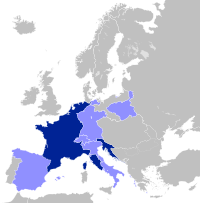
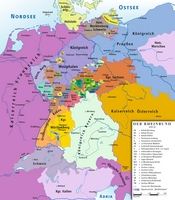
Principality of Salm
Principality of Salm Fürstentum Salm (German) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1803–1811 | |||||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||||
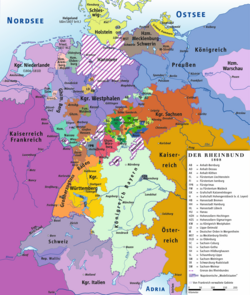 Map of the Principality of Salm within the Confederation of the Rhine in 1808. (South of Holland) | |||||||||||
| Status | Client of the First French Empire, State of the Confederation of the Rhine | ||||||||||
| Capital | Bocholt | ||||||||||
| Government | Principality | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Napoleonic Wars | ||||||||||
• Created from Cty Anholt and Bp Münster | 1803 | ||||||||||
• Joined Confed. of the Rhine | 1806 | ||||||||||
| 1811 | |||||||||||
• Mediatised to Prussia | 1815 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The second Principality of Salm (German: Fürstentum Salm) was a short-lived client state of Napoleonic France located in Westphalia.
History
[edit]The Principality of Salm was created in 1632 as a state of the Holy Roman Empire, and re-created in 1803 in order to compensate the princes of Salm-Kyrburg and Salm-Salm, who had lost their states to France in 1793–1795. The territory of the new principality was formally assigned by the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803. The new territory was not near most of the old territories of the princes, but instead extended the County of Anholt, which had been a minor possession of the prince of Salm-Salm. Most of the area was taken from the dissolved Bishopric of Münster.
The Principality of Salm was ruled jointly by the princes of Salm-Kyrburg and Salm-Salm, Frederick IV, Prince of Salm-Kyrburg, and Constantine, Prince of Salm-Salm;[1] each line had equal sovereign rights, but neither had a separate territory.[2] Salm became independent and joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806.[3] It was annexed by France in 1811. Its territory was given to Prussia by the Congress of Vienna in 1815; it became the westernmost part of the Prussian Province of Westphalia. The flag of Salm would be copied in 1871 by the newly created German Empire, who used the exact same flag.[4][5]
Geography
[edit]The capital of Salm was Bocholt.[6] Salm had an area of about 1,700 km2 and a population of about 59,000.[3] It covered approximately the same area as the present-day District of Borken.
References
[edit]- ^ Bénévent), Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord (prince de (1891). Memoirs of the Prince de Talleyrand. G.P. Putnam's sons.
- ^ Burg, Martijn van der (29 March 2021). Napoleonic Governance in the Netherlands and Northwest Germany: Conquest, Incorporation, and Integration. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-030-66658-3.
- ^ a b "Fürstentum Salm - Flagge in Lexikon und Shop". www.flaggenlexikon.de. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ "Salm-Salm 1386-1811 (Germany)". www.crwflags.com. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ "German Empire | Facts, History, Flag, & Map | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ "DNB, Katalog der Deutschen Nationalbibliothek". portal.dnb.de. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
External links
[edit]- Principality of Salm, at flaggenlexikon.de (in German and in English)
- Former countries in Europe
- Former principalities
- Principalities of the Holy Roman Empire
- States of the Confederation of the Rhine
- 1802 establishments in Europe
- 1811 disestablishments in Europe
- States and territories established in 1802
- Real unions
- Former states and territories of North Rhine-Westphalia
- States and territories disestablished in 1811