Tabula Affinitatum
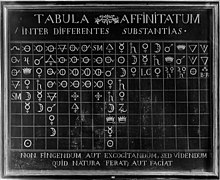
The Tabula Affinitatum is a table of chemical affinities between substances.[1]
Commissioned around 1766 by the pharmacist Hubert Franz Hoefer for the apothecary's shop of the Grand Duke of Florence, this large table of chemical substances was designed to guide the preparer of pharmaceutical remedies in identifying the compounds most likely to combine with one another. The table is modeled on Étienne-François Geoffroy's Table des différents Rapports observés entre différentes substances (Paris, 1718), from which it differs by adding a seventeenth column. The substances are identified by traditional alchemical symbols and the symbolic language in use in the seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries. The Florentine table does not, however, include the symbol of air. This means that it was compiled in a period when there was not yet a full awareness of the function of air as a chemically active substance, hence capable of combining with solids and liquids. A similar table is found among the plates of Diderot and d'Alembert's Grande Encyclopédie.
The oil painting is 1540 × 1300 mm and is displayed in the Museo Galileo, Florence.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Tabula affinitatum". Europeana collections. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- ^ "Museo Galileo - Tabula affinitatum". catalogue.museogalileo.it. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
Bibliography
[edit]Mara Miniati, ed. (1991). Museo di storia della scienza: catalogo. Giunti. p. 350, board n. 34. ISBN 88-09-20036-5.
Piccardi Giovanni (2004). Uberto Francesco Hoefer e la Tabula affinitatum. Nuncius. pp. 545–568.
Abbri Ferdinando (1979). La Tabula affinitatum dell'Istituto e Museo di storia della scienza di Firenze. Annali dell'Istituto e Museo di storia della scienza di Firenze. pp. 25–36.
