Rotaliida
| Rotaliida Temporal range: Middle Triassic - present,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Ammonia beccarii (Rotaliidae) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Rhizaria |
| Phylum: | Retaria |
| Subphylum: | Foraminifera |
| Class: | Globothalamea |
| Order: | Rotaliida Delage & Hérouard, 1896 |
| Suborders and superfamilies | |
|
See text | |
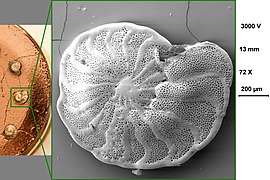
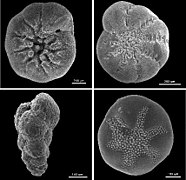
The Rotaliida are an order of Foraminifera, characterized by multilocular tests (shells) composed of bilamellar perforate hyaline lamellar calcite that may be optically radial or granular.
In form, rotaliid tests are typically enrolled, but may be reduced to biserial or uniserial, or may be encrusting with proliferated chambers. Chambers may be simple or subdivided by secondary partitions; the surface is smooth, papillate, costate, striate, or cancellate; the aperture is simple or with an internal toothplate, entosolenian tube, or hemicylindrical structure; it may have an internal canal or stolen systems.
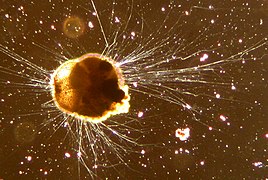
Rotaliids are primarily oceanic benthos, although some are common in shallower estuarine waters. They also include many important fossils, such as the nummulitids.
Taxonomy
[edit]The Rotaliida are now divided into the following superfamilies:[2]
- order Rotaliida Delage & Hérouard, 1896
- suborder Globigerinina Delage & Hérouard, 1896
- superfamily Globigerinitoidea Bermúdez, 1961
- superfamily Globigerinoidea Carpenter et al., 1862
- superfamily Globorotalioidea Cushman, 1927
- superfamily Globotruncanoidea Brotzen, 1942 †
- superfamily Guembelitrioidea Montanaro Gallitelli, 1957
- superfamily Hantkeninoidea Cushman, 1927
- superfamily Heterohelicoidea Cushman, 1927
- superfamily Planomalinoidea Bolli et al., 1957 †
- superfamily Rotaliporoidea Sigal, 1958 †
- superfamily Acervulinoidea Schultze, 1854
- superfamily Annulopatellinoidea Loeblich & Tappan, 1964
- superfamily Asterigerinoidea d'Orbigny, 1839
- superfamily Bolivinitoidea Cushman, 1927
- superfamily Bolivinoidea Glaessner, 1937
- superfamily Buliminoidea Jones, 1875
- superfamily Cassidulinoidea d'Orbigny, 1839
- superfamily Chilostomelloidea Brady, 1881
- superfamily Delosinoidea Parr, 1950
- superfamily Discorbinelloidea Sigal, 1952
- superfamily Discorboidea Ehrenberg, 1838
- superfamily Eouvigerinoidea Cushman, 1927 †
- superfamily Fursenkoinoidea Loeblich & Tappan, 1961
- superfamily Glabratelloidea Loeblich & Tappan, 1964
- superfamily Loxostomatoidea Loeblich & Tappan, 1962
- superfamily Nonionoidea Schultze, 1854
- superfamily Nummulitoidea Blainville, 1827
- superfamily Orbitoidoidea Schwager, 1876 †
- superfamily Planorbulinoidea Schwager, 1877
- superfamily Pleurostomelloidea Reuss, 1860 †
- superfamily Rotalioidea Ehrenberg, 1839
- superfamily Serioidea Holzmann & Pawlowski, 2017
- superfamily Siphoninoidea
- superfamily Turrilinoidea Cushman, 1927
- family Murrayinellidae Holzmann & Pawlowski, 2017
- suborder Globigerinina Delage & Hérouard, 1896
References
[edit]- ^ "Rotaliida". Mindat. Hudson Institute of Mineralogy. Retrieved 3 December 2020.
- ^ Rotaliida, World Foraminifera Database, accessed 27 November 2018
- Loeblich, Alfred R.; Tappan, Helen (1964). Moore, R.C. (ed.). Protista 2: Sarcodina Chiefly "Thecamoebians" and Foraminiferida. Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology. Vol. C (5th ed.). Geological Society of America. ISBN 978-0-8137-3003-5.
- Loeblich, Jr, Alfred R.; Tappan, Helen (1988). Foraminiferal genera and their classification. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co. ISBN 9780442259372.
- Gupta, Barun K. Sen, ed. (1999). Modern foraminifera (Repr. with corr. ed.). Dordrecht [u.a.]: Kluwer Acad. Publ. ISBN 0412824302.
External links
[edit]- Suborder ROTALIINA Delage and Hérouard, 1896 (Geological Survey of Iran)