Raltitrexed
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.180.242 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
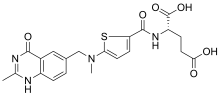
| Formula | C21H22N4O6S |
| Molar mass | 458.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Raltitrexed (Thaltitrexed, Tomudex, TDX, ZD 1694) is an antimetabolite drug used in cancer chemotherapy. It is an inhibitor of thymidylate synthase, and is manufactured by AstraZeneca.[1]
Uses
[edit]Used in treatment of colorectal cancer since 1998, it may also be used in the treatment of malignant mesothelioma.[2] Raltitrexed is approved for use in Canada and some European countries, but is not approved by the US FDA.[3][4]
Mechanism of action
[edit]Raltitrexed is chemically similar to folic acid and is in the class of chemotherapy drugs called folate antimetabolites, which inhibit one or more of three enzymes that use folate and derivatives as substrates: DHFR, GARFT and thymidylate synthase. Raltitrexed is fully active after polyglutamylation, which allows cellular retention of the drug.
By inhibiting Thymidylate synthase (TS), thus formation of precursor pyrimidine nucleotides, raltitrexed prevents the formation of DNA and RNA, which are required for the growth and survival of both normal cells and cancer cells.
Inhibition of L1210 cell growth in culture IC50 = 9 nM, is one of the strongest antimetabolites in use.
Structure and phase I clinical trial of the precursor drug, CB3717, was described in 1986.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Widemann BC, Balis FM, Godwin KS, McCully C, Adamson PC (1999). "The plasma pharmacokinetics and cerebrospinal fluid penetration of the thymidylate synthase inhibitor raltitrexed (Tomudex) in a nonhuman primate model". Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 44 (6): 439–43. doi:10.1007/s002800051116. PMID 10550563. S2CID 9006510.
- ^ Zuidema PJ (1976). "[Primary amebic meningoencephalitis]". Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 120 (11): 477. PMID 1256598.
- ^ "Pharmacogenetics in Colorectal Cancer".
- ^ "EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION on the granting of a product-specific waiver for raltitrexed (Tomudex)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. January 27, 2009.
- ^ Calvert AH, Alison DL, Harland SJ, et al. (August 1986). "A phase I evaluation of the quinazoline antifolate thymidylate synthase inhibitor, N10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolic acid, CB3717". J. Clin. Oncol. 4 (8): 1245–52. doi:10.1200/JCO.1986.4.8.1245. PMID 3734849.
