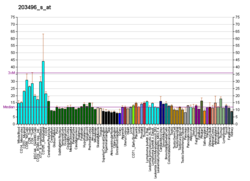
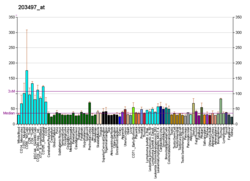
MED1
Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 also known as DRIP205 or Trap220 is a subunit of the Mediator complex and is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MED1 gene.[5][6][7] MED1 functions as a nuclear receptor coactivator.
| Med1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Med1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF10744 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR019680 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Function
[edit]The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with co-activators to direct transcriptional initiation by the RNA polymerase II apparatus. The mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 protein is a subunit of the CRSP (cofactor required for SP1 activation) complex, which, along with TFIID, is required for efficient activation by SP1. This protein is also a component of other multisubunit complexes [e.g., thyroid hormone receptor-(TR-) associated proteins that interact with TR and facilitate TR function on DNA templates in conjunction with initiation factors and cofactors]. It also regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and it is essential for adipogenesis. This protein is known to have the ability to self-oligomerize.[7]
Interactions
[edit]MED1 has been shown to interact with:
Protein family
[edit]This entry represents subunit Med1 of the Mediator complex. The Med1 forms part of the Med9 submodule of the Srb/Med complex. It is one of three subunits essential for viability of the whole organism via its role in environmentally-directed cell-fate decisions.[21]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000125686 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000018160 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zhu Y, Qi C, Jain S, Rao MS, Reddy JK (November 1997). "Isolation and characterization of PBP, a protein that interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor". J Biol Chem. 272 (41): 25500–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.41.25500. PMID 9325263.
- ^ Zhu Y, Qi C, Jain S, Le Beau MM, Espinosa R, Atkins GB, Lazar MA, Yeldandi AV, Rao MS, Reddy JK (October 1999). "Amplification and overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor binding protein (PBP/PPARBP) gene in breast cancer". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 96 (19): 10848–53. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610848Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.19.10848. PMC 17971. PMID 10485914.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: PPARBP PPAR binding protein".
- ^ Wang Q, Sharma D, Ren Y, Fondell JD (November 2002). "A coregulatory role for the TRAP-mediator complex in androgen receptor-mediated gene expression". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (45): 42852–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206061200. PMID 12218053.
- ^ a b Ito M, Yuan CX, Malik S, Gu W, Fondell JD, Yamamura S, Fu ZY, Zhang X, Qin J, Roeder RG (March 1999). "Identity between TRAP and SMCC complexes indicates novel pathways for the function of nuclear receptors and diverse mammalian activators". Mol. Cell. 3 (3): 361–70. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80463-3. PMID 10198638.
- ^ a b Kitagawa H, Fujiki R, Yoshimura K, Mezaki Y, Uematsu Y, Matsui D, Ogawa S, Unno K, Okubo M, Tokita A, Nakagawa T, Ito T, Ishimi Y, Nagasawa H, Matsumoto T, Yanagisawa J, Kato S (June 2003). "The chromatin-remodeling complex WINAC targets a nuclear receptor to promoters and is impaired in Williams syndrome". Cell. 113 (7): 905–17. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00436-7. PMID 12837248.
- ^ a b Kang YK, Guermah M, Yuan CX, Roeder RG (March 2002). "The TRAP/Mediator coactivator complex interacts directly with estrogen receptors alpha and beta through the TRAP220 subunit and directly enhances estrogen receptor function in vitro". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (5): 2642–7. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.2642K. doi:10.1073/pnas.261715899. PMC 122401. PMID 11867769.
- ^ Zilliacus J, Holter E, Wakui H, Tazawa H, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA (April 2001). "Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by 14—3-3-dependent intracellular relocalization of the corepressor RIP140". Mol. Endocrinol. 15 (4): 501–11. doi:10.1210/mend.15.4.0624. PMID 11266503.
- ^ Hittelman AB, Burakov D, Iñiguez-Lluhí JA, Freedman LP, Garabedian MJ (October 1999). "Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activation via AF-1-associated proteins". EMBO J. 18 (19): 5380–8. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.19.5380. PMC 1171607. PMID 10508170.
- ^ Maeda Y, Rachez C, Hawel L, Byus CV, Freedman LP, Sladek FM (July 2002). "Polyamines modulate the interaction between nuclear receptors and vitamin D receptor-interacting protein 205". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (7): 1502–10. doi:10.1210/mend.16.7.0883. PMID 12089346.
- ^ Malik S, Wallberg AE, Kang YK, Roeder RG (August 2002). "TRAP/SMCC/mediator-dependent transcriptional activation from DNA and chromatin templates by orphan nuclear receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (15): 5626–37. doi:10.1128/mcb.22.15.5626-5637.2002. PMC 133960. PMID 12101254.
- ^ Frade R, Balbo M, Barel M (December 2000). "RB18A, whose gene is localized on chromosome 17q12-q21.1, regulates in vivo p53 transactivating activity". Cancer Res. 60 (23): 6585–9. PMID 11118038.
- ^ Drané P, Barel M, Balbo M, Frade R (December 1997). "Identification of RB18A, a 205 kDa new p53 regulatory protein which shares antigenic and functional properties with p53". Oncogene. 15 (25): 3013–24. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201492. PMID 9444950.
- ^ Wallberg AE, Yamamura S, Malik S, Spiegelman BM, Roeder RG (November 2003). "Coordination of p300-mediated chromatin remodeling and TRAP/mediator function through coactivator PGC-1alpha". Mol. Cell. 12 (5): 1137–49. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00391-5. PMID 14636573.
- ^ Misra P, Qi C, Yu S, Shah SH, Cao WQ, Rao MS, Thimmapaya B, Zhu Y, Reddy JK (May 2002). "Interaction of PIMT with transcriptional coactivators CBP, p300, and PBP differential role in transcriptional regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (22): 20011–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201739200. PMID 11912212.
- ^ Yuan CX, Ito M, Fondell JD, Fu ZY, Roeder RG (July 1998). "The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor- associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (14): 7939–44. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95.7939Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.14.7939. PMC 20908. PMID 9653119.
- ^ Boube M, Joulia L, Cribbs DL, Bourbon HM (July 2002). "Evidence for a mediator of RNA polymerase II transcriptional regulation conserved from yeast to man". Cell. 110 (2): 143–51. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00830-9. PMID 12150923. S2CID 771362.
Further reading
[edit]- Lee JW, Choi HS, Gyuris J, Brent R, Moore DD (1995). "Two classes of proteins dependent on either the presence or absence of thyroid hormone for interaction with the thyroid hormone receptor". Mol. Endocrinol. 9 (2): 243–54. doi:10.1210/mend.9.2.7776974. PMID 7776974.
- Fondell JD, Ge H, Roeder RG (1996). "Ligand induction of a transcriptionally active thyroid hormone receptor coactivator complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93 (16): 8329–33. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.8329F. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.16.8329. PMC 38670. PMID 8710870.
- Drané P, Barel M, Balbo M, Frade R (1998). "Identification of RB18A, a 205 kDa new p53 regulatory protein that shares antigenic and functional properties with p53". Oncogene. 15 (25): 3013–24. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201492. PMID 9444950.
- Yuan CX, Ito M, Fondell JD, Fu ZY, Roeder RG (1998). "The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor- associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (14): 7939–44. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95.7939Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.14.7939. PMC 20908. PMID 9653119.
- Ryu S, Zhou S, Ladurner AG, Tjian R (1999). "The transcriptional cofactor complex CRSP is required for activity of the enhancer-binding protein Sp1". Nature. 397 (6718): 446–50. Bibcode:1999Natur.397..446R. doi:10.1038/17141. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0019-A36A-8. PMID 9989412. S2CID 4405569.
- Gu W, Malik S, Ito M, Yuan CX, Fondell JD, Zhang X, Martinez E, Qin J, Roeder RG (1999). "A novel human SRB/MED-containing cofactor complex, SMCC, involved in transcription regulation". Mol. Cell. 3 (1): 97–108. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80178-1. PMID 10024883.
- Ito M, Yuan CX, Malik S, Gu W, Fondell JD, Yamamura S, Fu ZY, Zhang X, Qin J, Roeder RG (1999). "Identity between TRAP and SMCC complexes indicates novel pathways for the function of nuclear receptors and diverse mammalian activators". Mol. Cell. 3 (3): 361–70. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80463-3. PMID 10198638.
- Rachez C, Lemon BD, Suldan Z, Bromleigh V, Gamble M, Näär AM, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Freedman LP (1999). "Ligand-dependent transcription activation by nuclear receptors requires the DRIP complex". Nature. 398 (6730): 824–8. Bibcode:1999Natur.398..824R. doi:10.1038/19783. PMID 10235266. S2CID 204992765.
- Näär AM, Beaurang PA, Zhou S, Abraham S, Solomon W, Tjian R (1999). "Composite co-activator ARC mediates chromatin-directed transcriptional activation". Nature. 398 (6730): 828–32. Bibcode:1999Natur.398..828N. doi:10.1038/19789. PMID 10235267. S2CID 23646963.
- Atkins GB, Hu X, Guenther MG, Rachez C, Freedman LP, Lazar MA (1999). "Coactivators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha". Mol. Endocrinol. 13 (9): 1550–7. doi:10.1210/mend.13.9.0343. PMID 10478845.
- Rachez C, Gamble M, Chang CP, Atkins GB, Lazar MA, Freedman LP (2000). "The DRIP complex and SRC-1/p160 coactivators share similar nuclear receptor-binding determinants but constitute functionally distinct complexes". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (8): 2718–26. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.8.2718-2726.2000. PMC 85487. PMID 10733574.
- Frade R, Balbo M, Barel M (2001). "RB18A, whose gene is localized on chromosome 17q12-q21.1, regulates in vivo p53 transactivating activity". Cancer Res. 60 (23): 6585–9. PMID 11118038.
- Zilliacus J, Holter E, Wakui H, Tazawa H, Treuter E, Gustafsson JA (2001). "Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by 14--3-3-dependent intracellular relocalization of the corepressor RIP140". Mol. Endocrinol. 15 (4): 501–11. doi:10.1210/mend.15.4.0624. PMID 11266503.
- Crawford SE, Qi C, Misra P, Stellmach V, Rao MS, Engel JD, Zhu Y, Reddy JK (2002). "Defects of the heart, eye, and megakaryocytes in peroxisome proliferator activator receptor-binding protein (PBP) null embryos implicate GATA family of transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (5): 3585–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107995200. PMID 11724781.
- Frade R, Balbo M, Barel M (2002). "RB18A regulates p53-dependent apoptosis". Oncogene. 21 (6): 861–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205177. PMID 11840331.
- Kang YK, Guermah M, Yuan CX, Roeder RG (2002). "The TRAP/Mediator coactivator complex interacts directly with estrogen receptors alpha and beta through the TRAP220 subunit and directly enhances estrogen receptor function in vitro". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (5): 2642–7. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.2642K. doi:10.1073/pnas.261715899. PMC 122401. PMID 11867769.
- Misra P, Qi C, Yu S, Shah SH, Cao WQ, Rao MS, Thimmapaya B, Zhu Y, Reddy JK (2002). "Interaction of PIMT with transcriptional coactivators CBP, p300, and PBP differential role in transcriptional regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (22): 20011–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201739200. PMID 11912212.
- Ge K, Guermah M, Yuan CX, Ito M, Wallberg AE, Spiegelman BM, Roeder RG (2002). "Transcription coactivator TRAP220 is required for PPAR gamma 2-stimulated adipogenesis". Nature. 417 (6888): 563–7. Bibcode:2002Natur.417..563G. doi:10.1038/417563a. PMID 12037571. S2CID 4432077.