Rhodocactus
| Rhodocactus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Rhodocactus grandifolius | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Cactaceae |
| Subfamily: | Pereskioideae |
| Genus: | Rhodocactus (A.Berger) F.M.Knuth[1] |
| Species | |
Rhodocactus is a genus of flowering plant in the cactus family Cactaceae, native to central South America.[2] Unlike most species of cacti, Rhodocactus has persistent leaves and a fully tree-like habit. The genus was sunk into a broadly circumscribed Pereskia, but molecular phylogenetic studies from 2005 onwards showed that with this circumscription Pereskia was paraphyletic, and in 2016, Rhodocactus was restored for southern South American species.
Description
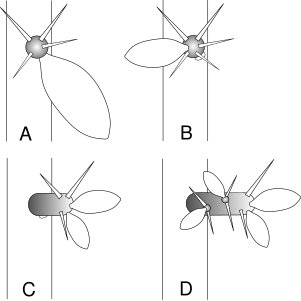
[edit]Like all cacti, Rhodocactus species have a succulent habit and specialized structures, areoles, that bear spines. They differ from most cacti in having persistent leaves. They grow as trees, 3–7 m (10–23 ft) tall. When mature, their stems develop bark, but its development is delayed, and all the species other than Rhodocactus nemorosus retain stomata. The areoles of Rhodocactus species can form "brachyblasts",[3] called "spur shoots" by Beat Leuenberger. The areole initially forms in the axil of a leaf (stage A in the diagram below). This leaf may be lost, leaving a leaf scar, and leaves may grow on the areole (stage B). The areole may then grow out to form a brachyblast – a short, very crowded shoot that bears leaves (stage C). Later this may form a longer, but still short shoot that has its own areoles (stage D).[4] Asai and Miyata regard the formation of brachyblast leaves as a distinguishing characteristic of the genus in comparison to Pereskia.[3] Rhodocactus flowers are about 3–5 cm (1.2–2.0 in) in diameter.[3]
-
Areole and brachyblast development in Rhodocactus
-
Areole on a young stem of R. grandiflorus is in the axis of the auxoblast leaf (stage A)
-
Areoles on this stem of R. grandiflorus have brachyblast leaves (stage B)
-
Short shoot of R. grandiflorus (stage D)
Taxonomy
[edit]Rhodocactus was originally described as a subgenus of Pereskia by Alwin Berger, and was raised to a genus in 1936 by Frederik Marcus Knuth.[1][3] The genus was later sunk back into in a broadly defined genus Pereskia. Molecular phylogenetic studies from 2005 onwards suggested that when circumscribed in this way, Pereskia was not monophyletic, and consisted of three clades.[5][6][3] By 2016, each clade was recognized as a separate genus, one of which is Rhodocactus. Only the type species of Knuth's circumscription of the genus, Rhodocactus grandifolius, belongs to the clade re-described as Rhodocactus. The other species were mostly newly transferred from Pereskia.[3]
A consensus cladogram from a 2005 study is shown below with the more recent generic assignments added. It shows that the three genera are basal to the rest of the cacti.[5]
|
Pereskia as previously defined |
Species
[edit]As of April 2021[update], Plants of the World Online accepted the following species:[2]
| Image | Scientific name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
 |
Rhodocactus bahiensis (Gürke) I.Asai & K.Miyata< | Brazil |
 |
Rhodocactus grandifolius (Haw.) F.M.Knuth | eastern and southern Brazil. |
 |
Rhodocactus nemorosus (Rojas Acosta) I.Asai & K.Miyata | Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and northeast Argentina. |
 |
Rhodocactus sacharosa (Griseb.) Backeb. | Bolivia and west-central Brazil to Paraguay and northern Argentina |
 |
Rhodocactus stenanthus (F.Ritter) I.Asai & K.Miyata | Brazil |
Species that have also been placed in Rhodocactus include:[3]
- Rhodocactus bleo (F.M.Knuth) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria bleo F.M.Knuth) Lodé
- Rhodocactus guamacho (F.A.C.Weber) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria guamacho (F.A.C.Weber) Lodé
- Rhodocactus horridus (DC.) F.M.Knuth = Pereskia horrida D.C.
- Rhodocactus lychnidiflorus (D.C.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria lychnidiflora (D.C.) Lodé
- Rhodocactus portulacifolius (L.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria portulacifolia (L.) Lodé
- Rhodocactus zinniiflorus (D.C.) F.M.Knuth = Leuenbergeria zinniiflora (D.C.) Lodé
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Rhodocactus (A.Berger) F.M.Knuth", The International Plant Names Index, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ a b "Rhodocactus (A.Berger) F.M.Knuth", Plants of the World Online, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ a b c d e f g Asai, Issaku & Miyata, Kazunori (2016), "An Emendation of Rhodocactus, a Genus Segregated from Pereskia (Cactaceae)" (PDF), Journal of Japanese Botany, 91: 7–12, archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-07-11, retrieved 2021-04-25
- ^ Leuenberger, Beat Ernst (1986), Pereskia (Cactaceae), Memoirs of the New York Botanical Garden, vol. 14, Bronx, NY: New York Botanical Garden, p. 11, ISBN 978-0-89327-307-1, retrieved 2021-05-02
- ^ a b Edwards, Erika J.; Nyffeler, Reto & Donoghue, Michael J. (2005), "Basal cactus phylogeny: implications of Pereskia (Cactaceae) paraphyly for the transition to the cactus life form", American Journal of Botany, 92 (7): 1177–1188, doi:10.3732/ajb.92.7.1177, PMID 21646140
- ^ Bárcenas, Rolando T.; Yesson, Chris & Hawkins, Julie A. (2011), "Molecular systematics of the Cactaceae", Cladistics, 27 (5): 470–489, doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2011.00350.x, PMID 34875796, S2CID 83525136