Portal:Volcanoes/Selected article/3
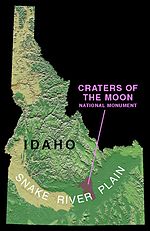
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve is a national monument and national preserve located in the Snake River Plain in central Idaho near Arco, Idaho. The features in this protected area are volcanic and represent one of the best preserved flood basalt areas in the continental United States. The Monument was established on May 2, 1924. In November 2000, a Presidential proclamation greatly expanded the Monument area. The National Park Service portions of the expanded Monument were designated as Craters of the Moon National Preserve in August 2002. It lies in parts of Blaine, Butte, Lincoln, Minidoka, and Power counties. The area is managed cooperatively by the National Park Service and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The Monument and Preserve encompass three major lava fields and about 400 mi² (1,000 km²) of sagebrush steppe grasslands to cover a total area of 1117 mi² (2,892 km²). All three lava fields lie along the Great Rift of Idaho, with some of the best examples of open rift cracks in the world, including the deepest known on Earth) at 800 feet (240 m). There are excellent examples of almost every variety of basaltic lava as well as tree molds (cavities left by lava-incinerated trees), lava tubes (a type of cave), and many other volcanic features.