Portal:Internet
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected articleRed vs. Blue is a science fiction comedy series created by Rooster Teeth Productions. The series is produced primarily by using the machinima technique of synchronizing video footage from computer and video games to pre-recorded dialogue and other audio. Footage is taken mostly from the multiplayer modes of the first-person shooter (FPS) video games Halo: Combat Evolved and Halo 2 on the Xbox video game console. Chronicling the story of two opposing teams of soldiers fighting a civil war in the middle of a desolate box canyon, the series is an absurdist parody of FPS games, military life, and other science fiction films. Begun in 2003 and having concluded its fourth season, Red vs. Blue has won four awards from the Academy of Machinima Arts & Sciences. The series is generally praised for its originality, and has been credited with bringing new popularity to machinima, helping it to gain more mainstream exposure, and attracting more people to the art form. Selected picture Leet (written 31337, 1337, and l33t), or Leetspeak, is a written argot used primarily on the Internet, which uses various combinations of alphanumerics to replace Latinate letters. The term is derived from the word "elite", and the usage it describes is a specialized form of shorthand. News
Wikinews Internet portal
WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Chad Meredith Hurley (born 1977) is co-founder and Chief Executive Officer of the popular San Bruno, California-based video sharing website YouTube, one of the biggest providers of videos on the Internet. In June 2006, he was voted 28th on Business 2.0's "50 people who matter" list. In October 2006 he sold YouTube for $1.65 billion to Google. Hurley worked in eBay's PayPal division before starting YouTube with fellow PayPal colleagues Steve Chen and Jawed Karim. One of his tasks at eBay involved designing the original PayPal logo. Newsweek describes Hurley as a user interface expert. He was primarily responsible for the tagging and video sharing aspects of YouTube. YouTube was born when the founders (Hurley, Chen, and Karim) wanted to share some videos from a dinner party with friends in San Francisco in January 2005. Sending the clips around by e-mail was a bust: The e-mails kept getting rejected because they were so big. Posting the videos online was a headache, too. So they got to work to design something simpler. In 11 months the site became one of the most popular sites on the Internet because the founders designed it so people can post almost anything they like on YouTube in minutes.
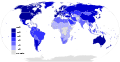
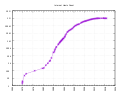
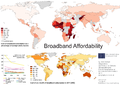
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMore Did you know...
Main topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |