Provisional Siberian Government (Omsk)
Provisional Siberian Government Врeменное Сиби́рское прави́тельство (Russian) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918 | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Capital | Omsk | ||||||||
| Common languages | Russian | ||||||||
| Government | Provisional Government | ||||||||
| Historical era | Russian Civil War | ||||||||
• Established | January 1918 | ||||||||
• Dissolved | September 1918 | ||||||||
| |||||||||

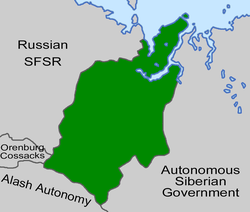
The Provisional Siberian Government (Russian: Вре́менное Сиби́рское прави́тельство, PSG) was a short-lived government in Siberia created by political Whites in 1918.
History
[edit]During January 1918, a Provisional Siberian Government (PSG) was established, and its government chose to locate in the eastern coastal city of Vladivostok. Most of the members of this first Siberian provisional government were members of the Socialist-Revolutionary Party (PSR), including the president of this government, Pyotr Derber.
On 1 June 1918, the West Siberian Commissariat was announced after the Revolt of the Czechoslovak Legion. According to William Henry Chamberlin, "...the initiative in setting up a new government was taken by three men, Markhov, Mikhailov and Lindberg, who described themselves as representatives of the Siberian Government and members of the All-Russian Constituent Assembly, and by the head of the Tomsk Zemstvo, Sidorov." On 30 June a new government took place through the efforts of the more conservative groups and army officers. According to Chamberlin, "The first sign of a swing to the right was the replacement of the Commissariat, which had been guided in its activities by the programme of the Socialist Revolutionary Party, by a group of Ministers of the Derber Government, headed by Pyotr Vologodsky, a jurist with the reputation of a moderate liberal." Autonomous Siberia's flag was green and white to symbolize the snows and forests. On 4 July, this Siberian government declared itself as the sole Siberian authority.[2]
The Derber government in Vladivostok refused to recognize the legitimacy of this new government based in Omsk. A reorganization of the Vladivostok government followed, with the name Provisional Government of Autonomous Siberia (PGAS) adopted. The PGAS in Vladivostok and new PSG in Omsk each refused to recognize the other, and each claimed to be the sole government of Siberia. The generals of the Siberian Army deferred to the Vologodskii government in Omsk, however, resulting in the marginalization of the Vladivostok regime.
During September 1918, after the State Meeting in Ufa, the Provisional Siberian Government (Omsk) was transitioned into a new government, the Provisional All-Russian Government, known informally as the Ufa Directory. Chamberlin states, "Vologodsky went to Eastern Siberia and obtained the abdication of the phantom Derber Cabinet in Vladivostok."[2]: 21
During November of 1918, a coup occurred in Omsk and installed Alexander Kolchak as the Supreme Ruler of Russia.[3]

See also
[edit]Sources
[edit]- ^ "Флаги и знамёна небольшевистских государственных образований на Востоке России (1918-1925 гг.) по воспоминаниям и историографии". Archived from the original on 2021-05-14. Retrieved 2022-02-22.
- ^ a b Chamberlin, William (1935). The Russian Revolution, 1917-1921, Volume Two. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp. 12–14.
- ^ Zenzinov, V. (Vladimir); André Savine Collection (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill) (1919). Gosudarstvennyi perevorot admirala Kolchaka v Omskie : 18 noiabria 1918 goda : sbornik dokumentov. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University Library. Parizh : V. Zenzinov.
Additional Reading
[edit]- "Гражданская война в России: катастрофа Белого движения в Сибири" ("Civil War in Russia: Catastrophe of White Movement in Siberia") - Moscow, "AST" Publishing House, 2005. ISBN 5-17-025035-5

