fiscal year". A company's accounting year, which has some relevance for corporation tax purposes, can be chosen by the company and often runs from 1 April to 31 March, in line with the fiscal year.
The British personal tax year runs from 6 to 5 April in the following year.[32]
Personal taxes
[edit]Income tax
[edit]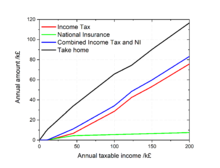
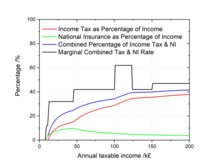
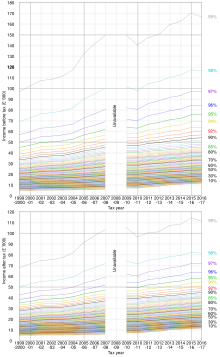
Income tax is the single largest source of government revenue in the United Kingdom, making up about 30 per cent of the total, followed by National Insurance contributions at around 20 per cent.[33] More than 25% of all income tax revenue is paid by the top 1% of taxpayers, i.e. taxpayers with the highest incomes, and 90% of all income tax revenue is paid by the top 50% of taxpayers with the highest incomes.[34] The Scottish Parliament has full control over income tax rates and thresholds on all non-savings and non-dividend income liable for tax by taxpayers resident in Scotland.[35] The Welsh Parliament also has some powers over income tax in Wales,[36] but they have not been used.[37]
Each person has an income tax personal allowance, and income up to this amount in each tax year is free of tax. Until the 2027/28 tax year, the tax-free allowance for under-65s with income less than £100,000 is £12,570.[38]
Any income above the personal allowance is taxed using a number of bands:
Taxpayer's income is assessed for tax according to a prescribed order, with income from employment using up the personal allowance and being taxed first, followed by savings income (from interest or otherwise unearned) and then dividends.
Foreign income of United Kingdom residents is taxed as United Kingdom income, but to prevent double taxation the United Kingdom has agreements with many countries to allow offset against United Kingdom tax what is deemed paid abroad. These deemed amounts paid abroad are not necessarily as much as actually paid.[39]
Rental income on a property investment business (such as a buy to let property) is taxed as other savings income, after allowing deductions including mortgage interest. The mortgage does not need to be secured against the property receiving the rent, subject to a maximum of the purchase prices of the property investment business properties (or the market value at the time they transferred into the business). Joint owners can decide how they divide income and expenses,[40][needs update] as long as one does not make a profit and the other a loss. Losses can be brought forward to subsequent years.
England, Wales and Northern Ireland
[edit]Current rates
[edit]| Rate | Dividend income | Savings income | Other income (inc. employment) | Tax bracket (of income above tax-free allowance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal allowance | 0% for £0–£500 (from 6 April 2024)[42] then 8.75% | 0% | 0% | £0–£12,570 |
| Basic rate | 8.75% | 20% | 20% | £12,571–£50,270 |
| Higher rate | 33.75% | 40% | 40% | £50,271–£125,140 |
| Additional rate | 39.35% | 45% | 45% | £125,141 and over |
This table reflects the removal of the 10% starting rate from April 2008, which also saw the 22% income tax rate drop to 20%. From April 2010, the Labour government introduced a 50% income tax rate for those earning more than £150,000. Income threshold for high taxation rate on income was decreased to £32,011 in 2013.[43] The coalition government raised this allowance in years following 2014, and the 50% tax bracket was reduced to its current 45% rate.[43]
Scotland
[edit]Since 2017 the Scottish Parliament has had the power to set the tax band thresholds (excluding the personal allowance) as well as the rates on all non-savings and non-dividend income of Scottish taxpayers.
| Rate | Income tax rate | Gross income |
|---|---|---|
| Starter rate | 19% | £12,571† – £14,732 |
| Basic rate | 20% | £14,733 – £25,688 |
| Intermediate rate | 21% | £25,689 – £43,662 |
| Higher rate | 42% | £43,663 – £125,140 †† |
| Top rate | 47% | Above £125,140 †† |
†Assumes individuals are in receipt of the Standard UK Personal Allowance.
††Those earning more than £100,000 will see their Personal Allowance reduced by £1 for every £2 earned over £100,000.
Exemptions on investment
[edit]
Certain investments carry a tax favoured status, including:
- UK Government Bonds (gilts)
- While all income is taxable, gains are exempt for income tax purposes.
- National Savings and Investments
- Certain investments via the state owned National Savings scheme are not subject to tax including Index linked Certificates (up to £15,000 per issue) and Premium Bonds, a scheme that issues monthly prizes in place of interest on individual holdings up to £50,000.
- Individual Savings Accounts (ISAs)
- Interest is paid tax free, while dividends are paid along with a tax credit to the investor which can then be offset against dividend tax due. For a basic rate tax payer this means they have no tax to pay on a dividend. There is no overall limit on how much a person can have invested in ISA accounts, but additional investments are currently limited to £20,000 per person per year, either in cash funds, mutual funds (Units Trusts and OEICs), or individual self-selected shares.[45]
- Pension funds
- These have the same tax treatment as ISAs in terms of growth. Full tax relief is also given at the individual's marginal rate on contributions or, in the case of an employer contributions, it is treated as an expense and is not taxed on the employee as a benefit in kind. Aside from a tax free lump sum of 25% of the fund, benefits taken from pension funds are taxable.
- Venture Capital Trusts
- These are investments in smaller companies or funds of holdings in such companies over a minimum term of five years. These are not taxable and qualify for 30 per cent tax relief against an individual's income.
- Enterprise Investment Schemes
- A non-taxable investment into smaller company shares over three years that qualifies for 30 per cent tax relief. The facility also allows an individual to defer capital gains liabilities (these gains can be stripped out in future years using the annual CGT allowance).
- Seed Enterprise Investment Schemes
- A non-taxable investment into smaller company shares over three years that qualifies for 50 per cent tax relief. The facility also allows an individual to defer capital gains liabilities (these gains can be stripped out in future years using the annual CGT allowance).
- These include offshore and onshore investment bonds issued by insurance companies. The main difference between the two is that corporation tax paid by the onshore bond means that gains in the onshore bond are treated as if basic rate tax has been paid (this cannot be reclaimed by zero or starting rate tax payers). With both versions up to 5 per cent for each complete year of investment can be taken without an immediate tax liability (subject to a maximum total of 100 per cent of the original investment). On this basis, investors can plan an income stream while deferring any chargeable withdrawals until they are on a lower rate of tax, are no longer a United Kingdom resident, or their death.
- Offshore trusts and companies
- Trusts can be offshore if all trustees are non-resident. Such trusts can own foreign-operated companies. Corporation tax rates can be lower in some countries and where we still have double taxation treaties. However, since anti-avoidance rules have been introduced for taxation of trusts, these structures are not advantageous for someone who will remain resident.
Exceptions
[edit]Many holdings and income from them are exempt for "historical reasons". These include:
- Special, low tax arrangements for the monarchy, such as the arrangement used by the British Royal Family to avoid inheritance tax.[citation needed]
- Reduced income tax for special classes of person. For instance non-doms, who are resident in the United Kingdom but not "domiciled", are not subject to UK income tax on their non-UK income provided the remittance basis of taxation is claimed (or applies automatically) and the non-UK income is not remitted to the UK. After seven years of tax residence, the remittance basis can carry a substantial tax charge and UK residents will usually be deemed to be domiciled of the UK after fifteen years of residence without a gap of five years.[46]
- An Act of Parliament to protect the Earl of Abingdon and his heirs and assignees from paying income tax on the tolls on the Swinford Toll Bridge.
- The income of charities is usually exempt from United Kingdom income tax.
Inheritance tax
[edit]Inheritance tax is levied on "transfers of value", meaning:
- the estates of deceased persons;
- gifts made within seven years of death (known as Potentially Exempt Transfers or "PETs");
- "lifetime chargeable transfers", meaning transfers into certain types of trust. See Taxation of trusts (United Kingdom).
The first slice of cumulative transfers of value (known as the "nil rate band") is free of tax. This threshold is currently set at £325,000 (tax year 2012/13)[47] and has recently[when?] failed to keep up with house price inflation[neutrality is disputed] with the result that some 6 million households currently fall within the scope of inheritance tax. Over this threshold the rate is 40 per cent on death or 36 per cent if the estate qualifies for a reduced rate as a result of a charitable donation.[47][48]
Since October 2007, married couples and registered civil partners can effectively increase the threshold on their estate when the second partner dies – to as much as £650,000 in 2012–13. Their executors or personal representatives must transfer the first spouse or civil partner's unused Inheritance Tax threshold or 'nil rate band' to the second spouse or civil partner when they die.[47]
Transfers of value between United Kingdom-domiciled spouses are exempt from tax. Recent changes to the tax brought in by the Finance Act 2008 mean that nil-rate bands are transferable between spouses to reduce this burden – something which previously could only be done by setting up complex trusts.[citation needed]
Gifts made more than seven years prior to death are not taxed; if they are made between three and seven years before death a tapered inheritance tax rate applies. There are some important exceptions to this treatment: the most important is the "reservation of benefit rule", which says that a gift is ineffective for inheritance tax purposes if the giver benefits from the asset in any way after the gift (for example, by gifting a house but continuing to live in it).
Inheritance Tax is not levied on the estate of persons who died "on active service" or from the effects of wounds sustained on such service...regardless of how long after that may be if it can be proven as the cause of death. In addition as the deceased spouse is subject to an exemption that full nil rate band is transferable to the surviving spouse's estate on the survivor's death.[49]
Council Tax
[edit]Council tax is the system of local taxation used in England,[50] Scotland[51] and Wales[52] to part fund the services provided by local government in each country. It was introduced in 1993 by the Local Government Finance Act 1992, as a successor to the unpopular Community Charge ("poll tax"), which had (briefly) replaced the Rates system. The basis for the tax is residential property, with discounts for single people. As of 2008, the average annual levy on a property in England was £1,146.[53] In 2006–2007 council tax in England amounted to £22.4 billion[54] and an additional £10.8 billion in sales, fees and charges.[55][needs update]. In Scotland from April 2024, all but three of the Scottish local councils introduced a 100% "additional levy" on second homes. Unfortunately this change was introduced very close to the beginning of the 2024-25 Council Tax year beginning, and it is unclear what procedures Councils have in place for identifying second homes. Many second home owners have been left in a state of confusion regarding how this change will be implemented upon them.
In October 2024, Local authorities in England had warned of a potential £54 billion funding shortfall due to rising costs in social care and school transport, according to a report from the County Councils Network (CCN). Over the next five years, councils faced significant financial challenges, with 83% of anticipated service cost increases attributed to adult social care, children's services, and home-to-school transport.[56]
Sales taxes and duties
[edit]Value added tax
[edit]The third largest source of government revenues is value added tax (VAT), charged at 20 per cent on supplies of goods and services. It is therefore a tax on consumer expenditure.
Certain goods and services are exempt from VAT, and others are subject to VAT at a lower rate of 5 per cent (the reduced rate, such as domestic gas supplies) or 0 per cent ("zero-rated", such as most food and children's clothing).[57] Exemptions are intended to relieve the tax burden on essentials while placing the full tax on luxuries, but disputes based on fine distinctions arise, such as the "Jaffa Cake Case" which hinged on whether Jaffa Cakes were classed as (zero-rated) cakes—as was eventually decided—or (fully taxed) chocolate-covered biscuits.[citation needed] Until 2001, VAT was charged at the full rate on sanitary towels.[58]
VAT was introduced in 1973, in consequence of Britain's entry to the European Economic Community, at a standard rate of 10 per cent. In July 1974, the standard rate became 8 per cent and from October that year petrol was taxed at a new higher rate of 25 per cent. In the budget of April 1975 the higher rate was extended to a wide range of "luxury" goods. In the budget of April 1976 the 25 per cent higher rate was reduced to 12.5 per cent. On 18 June 1979, the higher rate was scrapped and VAT set at a single rate of 15 per cent. In 1991 this became 17.5 per cent, though when domestic fuel and power was added to the scheme in 1994, it was charged at a new, lower rate of 8 per cent.[59]
In September 1997 this lower rate of 8 per cent was reduced to 5 per cent and was extended to cover various energy-saving materials (from 1 July 1998), sanitary protection (from 1 January 2001), children's car seats (from 1 April 2001), conversion and renovation of certain residential properties (from 12 May 2001), contraceptives (from 1 July 2006) and smoking cessation products (from 1 July 2007).[citation needed]
On 1 December 2008, VAT was reduced to 15 per cent, as a reaction to the late-2000s recession, by Chancellor Alistair Darling.[citation needed]
On 1 January 2010, VAT returned to 17.5 per cent.[citation needed]
On 4 January 2011, VAT was raised to 20 per cent by Chancellor George Osborne, where it remains.
Excise duties
[edit]Excise duties are charged on, amongst other things, motor fuel, alcohol, tobacco, betting and vehicles.
Stamp duty
[edit]Stamp duty is charged on the transfer of shares and certain securities at a rate of 0.5 per cent. Modernised versions of stamp duty, stamp duty land tax and stamp duty reserve tax, are charged respectively on the transfer of real property and shares and securities, at rates of up to 4 per cent and 0.5 per cent respectively.[60]
Motoring taxation
[edit]Motoring taxes include: fuel duty (which itself also attracts VAT), and Vehicle Excise Duty. Other fees and charges include the London congestion charge, various statutory fees including that for the compulsory vehicle test and that for vehicle registration, and in some areas on-street parking (as well as associated charges for violations).
Business taxes
[edit]Corporate Tax
[edit]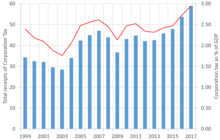
Corporation tax is a tax levied in the United Kingdom on the profits made by companies and on the profits of permanent establishments of non-UK resident companies and associations that trade in the EU.
Corporation tax forms the fourth-largest source of government revenue (after income, NIC, and VAT). Prior to the tax's enactment on 1 April 1965, companies and individuals paid the same income tax, with an additional profits tax levied on companies. The Finance Act 1965[64] replaced this structure for companies and associations with a single corporate tax, which borrowed its basic structure and rules from the income tax system. Since 1997, the United Kingdom's Tax Law Rewrite Project[65] has been modernising the United Kingdom's tax legislation, starting with income tax, while the legislation imposing corporation tax has itself been amended; the rules governing income tax and corporation tax have thus diverged.
Business rates
[edit]Business rates is the commonly used name of non-domestic rates, a rate or tax charged to occupiers of non-domestic property. Business rates form part of the funding for local government, and are collected by them, but rather than receipts being retained directly they are pooled centrally and then redistributed. In 2005–06, £19.9 billion was collected in business rates, representing 4.35 per cent of the total United Kingdom tax income.[66]
Business rates are a property tax, where each non-domestic property is assessed with a rateable value, expressed in pounds. The rateable value broadly represents the annual rent the property could have been let for on a particular valuation date according to a set of assumptions. The actual bill payable is then calculated using a multiplier set by central government, and applying any reliefs.[67]
Plastic packaging tax
[edit]Plastic Packaging Tax was introduced on 1 April 2022.[68]
Business and personal taxes
[edit]Some taxes are, depending on the circumstances, paid by both individuals and companies, and government
National Insurance contributions
[edit]The second largest source of government revenue is National Insurance contributions (NICs). NICs are payable by employees, employers and the self-employed and in the 2010–2011 tax year £96.5 billion was raised, 21.5 per cent of the total collected by HMRC.[69]
Employees and employers pay contributions according to a complex classification based on employment type and income. Class 1 (employed persons) NIC is charged at several rates depending on various income thresholds and a number of other factors including age, the type of occupational pension scheme contributed to by the employee and/or employer and whether or not the employee is an ocean-going mariner. Certain married women who opted to pay reduced contributions (in return for reduced benefits) prior to 1977 retain this right for historical reasons.
Employers also pay contributions on many benefits in kind provided to employees (such as company cars) and on tax liabilities met on behalf of employees via a "PAYE Settlement Agreement".
There are separate arrangements for self-employed persons, who are normally liable to Class 2 flat rate NIC and Class 4 earnings-related NIC, and for some voluntary sector workers.
Health and social care levy
[edit]On 7 September 2021, Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced that a new tax would be introduced from April 2023 in order to fund the National Health Service backlogs arising as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and the reform of social care in England.[70] The tax would have a similar application to NICs and will be charged to both employees and employers at a rate of 1.25% on an individual's earnings. However, it would also be payable beyond State Pension Age, which is not the case for NICs. From April 2022 to March 2023, the 1.25% increase would temporarily apply to NICs. The aim was to give HMRC time to make the changes required in order for the levy to be introduced. The Truss ministry reversed the implementation of this tax and reverted the NICs as of 6 November 2022.
Capital gains tax
[edit]Capital gains are subject to tax at 10 or 20 per cent (18 or 28 for capital gains relating to residential property)(for individuals) or at the applicable marginal rate of corporation tax (for companies).
The basic principle is the same for individuals and companies - the tax applies only on the disposal of a capital asset, and the amount of the gain is calculated as the difference between the disposal proceeds and the "base cost", being the original purchase price plus allowable related expenditure. However, from 6 April 2008, the rate and reliefs applicable to the chargeable gain differ between individuals and companies. Companies apply "indexation relief" to the base cost, increasing it in accordance with the Retail Prices Index so that (broadly speaking) the gain is calculated on a post-inflation basis (with different rules apply for gains accrued prior to March 1982). The gain is then subject to tax at the applicable marginal rate of corporation tax.
Individuals are taxed at a flat rate of 18 per cent (or since 22 June 2010, 28 per cent for higher rate taxpayers) with no indexation relief. However, if claiming Entrepreneurs' Relief the rate remains 10 per cent. Capital losses from prior years can be brought forward.
Expenditure on a business (such as a property business) made by an individual can be claimed as an allowance against Capital Gains. Whether expenditure is claimable against income (potentially reducing income tax) or capital (potentially reducing capital gains tax) depends on whether there was improvement of the property: if there was none, it is against income; if there was some, then it is against capital.
Transfers between husband and wife or between civil partners do not crystallise a capital gain, but instead transfer the purchase price (book cost). Otherwise, transfers made as gifts are treated for CGT purposes as being made at the market value at the date of transfer.
Tax gap
[edit]The 'tax gap' is the difference between the amount of tax that should, in theory, be collected by HMRC, against what is actually collected. The tax gap for the UK in 2013–14 was £34 billion, or 6.4 per cent of total tax liabilities.[71] It can be broken down by tax type
| Tax | Amount |
|---|---|
| Income Tax, National Insurance and Capital Gains Tax | £14.0 billion |
| VAT | £13.1 billion |
| Corporation Tax | £3.0 billion |
| Excise duties | £2.7 billion |
and behaviour
| Behaviour | Amount |
|---|---|
| Hidden economy | £6.2 billion |
| Criminal attacks | £5.1 billion |
| Legal interpretation | £4.9 billion |
| Evasion | £4.4 billion |
| Failure to take reasonable care | £3.9 billion |
| Avoidance | £2.6 billion |
| Total loss | £27.1 billion |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ "A brief guide to the public finances". Office for Budget Responsibility. Retrieved 25 October 2024.
- ^ Stephen Dowell, History of Taxation and Taxes in England (Routledge, 2013)
- ^ a b c UK Retail Price Index inflation figures are based on data from Clark, Gregory (2017). "The Annual RPI and Average Earnings for Britain, 1209 to Present (New Series)". MeasuringWorth. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ "A tax to beat Napoleon". HM Revenue & Customs. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- ^ Allen Horstman, "'Taxation in the Zenith': Taxes and Classes in the United Kingdom, 1816–1842", Journal of European Economic History (2003) 32#1 pp. 111–137.
- ^ Stephen Dowell, History of Taxation and Taxes in England (Routledge, 2013)
- ^ A.J.P. Taylor, English History 1914-1945 (1965) pp 40 – 41.
- ^ M. J. Daunton, "How to Pay for the War: State, Society and Taxation in Britain, 1917–24," English Historical Review (1996) 111# 443 pp. 882–919
- ^ Rates of Surtax 1948 to 1973
- ^ "IFS: Long-Term trends in British Taxation and Spending" (PDF).
- ^ "Thatcher Economics". National Review.
- ^ "Economy: 1979 Budget (Howe 1) - Margaret Thatcher Foundation". www.margaretthatcher.org.
- ^ "Economy: 1988 Budget (Lawson 5) - Margaret Thatcher Foundation". www.margaretthatcher.org.
- ^ Winnett, Robert (12 December 2012). "Two-thirds of millionaires disappeared from official statistics to avoid 50p tax rate". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Cut to top rate of tax helped raise an extra £8bn, Osborne claims". Archived from the original on 2 March 2016.
- ^ "Effect of the additional rate of income tax on receipts". Office for Budget Responsibility. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ "UK Government Web Archive" (PDF). webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ "Did cutting the 50p rate of tax raise £8 billion?". Full Fact. 4 March 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ "Income tax to be cut by 1p from April". BBC News. 23 September 2022.
- ^ "The Growth Plan". UK Government (Standard). 23 September 2022. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
- ^ "REV BN 40: Tax Treatment of Pre-Owned Assets".
- ^ HM Revenue & Customs.
- ^ HMRC Manuals.
- ^ "Tax on foreign income". GOV.UK.
- ^ "Deemed Domicile Rules". HM Revenue & Customs. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ^ "The Difference Between Domicile and Residence". Tax Residence Guide. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ^ "Planning for deemed domicile after 15 years". Tax Journal. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ^ "Double tax treaties". Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales. Archived from the original on 21 April 2012. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- ^ See IR20 - Residents and non-residents.
- ^ "Tax on foreign income". UK Government. n.d. Retrieved 9 April 2022.
- ^ "Chancellor Rishi Sunak defends wife Akshata Murty in row over non-dom status". BBC News. 8 April 2022.
- ^ "Your National Insurance record and new State Pension". nidirect (National Insurance). n.d. Retrieved 9 April 2022.
- ^ HMRC NI calculator
- ^ "Reality Check: Are lower earners bearing the tax burden?". BBC News. 19 April 2017. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ^ "Income tax powers officially devolved to Holyrood". BBC. 30 October 2016.
- ^ "Tax is changing in Wales". GOV.UK. 5 April 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ "Income Tax in Wales". GOV.UK. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ "At-a-glance summary". HM Government. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "Tax treaties". HM Revenue & Customs. 14 June 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "HM Revenue & Customs: Tax Bulletin Issue 2". www.hmrc.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 14 February 2006.
- ^ "Budget 2021: Key points at-a-glance". BBC News. 3 March 2021. Retrieved 3 March 2021.
- ^ "Tax on dividends". GOV.UK. Government Digital Service. Archived from the original on 1 October 2024. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
- ^ a b "Rates and allowances for Income Tax". HM Revenue & Customs. 6 April 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "Income Tax rates and Personal Allowances". mygov.scot.
- ^ "What is an ISA?". Money Supermarket. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Wintour, Patrick (1 December 2009). "David Cameron tells Zac Goldsmith to end 'non-dom' tax status". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- ^ a b c "Inheritance Tax - GOV.UK". www.hmrc.gov.uk.
- ^ "Inheritance Tax - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ "Inheritance Tax: exemption for emergency service personnel and humanitarian aid workers - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk.
- ^ Communities and Local Government - Council Tax: The Facts Archived 6 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Council Tax in Scotland Scottish Government publications
- ^ Council Tax a guide Valuation Office Agency
- ^ Average council tax and % change 1999–00 to 2008–09 Archived 4 December 2009 at the Wayback Machine Communities and local government - figures released 27 March 2008
- ^ Office of the Deputy Prime Minister, Statistical Release: Levels of council tax set by local authorities in England 2006–07, 2006 cited by.
- ^ Communities and Local Government in Local Government Finance Statistics: Revenue Outturn Service Expenditure Summary 2006–07. cited by
- ^ Culbertson, Alix (3 October 2024). "Rising cost of social care and school transport to cause £54bn blackhole for councils". Sky News. Archived from the original on 3 October 2024. Retrieved 3 October 2024.
- ^ "Introduction to VAT". HM Revenue & Customs. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
- ^ "VAT Notice 701/18: women's sanitary protection products - GOV.UK". customs.hmrc.gov.uk. 4 January 2021.
- ^ Peter Victor (30 July 1995). "A brief history of VAT". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 26 May 2022. Retrieved 13 January 2011.
- ^ "Stamp Duty Land Tax Rates From 23/03/06 including archived Budget and Finance Bill information". HM Revenue & Customs. 23 March 2006. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- ^ "HMRC Corporation Tax Statistics 2017" (PDF). p. 19.
Includes Bank Levy, Bank Surcharge and Diverted Profits Tax
- ^ "National Statistics dataset – HM Revenue and Customs receipts" (PDF).
- ^ "Gross Domestic Product at market prices: Current price: Seasonally adjusted £m".
- ^ "Finance Act 1965 (c. 25), from UK Statute Law Database". UK Statutory Publications Office, Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ Tax Law Rewrite, HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC), retrieved 17 April 2007
- ^ Public Finances Databank (see section C4), HM Treasury, retrieved 26 March 2007. Percentage based on Net taxes & NICs conts.
- ^ The rates bill - How is it calculated? Archived 10 May 2007 at the Wayback Machine, mybusinessrates.gov.uk
- ^ HMRC, Plastic Packaging Tax, updated 20 April 2023, accessed 12 December 2023
- ^ "HM Revenue and Customs receipts" (PDF). hmrc.gov.uk. Retrieved 11 November 2011.
- ^ "Boris Johnson unveils £12bn-a-year tax rise to pay for NHS and social care". TheGuardian.com. 7 September 2021.
- ^ "Measuring tax gaps 2015 edition" (PDF).
Sources
[edit]- Stephen Dowell, History of Taxation and Taxes in England (Routledge, 2013)


