Ganglion cyst
| Ganglion cyst | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ganglia, synovial cyst,[1] Gideon's disease, Olamide's cyst, Bible cyst, Bible bump[2] |
 | |
| Cyst on dorsum of left hand close to the wrist | |
| Specialty | Plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery, hand surgery |
| Symptoms | Small soft bump associated with a joint or tendon sheath[3] |
| Complications | Only with operative treatment |
| Usual onset | Any age |
| Diagnostic method | Typically based on signs[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Lipoma, extensor tenosynovitis[4] |
| Treatment | Watchful waiting, splinting the affected joint, needle aspiration, surgery[3] |
| Prognosis | Not serious[3] |
| Frequency | ~3 per 10,000 per year (wrist and hand)[5] |
A ganglion cyst is a fluid-filled bump associated with a joint or tendon sheath.[3] It most often occurs at the back of the wrist, followed by the front of the wrist.[3][4]
The cause is unknown.[3] The underlying mechanism is believed to involve an outpouching of the synovial membrane.[4] Diagnosis is typically based on examination. The ability to shine through the bump or any past decrease in size supports the diagnosis of the bump as a ganglion cyst.[4] Ganglion cysts are usually obvious upon observation. Medical imaging may be considered on infrequent occasions to rule out another diagnosis.[3][4]
Treatment is not necessary. Options for treatment include needle aspiration or surgery.[3] About half the time, they resolve on their own.[4] About three per 10,000 people newly develop ganglion of the wrist or hand a year.[5]
Presentation
[edit]The average size of these cysts is 2 centimetres (0.79 in), but excised cysts of more than 5 centimetres (2.0 in) have been reported.[6] The size of the cyst may vary over time. Between 50 and 70% of all masses on the hand and wrist are ganglion cysts.[7][8]
Wrist
[edit]They commonly are found near the wrist joint, especially at the scapholunate area.[9]
Common wrist ganglions include:
- dorsal wrist ganglion[10][11]
- volar wrist ganglion[10][12]
- extensor retinaculum ganglion[10]
- occult ganglion[10][12]
- intraosseous ganglion[10]
- mucous cyst[10][12]
Foot
[edit]In a 2007 study of patients in Glasgow whose foot lumps were removed surgically, 39 of 101 cases were ganglion cysts. The study replicated earlier findings that no ganglion cysts were found on the sole or heel. The authors wrote, "Although lumps in these areas may be ganglia, the surgeon should probably consider other diagnoses in the first instance." The researchers noted a preponderance of occurrence among females (85%) and that 11 of the other cases had been misdiagnosed as ganglion cysts before surgery.[13]
Ganglion cysts are not limited to the hands and feet. They may occur near the knee, commonly near the cruciate ligaments, but they may occur at the origins of the gastrocnemius tendon, and anteriorly on Hoffa's infrapatellar fat pad.[14] At the shoulder, they typically occur at the acromioclavicular joint or along the biceps tendon.[15]
Other
[edit]From their common origin at a joint or tendon, ganglion cysts may form in a wide range of locations. Rarely, intraosseous ganglion cysts occur, sometimes in combination with a cyst in the overlying soft tissue.[6][16] Rare cases of intramuscular ganglion cysts in the gastrocnemius muscle of the calf have been reported.[17][18] It is possible for a cyst to be considerably displaced from the joint. In one extreme case, a ganglion cyst was observed to propagate extensively via the conduit of the common peroneal nerve sheath to a location in the thigh; in such cases surgery to the proximal joint to remove the articular connection may remove the need for a riskier, more extensive surgery in the neural tissue of the thigh.[19] The cysts may intrude into the spine, which may cause pain and dysesthesia in distant extremities.[20]
Cystic adventitial disease, in which a cyst occurs within the popliteal artery near the knee, has been proposed recently to occur by an articular mechanism, with a conduit leading from the joint, similar to the development of ganglion cysts, that spreads within the peroneal nerve.[21] One uncommon location of the cysts are in the muscle tendons of the hand, such as the extensor digitorum superficialis.[22]
Cysts that were compressing one or more nerves and causing bone erosions have been reported to occur near the shoulder joint.[23]
-
Cyst on right wrist
-
Cyst on dorsum of right foot
-
Cyst on a finger
-
Small cyst on right index finger
-
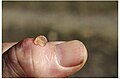
small cyst on thumb lanced with red-hot needle
-
Ganglion cyst on the palmar side of the left wrist
Causes
[edit]The most commonly accepted probable cause of ganglion cysts is the herniation hypothesis, by which they are thought to occur as an out-pouching or distention of a weakened portion of a joint capsule or tendon sheath. This description is based on the observations that the cysts occur close to tendons and joints. The microscopic anatomy of the cyst resembles that of tenosynovial tissue. The fluid is similar in composition to synovial fluid. Dye injected into the joint frequently ends up in the cyst. Dye injected into the cyst rarely enters the joint, however, which has been attributed to the apparent formation of an effective and one-way "check valve", allowing fluid out of the joint, but not back in.[6]
In synovials, post-traumatic degeneration of connective tissue and inflammation have been considered as causes. Other possible mechanisms for the development of ganglion cysts include repeated mechanical stress, facet arthrosis, myxoid degeneration of periarticular fibrous tissues and liquefaction with chronic damage, increased production of hyaluronic acid by fibroblasts, and a proliferation of mesenchymal cells.[20][24]
Diagnosis
[edit]
Ganglion cysts are diagnosed easily, as they are visible and pliable to touch.
Ultrasonography (US) may be used to increase diagnostic confidence in clinically suspected lesions or to view smaller "occult" cysts as a cause of dorsal wrist pain with forceful extension.
Treatment
[edit]At least 33% resolve without treatment within six years, and 50% within 10 years.[25]
Surgical excision is the primary discretionary, elective treatment option for ganglion cysts. Alternatively, a hypodermic needle may be used to drain the fluid from the cyst (via aspiration).[26] The recurrence rate is about 50% following aspiration of a ganglion cyst.
Complications
[edit]Complications of treatment may include joint stiffness and scar formation.[26] Recurrence of the lesion is more common following excision of a volar ganglion cyst in the wrist. Incomplete excision that fails to include the stalk or pedicle also may lead to recurrence, as will failing to execute a layered closure of the incision.[27]
Prognosis
[edit]Recurrence rate is higher in aspirated cysts than in excised ones.[28] Ganglion cysts have been found to recur following surgery in 12%[29] to 41%[30] of patients.
A six-year outcome study of the treatment of ganglion cysts on the dorsal wrist compared excision, aspiration, and no treatment. Neither excision nor aspiration provided long-term benefit better than no treatment. Of the untreated ganglion cysts, 58% resolved spontaneously; the postsurgery recurrence rate in this study was 39%.[31] A similar study in 2003 of ganglion cysts occurring on the palmar surface of the wrist states: "At 2- and 5-year follow-up, regardless of treatment, no difference in symptoms was found, regardless of whether the palmar wrist ganglion was excised, aspirated, or left alone."[32]
Etymology
[edit]Being a misnomer that has persisted into modern times,[33] the ganglion cyst is unrelated to the neural "ganglion" or "ganglion cell"; its etymology traces back to the ancient Greek γάγγλιον, a "knot" or "swelling beneath the skin",[34] which extends to the neural masses by analogy. Generally, Hippocrates is credited with the description of these cysts.[6][35]
"Bible bump"
[edit]A historical method of treatment for a ganglion cyst was to strike the lump with a large, heavy book, causing the cyst to rupture and drain into the surrounding tissues. Historically, a Bible, usually the largest (or only book) in a household, was employed for this treatment. This practice led to the nickname of "Bible bumps" or "Gideon's disease" for the cysts.[2][36] This treatment risks injuring the person and thus is not recommended.[37][38][39]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "National Library of Medicine - Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) - Ganglion Cyst". Archived from the original on March 10, 2016. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- ^ a b "E-hand.com The Electronic Textbook of Hand Surgery". The American Society for Surgery of the Hand assh.com. Archived from the original on March 9, 2014. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ganglion Cyst of the Wrist and Hand-OrthoInfo". orthoinfo.aaos.org. March 2013. Archived from the original on 6 July 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g Ferri FF (2014). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2015 E-Book: 5 Books in 1. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 472. ISBN 9780323084307. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ a b Cooney WP (2011). The Wrist: Diagnosis and Operative Treatment. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1089. ISBN 9781451148268. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10.
- ^ a b c d Craig A. Camasta, DPM (1993). "excision of the ganglion cyst" (PDF). Podiatry Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-11-01.
- ^ Stretanski MF (2020-01-01), Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD (eds.), "Chapter 32 - Hand and Wrist Ganglia", Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (Fourth Edition), Philadelphia: Content Repository Only!, pp. 169–173, ISBN 978-0-323-54947-9, retrieved 2020-10-24
- ^ Fess EE, Gettle KS, Philips CA, Janson JR, eds. (2005-01-01), "CHAPTER 17 - Splinting for Work, Sports, and the Performing Arts", Hand and Upper Extremity Splinting (Third Edition), Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 456–479, doi:10.1016/b978-080167522-5.50022-8, ISBN 978-0-8016-7522-5, retrieved 2020-10-24
- ^ "Ganglion cysts". The British Society for Surgery of the hand. BSSH. Archived from the original on April 7, 2017. Retrieved April 6, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f Pal J, Wallman J (2014-01-01), Cooper C (ed.), "36 - Ganglions and Tumors of the Hand and Wrist", Fundamentals of Hand Therapy (Second Edition), St. Louis: Mosby, pp. 500–507, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-09104-6.00036-5, ISBN 978-0-323-09104-6, retrieved 2020-10-24
- ^ Kirk Watson H, Sorelle J (2010-01-01), Slutsky DJ (ed.), "CHAPTER 45 - Dorsal Wrist Syndrome and Rotatory Subluxation of the Scaphoid", Principles and Practice of Wrist Surgery, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 487–491, ISBN 978-1-4160-5646-1, retrieved 2020-10-24
- ^ a b c Cooper C (2007-01-01), Cooper C (ed.), "Chapter 21 - Ganglion Cysts and Other Common Tumors of the Hand and Wrist", Fundamentals of Hand Therapy, Saint Louis: Mosby, pp. 412–420, doi:10.1016/b0-32-303386-5/50024-2, ISBN 978-0-323-03386-2, retrieved 2020-10-24
- ^ Duncan JM Macdonald, et al. (August 2007). "The Differential Diagnosis of Foot Lumps: 101 Cases Treated Surgically in North Glasgow Over 4 Years". Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 89 (3): 272–275. doi:10.1308/003588407x168235. PMC 1964714. PMID 17394713.
- ^ Jon Arthur Jacobson (2007). Fundamentals of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1416035930. Archived from the original on 2014-07-04.
- ^ Arend CF. Ultrasound of the Shoulder. Master Medical Books, 2013. Sample chapter available on acromioclavicular joint ganglion Archived 2014-05-18 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Muir B, Kissel JA, Yedon DF (December 2011). "Intraosseous ganglion cyst of the humeral head in a competitive flat water paddler: case report". J Can Chiropr Assoc. 55 (4): 294–301. PMC 3222705. PMID 22131566. (includes MRI images)
- ^ Jae Jeong Park, et al. (2010). "Case Report : Intramuscular Ganglion Cyst of the Gastrocnemius Muscle". Korean Journal of Dermatology. Archived from the original on 2013-06-17.
- ^ Park S, Jin W, Chun YS, Park SY, Kim HC, Kim GY, Park JS, Ryu KN (October 2009). "Ruptured intramuscular ganglion cyst in the gastrocnemius medialis muscle: sonographic appearance". Journal of Clinical Ultrasound. 37 (8): 478–81. doi:10.1002/jcu.20609. PMID 19618443. S2CID 20586520.
- ^ Robert J. Spinner, et al. (2012). "Re: Pure Peroneal Intraneural Ganglion Cyst: Hindsight is 20/20" (PDF). Turkish Neurosurgery. pp. 527–528. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-10-14.
- ^ a b Sang Woo Kim, et al. (April 2011). "A Ganglion Cyst in the Second Lumbar Intervertebral Foramen". J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 49 (4): 237–240. doi:10.3340/jkns.2011.49.4.237. PMC 3098430. PMID 21607185. (original source cites eight additional references for the quoted paragraph)
- ^ R. J. Spinner, et al. (2012-08-29). "Evidence to support that adventitial cysts, analogous to intraneural ganglion cysts, are also joint-connected". Clin. Anat. 26 (2): 267–81. doi:10.1002/ca.22152. PMID 22933403. S2CID 37986961.
- ^ Meza-Hernandez J, González-Cantú I, Jimenez-Jimenez J, Ramirez-Sosa L, Martínez-Wagner R. Synovial Cyst of the extensor digitorum superficialis: A case report. JPRAS Open. 2024 Feb 28;40:145-149. doi:10.1016/j.jpra.2024.02.014. PMID: 38854624; PMCID: PMC11156691.
- ^ Field LD (2003). MasterCases: Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. Thieme. p. 241. ISBN 9780865778733.
- ^ Ribes R (2010). Learning Musculoskeletal Imaging. Springer. p. 197. ISBN 9783540880004.
- ^ "Clinical treatments for wrist ganglia" (PDF). ROYAL AUSTRALASIAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2018.
- ^ a b The Gale encyclopedia of surgery: a guide for patients and caregivers, Volume 1. Gale. 2003. pp. 560. ISBN 9780787677213.
- ^ Camasta, Craig A., DPM, Excision of the Ganglion Cyst Archived 2013-11-01 at the Wayback Machine, podiatryinstitute.com, update 1993, 1993 33 pdf, pages 181–5
- ^ Pocket Guide to Musculoskeletal Diagnosis. Springer. 2005. p. 63. ISBN 9781597450096.
- ^ Gallego S, Mathoulin C (2010). "Arthroscopic resection of dorsal wrist ganglia: 114 cases with minimum follow-up of 2 years". Arthroscopy. 26 (12): 1675–1682. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2010.05.008. PMID 20952152.
- ^ Lidder S, Ranawat V, Ahrens P (2009). "Surgical excision of wrist ganglia; literature review and nine-year retrospective study of recurrence and patient satisfaction". Orthop Rev. 1 (1): e5. doi:10.4081/or.2009.e5. PMC 3143961. PMID 21808669.
- ^ Dias JJ, Dhukaram V, Kumar P (October 2007). "The natural history of untreated dorsal wrist ganglia and patient reported outcome 6 years after intervention". The Journal of Hand Surgery, European Volume. 32 (5): 502–8. doi:10.1016/J.JHSE.2007.05.007. PMID 17950209. S2CID 21853864.
- ^ Dias J, Buch K (Apr 2003). "Palmar wrist ganglion: does intervention improve outcome? A prospective study of the natural history and patient-reported treatment outcomes". J Hand Surg Br Vol. 28 (2): 172–6. doi:10.1016/s0266-7681(02)00365-0. PMID 12631492. S2CID 44865301.
- ^ J.C. Segen (1992). The Dictionary of Modern Medicine. CRC Press. ISBN 9781850703211. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. (see the entry for aneurysmal bone cyst, which "like pyogenic granuloma and ganglion cyst, a misnomer that has withstood the sands of time and the dint of logic")
- ^ "Etymology of the Greek word ganglion (γάγγλιον)". Archived from the original on 2013-10-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ See Hippocrates' "On the Articulations" (part 40) at Wikisource
- ^ Dacombe PJ, Robinson, J (Mar 27, 2012). "Falling Up the Stairs: the Equivalent of 'Bashing it with a Bible' for an ACL Ganglion Cyst of the Knee". BMJ Case Reports. 2012: bcr0120125591. doi:10.1136/bcr.01.2012.5591. PMC 3316796. PMID 22605799.
- ^ Hammond C. "Should you bash a 'bible bump'?". Retrieved 2018-08-09.
- ^ "Ganglions". Archived from the original on 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2009-05-27.
- ^ Hammond C. "Should you bash a 'bible bump'?". Retrieved 24 November 2018.