Posterior ethmoidal nerve
| Posterior ethmoidal nerve | |
|---|---|
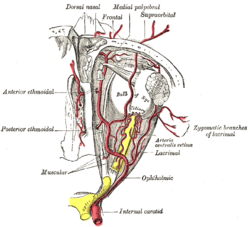 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Nerve not pictured, but location is similar to artery.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Nasociliary nerve |
| Innervates | Sphenoidal sinus, ethmoidal sinus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ethmoidalis posterior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.028 |
| TA2 | 6207 |
| FMA | 52714 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The posterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)). It provides sensory innervation to the sphenoid sinus and ethmoid sinus, and part of the dura mater in the anterior cranial fossa.
Structure
[edit]Origin
[edit]The posterior ethmoidal nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve.[1]
Course
[edit]It passes through the posterior ethmoidal foramen alongside the posterior ethmoidal artery.[2]
Branches
[edit]Within the anterior cranial fossa, it issues a branch to which innervates part of the dura mater.[3][4]
It gives branches to the sphenoid sinus and the ethmoid sinus.[1]
Variation
[edit]The posterior ethmoidal nerve is absent in a significant proportion of people.[5] This may be around 30%.
Function
[edit]The posterior ethmoidal nerve supplies sensation to the sphenoid sinus and the ethmoid sinus.[1] It also supplies sensation to part of the dura mater in the anterior cranial fossa.[3][4]
Other animals
[edit]The posterior ethmoidal nerve is present in other animals, including horses.[6][7] Headshaking can sometimes be treated with analgesia or neurectomy of the posterior ethmoidal nerve.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Barral, Jean-Pierre; Croibier, Alain (2009). "15 - Ophthalmic nerve". Manual Therapy for the Cranial Nerves. Churchill Livingstone. pp. 115–128. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-3100-7.50018-5. ISBN 978-0-7020-3100-7.
- ^ Semmer, A. E.; McLoon, L. K.; Lee, M. S. (2010). "Orbital Vascular Anatomy". Encyclopedia of the Eye. Academic Press. pp. 241–251. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-374203-2.00284-0. ISBN 978-0-12-374203-2.
- ^ a b Shimizu, Toshihiko; Suzuki, Norihiro (2010). "3 - Biological sciences related to headache". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 97. Elsevier. pp. 35–45. doi:10.1016/S0072-9752(10)97003-6. ISBN 978-0-444-52139-2. ISSN 0072-9752. PMID 20816409.
- ^ a b Seker, Askin; Martins, Carolina; Rhoton Jr., Albert L. (2010). "2 - Meningeal Anatomy". Meningiomas. Saunders. pp. 11–51. doi:10.1016/B978-1-4160-5654-6.00002-7. ISBN 978-1-4160-5654-6.
- ^ Rea, Paul (2016). "2 - Head". Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and Neck. Academic Press. pp. 21–130. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803633-4.00002-8. ISBN 978-0-12-803633-4.
- ^ "11 - Disorders of the nervous system". Knottenbelt and Pascoe's Color Atlas of Diseases and Disorders of the Horse (2nd ed.). Saunders. 2014. pp. 400–442. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7234-3660-7.00011-0. ISBN 978-0-7234-3660-7.
- ^ a b Carr, Elizabeth A.; Maher, Omar (2014). Equine Sports Medicine and Surgery (2nd ed.). Saunders. pp. 503–526. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4771-8.00024-7. ISBN 978-0-7020-4771-8.
External links
[edit]- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_45/45-6.HTM
