Portal:Rocketry
The Rocketry Portal

A rocket (from Italian: rocchetto, lit. ''bobbin/spool'', and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere.
Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity.
Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significant scientific, interplanetary and industrial use did not occur until the 20th century, when rocketry was the enabling technology for the Space Age, including setting foot on the Moon. Rockets are now used for fireworks, missiles and other weaponry, ejection seats, launch vehicles for artificial satellites, human spaceflight, and space exploration.
Chemical rockets are the most common type of high power rocket, typically creating a high speed exhaust by the combustion of fuel with an oxidizer. The stored propellant can be a simple pressurized gas or a single liquid fuel that disassociates in the presence of a catalyst (monopropellant), two liquids that spontaneously react on contact (hypergolic propellants), two liquids that must be ignited to react (like kerosene (RP1) and liquid oxygen, used in most liquid-propellant rockets), a solid combination of fuel with oxidizer (solid fuel), or solid fuel with liquid or gaseous oxidizer (hybrid propellant system). Chemical rockets store a large amount of energy in an easily released form, and can be very dangerous. However, careful design, testing, construction and use minimizes risks. (Full article...)
Selected article -

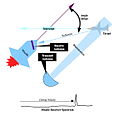
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision. Modern cruise missiles are capable of traveling at high subsonic, supersonic, or hypersonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory. (Full article...)
In the news
- 19 November 2024 –
- SpaceX launches their sixth Starship rocket at the Boca Chica launch pad in Brownsville, Texas, U.S. (Reuters)
- 6 November 2024 – Israel–Hezbollah conflict
- Hezbollah fires rockets at Tel Aviv, Israel, with a rocket striking Ben Gurion Airport. (Yedioth Ahronoth)
- 29 October 2024 – Israel–Hezbollah conflict
- Eight Austrian Army soldiers and peacekeepers are injured when a rocket, likely fired by Hezbollah, hits the UNIFIL headquarters in Naqoura, Lebanon. (Al Jazeera) (Al Arabiya)
- 28 October 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- At least 21 people are injured when Russian guided bombs and rocket artillery hit Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. (Reuters)
- 25 October 2024 – Israel–Hezbollah conflict
- Two people are killed and six others are injured when a rocket fired from Lebanon hits a building in the town of Majd al-Krum in northern Israel. (The Jerusalem Post)
Topics
List articles
Things to do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus