Quinizarine Green SS
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
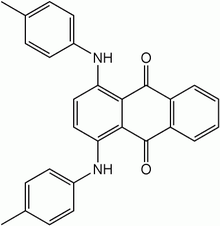
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Bis(4-methylanilino)anthracene-9,10-dione | |
| Other names
C.I. Solvent Green 3; 1,4-bis[(4-methylphenyl)amino]-9,10-Anthracenedione; D & C Green No.6; 1,4-Bis(p-tolylamino)anthraquinone; 1,4-Bis(p-toluidino)anthraquinone; C.I. 61565; Oil Green G;
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.464 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H22N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 418.496 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Black powder[1] |
| Melting point | 220 to 221 °C (428 to 430 °F; 493 to 494 K)[1] |
| Insoluble[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Quinizarine Green SS, also called Solvent Green 3 is an anthraquinone derivative. It is a black powder that is soluble in polar organic solvents, but insoluble in water. It is used as a dye for adding greenish coloring to cosmetics and medications. It is used in some colored smoke formulations.
According to X-ray crystallography, the anthroquinone portion of the molecule is planar. Both amine protons form hydrogen bonds to the carbonyls.[2]

This dye is a component in some smoke grenades, and questions have been raised about its toxicity.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c C.I. SOLVENT GREEN 3
- ^ T.Saito; Chong-yang Liu; V.M. Lynch; A.J. Bard (1997). "Orientational Dependence of the Color and Photoconductivity of 1,4-Di-p-toluidinoanthraquinone Single Crystals". Chem. Mater. 210 (6): 1318. doi:10.1021/cm960652f.
- ^ National Research Council (US) Subcommittee on Military Smokes Obscurants (1999). Toxicity of Military Smokes and Obscurants. doi:10.17226/9645. ISBN 978-0-309-06599-3. PMID 25077233.
