Steroidogenic enzyme
Appearance
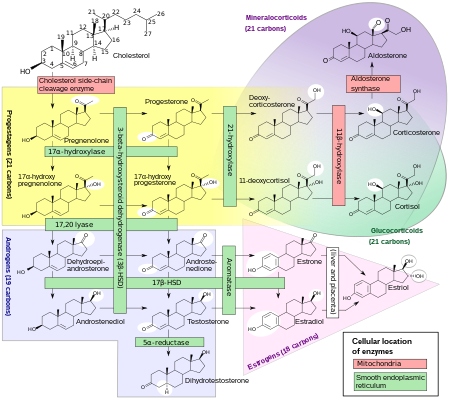
Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis.[2][3][4][5] They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids (androgens, estrogens, and progestogens) and corticosteroids (glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids), as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol.[3][4][5] Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.[3][4][5]
List of steroidogenic enzymes
[edit]- Steroid desmolases
- Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme (20,22-desmolase) – steroid synthesis
- 17,20-Lyase (17,20-desmolase) – androgen synthesis
- Steroid hydroxylases
- 11β-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis
- 17α-Hydroxylase – androgen and glucocorticoid synthesis
- 18-Hydroxylase (aldosterone synthase) – mineralocorticoid synthesis
- 21-Hydroxylase – corticosteroid synthesis
- Cytochrome P450 (CYP1, 2, 3) – estrogen metabolism
- Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (and ketosteroid reductases)
- 3α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – androgen, progestogen, and neurosteroid synthesis and metabolism
- 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4-isomerase (1, 2) – androgen, progestogen, and neurosteroid synthesis
- 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (1, 2) – corticosteroid synthesis and metabolism
- 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (1–15) – androgen, estrogen, and progestogen synthesis and metabolism
- 20α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – progestogen synthesis and metabolism
- 20β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase – progestogen synthesis and metabolism

- Steroid reductases
- 5α-Reductase (1, 2, 3) – androgen and neurosteroid synthesis, progestogen metabolism
- 5β-Reductase – androgen and progestogen metabolism, neurosteroid synthesis
- Conjugation (and deconjugation)
- Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT2Bs) – steroid metabolism[6]
- Glucuronidase (β-glucuronidase) – steroid synthesis[7]
- Steroid sulfotransferase (SULT1A1, 1E1, 2A1, 2B1a, 2B1b) – steroid metabolism, neurosteroid synthesis[8]
- Steroid sulfatase – steroid synthesis, neurosteroid metabolism[8]
- Others
- Aromatase (estrogen synthetase) – estrogen synthesis
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Häggström, Mikael; Richfield, David (2014). "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.005.
- ^ Hanukoglu I (Dec 1992). "Steroidogenic enzymes: structure, function, and role in regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 43 (8): 779–804. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(92)90307-5. PMID 22217824. S2CID 112729.
- ^ a b c Payne AH, Hales DB (2004). "Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones". Endocr. Rev. 25 (6): 947–70. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0030. PMID 15583024.
- ^ a b c Luu-The V, Labrie F (2010). "The Intracrine Sex Steroid Biosynthesis Pathways". Neuroendocrinology: The Normal Neuroendocrine System. Progress in Brain Research. Vol. 181. pp. 177–92. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)81010-2. ISBN 9780444536174. PMID 20478438.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Honour JW (2009). "Diagnosis of diseases of steroid hormone production, metabolism and action". J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 1 (5): 209–26. doi:10.4274/jcrpe.v1i5.209. PMC 3005746. PMID 21274298.
- ^ Guillemette C, Lévesque E, Harvey M, Bellemare J, Menard V (2010). "UGT genomic diversity: beyond gene duplication". Drug Metab. Rev. 42 (1): 24–44. doi:10.3109/03602530903210682. hdl:20.500.11794/10528. PMID 19857043. S2CID 32737680.
- ^ William Fishman (2 December 2012). Metabolic Conjugation and Metabolic Hydrolysis, Volume II. Elsevier. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-323-14308-0.
- ^ a b Mueller JW, Gilligan LC, Idkowiak J, Arlt W, Foster PA (2015). "The Regulation of Steroid Action by Sulfation and Desulfation". Endocr. Rev. 36 (5): 526–63. doi:10.1210/er.2015-1036. PMC 4591525. PMID 26213785.
