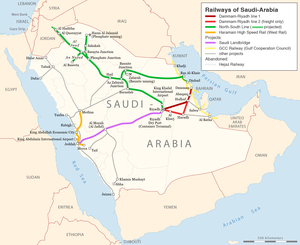
Saudi Landbridge Project
| Saudi Landbridge | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||
| Status | Planned | ||
| Owner | Saudi Railway Company (SAR) | ||
| Termini |
| ||
| Service | |||
| Operator(s) | Saudi Railway Company (SAR) | ||
| Technical | |||
| Track length | Jeddah-Riyadh; 950 kilometres (590.3 mi) and Jubail-Dammam; 115 kilometres (71.5 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||
| |||
The Saudi Landbridge is a railway line currently under development by the Saudi Railway Company (SAR).[1]
The 950 km (594 miles) ‘’Landbridge Line” has been planned to link Jeddah on the Red Sea coast with Riyadh, where it would link up with both the North-South Railway and the lines to Dammam, although no plan for construction has been announced.[2]
Intended mainly for freight,[3] the railway will connect Jeddah on the Red Sea coast with the Saudi Arabian capital Riyadh.[4] The existing 450km line between Riyadh and Dammam will be upgraded,[5] and a second 115km new line is planned to connect Dammam with Jubail on the coast of the Persian Gulf. [4][3] The line between Jubail and Dammam was inaugurated on April 28, 2024. The newly constructed lines will be single track, but the infrastructure (including bridges and tunnels) will be designed to permit a future upgrade to dual track.[5] The project is part of the Saudi vision 2030 that aims at being a logistic hub that connects the three contracts together.[6]
History
[edit]On 21 April 2008 the Tarabot consortium of seven Saudi companies and Asciano of Australia, was named as preferred bidder for the 50-year build, own the concession for the Landbridge project, with financial close planned within 12 months.[7]
Completion was planned for 2010,[8] however financial close could not be agreed.[9]
On 10 October 2011 the government decided the project would go ahead, but as a state project.[3] The cost was put at up to USD 7 billion.[3]
In July 2013, the contract for the design of the 958-kilometre Jeddah-Riyadh section of the project was awarded. The Saudi Public Investment Fund (PIF) awarded the contract to prepare the detailed design of the project to Italferr in August 2015. At the Middle East Rail 2017 conference and exhibition in Dubai on 7 March 2017, SRO President Rumaih Al Rumaih announced that the detailed design for the project had been completed.[10] The project will be developed on a build, operate and transfer (BOT) basis.[11]
See also
[edit]External links
[edit]- Saudi Railways Organization
- The Landbridge-dedicated page on the Saudi Railways site
- An estimated route map
References
[edit]- ^ "BAFOs Submitted for Saudi Landbridge Project". Infranews. 2008-02-28. Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ Trains of the Desert in "The Railway Magazine" (UK), April 2023, No 1,465, Volume 169; pages 32-35
- ^ a b c d "Saudi Landbridge to go ahead as state project". Railway Gazette International. 2011-10-11.
- ^ a b Saudi Landbridge Project Archived 2008-01-13 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- ^ a b "Saudi Landbridge Rail Project". Ashurst. August 2005. Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- ^ "Saudi, Chinese officials meet at Belt and Road Forum in Beijing". Arab News. 2019-04-26. Retrieved 2019-05-01.
- ^ "Saudi Landbridge preferred bidder named". Railway Gazette International. 2008-04-21.
- ^ Christian Wolmar (August 2005). "The groundbreaking Saudi rail-link". Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- ^ "Saudi Landbridge PFI to be reviewed". Railway Gazette International. 2009-07-08.
- ^ "Saudi completes design of railway project linking two coasts | Zawya MENA Edition". Zawya. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ "KSA Business: Saudi Arabia readies design for 950-km railway project".