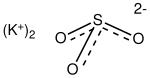
Potassium sulfite
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium sulfite
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.279 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K2SO3 | |
| Molar mass | 158.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 2.49 g/cm3[1] |
| Soluble | |
| Acidity (pKa) | 8 |
| −64.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Potassium sulfate Potassium selenite |
Other cations
|
Sodium sulfite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium sulfite is the inorganic compound with the formula K2SO3. It is the salt of potassium cation and sulfite anion. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water. Potassium sulfite is used for preserving food and beverages.[2]
Production and reactions
[edit]Potassium sulfite is produced by the thermal decomposition of potassium metabisulfite at 190 °C:[3]
- K2S2O5 → K2SO3 + SO2
Structure
[edit]The structure of solid K2SO3, as assessed by X-ray crystallography. The S-O distances are 1.515 Å, and the O-S-O angles are 105.2°[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Andersen, Leif; Strömberg, Dan; Nevala, H.; Pohjola, S.; Niinistö, Lauri; Volden, Hans V.; Weidlein, Johann; Zingaro, Ralph A. (1986). "The Structure of Potassium Sulfite". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 40a: 479–480. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.40a-0479.
- ^ "Potassium sulfite (225)". Codex Alimentarius. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ Johnstone, H. F. (1946). "Sulfites and Pyrosulfites of the Alkali Metals". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 2. pp. 162–167. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch49. ISBN 9780470132333.
