Splenomegaly
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (April 2022) |  |
| Splenomegaly | |
|---|---|
 | |
| CT scan in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, showing splenomegaly. Yellow arrows point at the spleen. | |
| Specialty | General surgery |
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen.[1] The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension.[2]
Definition
[edit]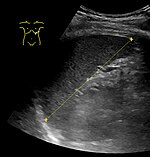
The standard system for classifying splenomegaly on radiography is:[3][4]
- Normal (not splenomegaly): the largest dimension is less than 11 cm
- Moderate splenomegaly: the largest dimension is between 11 and 20 cm
- Severe splenomegaly: the largest dimension is greater than 20 cm
Also, a cutoff of a craniocaudal height of 13 cm is also used to define splenomegaly.[5] In addition, individual intervals have been established:
| Height | Spleen length | |
|---|---|---|
| Women | Men | |
| 155 – 159 cm | 6.4 – 12 cm | |
| 160 – 164 cm | 7.4 - 12.2 cm | 8.9 - 11.3 cm |
| 165 – 169 cm | 7.5 – 11.9 cm | 8.5 – 12.5 cm |
| 170 – 174 cm | 8.3 – 13.0 cm | 8.6 – 13.1 cm |
| 175 – 179 cm | 8.1 – 12.3 cm | 8.6 – 13.4 cm |
| 180 – 184 cm | 9.3 – 13.4 cm | |
| 185 – 189 cm | 9.3 – 13.6 cm | |
| 190 – 194 cm | 9.7 – 14.3 cm | |
| 195 – 199 cm | 10.2 – 14.4 cm | |
| Age | Cutoff[7] |
|---|---|
| 3 months | 6.0 cm |
| 6 months | 6.5 cm |
| 12 months | 7.0 cm |
| 2 years | 8.0 cm |
| 4 years | 9.0 |
| 6 years | 9.5 cm |
| 8 years | 10.0 cm |
| 10 years | 11.0 cm |
| 12 years | 11.5 cm |
| 15 years |
|
For children, the cutoffs for splenomegaly are given in this table, when measuring the greatest length of the spleen between its dome and its tip, in the coronal plane through its hilum while breathing quietly.[7]
At autopsy, splenomegaly can be defined as a spleen weight above the upper limit of the standard reference range of 230 g (8.1 oz).[8][9]
Splenomegaly refers strictly to spleen enlargement, and is distinct from hypersplenism, which connotes overactive function by a spleen of any size. Splenomegaly and hypersplenism should not be confused. Each may be found separately, or they may coexist. Clinically, if a spleen is palpable (felt via external examination), it means it is enlarged as it has to undergo at least twofold enlargement to become palpable. However, the tip of the spleen may be palpable in a newborn baby up to three months of age.[10]
Calculators have been developed for measurements of spleen size based on CT, US, and MRI findings.[11]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]Symptoms may include abdominal pain, chest pain, chest pain similar to pleuritic pain when stomach, bladder or bowels are full, back pain, early satiety due to splenic encroachment, or the symptoms of anemia due to accompanying cytopenia.
Signs of splenomegaly may include a palpable left upper quadrant abdominal mass or splenic rub. It can be detected on physical examination by using Castell's sign, Traube's space percussion or Nixon's sign, but an ultrasound can be used to confirm diagnosis. In patients where the likelihood of splenomegaly is high, the physical exam is not sufficiently sensitive to detect it; abdominal imaging is indicated in such patients.[12]
In cases of infectious mononucleosis splenomegaly is a common symptom and health care providers may consider using abdominal ultrasonography to get insight into a person's condition.[13] However, because spleen size varies greatly, ultrasonography is not a valid technique for assessing spleen enlargement and should not be used in typical circumstances or to make routine decisions about fitness for playing sports.[13]
Causes
[edit]The most common causes of splenomegaly in developed countries are infectious mononucleosis, splenic infiltration with cancer cells from a hematological malignancy and portal hypertension (most commonly secondary to liver disease, and sarcoidosis). Splenomegaly may also come from bacterial infections, such as syphilis or an infection of the heart's inner lining (endocarditis).[14] Splenomegaly also occurs in mammals parasitized by Cuterebra fontinella.[15]
The possible causes of moderate splenomegaly (spleen <1000 g) are many, and include:

The causes of massive splenomegaly (spleen >1000 g) are
Pathophysiology
[edit]Splenomegaly can be classified based on its pathophysiologic mechanism:
- Congestive, by pooled blood (e.g., portal hypertension)
- Infiltrative, by invasion by cells foreign to the splenic environment (e.g., metastases, myeloid neoplasms, lipid storage diseases)
- Immune, by an increase in immunologic activity and subsequent hyperplasia (e.g., endocarditis, sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Neoplastic, when resident immune cells originate a neoplasm (e.g., lymphoma).
Diagnosis
[edit]Abdominal CT is the most accurate. The spleen needs to be 2–3 times larger than normal to be palpable below the costal margin in physical examination.
Treatment
[edit]If the splenomegaly underlies hypersplenism, a splenectomy is indicated and will correct the hypersplenism. However, the underlying cause of the hypersplenism will most likely remain; consequently, a thorough diagnostic workup is still indicated, as, leukemia, lymphoma and other serious disorders can cause hypersplenism and splenomegaly. After splenectomy, however, patients have an increased risk for infectious diseases.
Patients undergoing splenectomy should be vaccinated against Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Meningococcus. They should also receive annual influenza vaccinations. Long-term prophylactic antibiotics may be given in certain cases.
As an adaptation
[edit]An enlarged spleen may be an inherited, adaptive trait selected in populations that need extra oxygen carry capacity such as deep sea divers.[22][23] The Sama-Bajau people, notable for free-diving, have spleens that are 50% larger than those of nearby ethnic groups.[24][23]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Chapman, J; Azevedo, AM (2018), "article-29386", Splenomegaly, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 28613657, retrieved 2019-02-26
- ^ Ghazi, Ali (2010). "Hypercalcemia and huge splenomegaly presenting in an elderly patient with B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a case report". Journal of Medical Case Reports. 4 (334): 330. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-4-330. PMC 2974746. PMID 20959010.
- ^ Neetu Radhakrishnan. "Splenomegaly". Medscape. Retrieved February 16, 2018. Updated Apr. 2012 (referring the classification system to Poulin et al.
- ^ Page 1964 in: Florian Lang (2009). Encyclopedia of Molecular Mechanisms of Disease. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783540671367.
- ^ Saboo, S S; Krajewski, K M; O'Regan, K N; Giardino, A; Brown, J R; Ramaiya, N; Jagannathan, J P (2012). "Spleen in haematological malignancies: spectrum of imaging findings". The British Journal of Radiology. 85 (1009): 81–92. doi:10.1259/bjr/31542964. ISSN 0007-1285. PMC 3473934. PMID 22096219.
- ^ Chow, Kai Uwe; Luxembourg, Beate; Seifried, Erhard; Bonig, Halvard (2016). "Spleen Size Is Significantly Influenced by Body Height and Sex: Establishment of Normal Values for Spleen Size at US with a Cohort of 1200 Healthy Individuals". Radiology. 279 (1): 306–313. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015150887. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 26509293.
- ^ a b Rosenberg, H K; Markowitz, R I; Kolberg, H; Park, C; Hubbard, A; Bellah, R D (1991). "Normal splenic size in infants and children: sonographic measurements". American Journal of Roentgenology. 157 (1): 119–121. doi:10.2214/ajr.157.1.2048509. ISSN 0361-803X. PMID 2048509.
- ^ Molina, D. Kimberley; DiMaio, Vincent J.M. (2012). "Normal Organ Weights in Men". The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 33 (4): 368–372. doi:10.1097/PAF.0b013e31823d29ad. ISSN 0195-7910. PMID 22182984. S2CID 32174574.
- ^ Molina, D. Kimberley; DiMaio, Vincent J. M. (2015). "Normal Organ Weights in Women". The American Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology. 36 (3): 182–187. doi:10.1097/PAF.0000000000000175. ISSN 0195-7910. PMID 26108038. S2CID 25319215.
- ^ Pelizzo, G.; Guazzotti, M.; Klersy, C.; Nakib, G.; Costanzo, F.; Andreatta, E.; Bassotti, G.; Calcaterra, V. (2018). "Spleen size evaluation in children: Time to define splenomegaly for pediatric surgeons and pediatricians". PLOS ONE. 13 (8): e0202741. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1302741P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0202741. PMC 6107197. PMID 30138410.
- ^ "Splenic Index & Volume Calculator (CT/MRI/US)+ Expected Normal". Rad At Hand. Retrieved 2024-07-15.
- ^ Grover SA, Barkun AN, Sackett DL (1993). "The rational clinical examination. Does this patient have splenomegaly?". JAMA. 270 (18): 2218–21. doi:10.1001/jama.270.18.2218. PMID 8411607. Ovid full text
- ^ a b American Medical Society for Sports Medicine (24 April 2014), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Medical Society for Sports Medicine, retrieved 29 July 2014, which cites
- Putukian, M; O'Connor, FG; Stricker, P; McGrew, C; Hosey, RG; Gordon, SM; Kinderknecht, J; Kriss, V; Landry, G (Jul 2008). "Mononucleosis and athletic participation: an evidence-based subject review". Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine. 18 (4): 309–15. doi:10.1097/jsm.0b013e31817e34f8. PMID 18614881. S2CID 23780443.
- Spielmann, AL; DeLong, DM; Kliewer, MA (Jan 2005). "Sonographic evaluation of spleen size in tall healthy athletes". AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology. 184 (1): 45–9. doi:10.2214/ajr.184.1.01840045. PMID 15615949.
- ^ Kaiser, Larry R.; Pavan Atluri; Giorgos C Karakousis; Paige M Porrett (2006). The surgical review: an integrated basic and clinical science study guide. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5641-3.
- ^ Durden LA (1995). "Bot Fly (Cuterebra fontinella fontinella) Parasitism of Cotton Mice (Peromyscus gossypinus) on St. Catherines Island, Georgia". The Journal of Parasitology. 81 (5): 787–790. doi:10.2307/3283977. JSTOR 3283977. PMID 7472877.
- ^ Sproat, LO.; Pantanowitz, L.; Lu, CM.; Dezube, BJ. (Dec 2003). "Human immunodeficiency virus-associated hemophagocytosis with iron-deficiency anemia and massive splenomegaly". Clin Infect Dis. 37 (11): e170–3. doi:10.1086/379613. PMID 14614691.
- ^ Friedman, AD.; Daniel, GK.; Qureshi, WA. (Jun 1997). "Systemic ehrlichiosis presenting as progressive hepatosplenomegaly". South Med J. 90 (6): 656–60. doi:10.1097/00007611-199706000-00017. PMID 9191748.
- ^ Neufeld EF, Muenzer J (1995). "The mucopolysaccharidoses". In Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds.). The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease.7th ed. Vol. 2. McGraw-Hill, New York. pp. 2465–94.
- ^ Suvajdzić, N.; Cemerikić-Martinović, V.; Saranović, D.; Petrović, M.; Popović, M.; Artiko, V.; Cupić, M.; Elezović, I. (Oct 2006). "Littoral-cell angioma as a rare cause of splenomegaly". Clinical and Laboratory Haematology. 28 (5): 317–20. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2257.2006.00801.x. PMID 16999722.
- ^ Dascalescu, CM.; Wendum, D.; Gorin, NC. (Sep 2001). "Littoral-cell angioma as a cause of splenomegaly". N Engl J Med. 345 (10): 772–3. doi:10.1056/NEJM200109063451016. PMID 11547761.
- ^ Ziske, C.; Meybehm, M.; Sauerbruch, T.; Schmidt-Wolf, IG. (Jan 2001). "Littoral cell angioma as a rare cause of splenomegaly". Ann Hematol. 80 (1): 45–8. doi:10.1007/s002770000223. PMID 11233776. S2CID 29326931.
- ^ Rappaport, Lisa (19 April 2018). "Large spleen helps explain deep-diving skills of Southeast Asian 'sea nomads'". Reuters. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- ^ a b Ilardo, M. A.; Moltke, I.; Korneliussen, T. S.; Cheng, J.; Stern, A. J.; Racimo, F.; de Barros Damgaard, P.; Sikora, M.; Seguin-Orlando, A.; Rasmussen, S.; van den Munckhof, I. C. L.; ter Horst, R.; Joosten, L. A. B.; Netea, M. G.; Salingkat, S.; Nielsen, R.; Willerslev, E. (2018-04-18). "Physiological and Genetic Adaptations to Diving in Sea Nomads". Cell. 173 (3): 569–580.e15. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.054. PMID 29677510.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (19 April 2018). "Bodies Remodeled for a Life at Sea". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 23 April 2018.
External links
[edit]- Splenomegaly and hypersplenism at patient.info
