Portal:Politics
| Main | Topics and categories | Tasks and projects |
The Politics portal
Politics (from Ancient Greek πολιτικά (politiká) 'affairs of the cities') is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science.
Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it.
A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including warfare against adversaries. Politics is exercised on a wide range of social levels, from clans and tribes of traditional societies, through modern local governments, companies and institutions up to sovereign states, to the international level.
In modern nation states, people often form political parties to represent their ideas. Members of a party often agree to take the same position on many issues and agree to support the same changes to law and the same leaders. An election is usually a competition between different parties.
A political system is a framework which defines acceptable political methods within a society. The history of political thought can be traced back to early antiquity, with seminal works such as Plato's Republic, Aristotle's Politics, Confucius's political manuscripts and Chanakya's Arthashastra. (Full article...)
Selected article

Regulamentul Organic (Romanian: [reɡulaˈmentul orˈɡanik], English: Organic Regulation; French: Règlement Organique; Russian: Органический регламент, romanized: Organichesky reglament) was a quasi-constitutional organic law enforced in 1831–1832 by the Imperial Russian authorities in Moldavia and Wallachia (the two Danubian Principalities that were to become the basis of the modern Romanian state). The document partially confirmed the traditional government, including rule by the hospodars, and set up a common Russian protectorate which lasted until 1854. The Regulament itself remained in force until 1858. Conservative in its scope, it also engendered a period of unprecedented reforms which provided a setting for the Westernization of the local society. The Regulament offered the two Principalities their first common system of government.
Featured picture

David Ben-Gurion (born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first Prime Minister of Israel. Adopting the name of Ben-Gurion in 1909, he rose to become the preeminent leader of the Jewish community in British-ruled Mandatory Palestine from 1935 until the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, which he led until 1963 with a short break in 1954–55.
The governor of Arkansas is the head of government of the U.S. state of Arkansas. The governor is the head of the executive branch of the Arkansas government and is charged with enforcing state laws. They have the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Arkansas General Assembly, to convene the legislature, and to grant pardons, except in cases of treason and impeachment.
The state has had 46 elected governors, as well as 11 acting governors who assumed powers and duties following the resignation or death of the governor. Before becoming a state, Arkansas Territory had four governors appointed to it by the president of the United States. Orval Faubus (1955–1967) served the longest term as governor, being elected six times to serve 12 years. Bill Clinton (1979–1981; 1983–1992), elected five times over two distinct terms, fell only one month short of 12 years, and Mike Huckabee (1996–2007) served 10 years for two full four-year terms. The shortest term for an elected governor was the 38 days served by John Sebastian Little before his nervous breakdown; one of the acting successors to his term, Jesse M. Martin, took office only three days before the end of the term, the shortest term overall. (Full article...)

The governor of New York is the head of government of the U.S. state of New York, the head of the executive branch of New York's state government, and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The officeholder has a duty to enforce state laws, to convene the New York State Legislature, the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the legislature, as well as to grant pardons, except in cases of treason and impeachment.
Fifty-seven people have served as state governor, four of whom served non-consecutive terms (George Clinton, DeWitt Clinton, Horatio Seymour, and Al Smith); the official numbering lists each governor only once. There has only been one female governor so far: Kathy Hochul. This numbering includes one acting governor: the lieutenant governor who filled the vacancy after the resignation of the governor, under the 1777 Constitution. The list does not include the prior colonial governors nor those who have acted as governor when the governor was out of state, such as Lieutenant Governor Timothy L. Woodruff during Theodore Roosevelt's vice presidential campaign in 1900, or Acting Speaker of the New York State Assembly Moses M. Weinstein, who acted as governor for 10 days in 1968 while the governor, the lieutenant governor and the senate majority leader were out of the state, attending the Republican National Convention in Miami. (Full article...)

There are 95 counties in the U.S. State of Tennessee. As of 2023, Shelby County was both Tennessee's most populous county, with 910,042 residents, and the largest county in area, covering an area of 755 sq mi (1,955 km2). The least populous county was Pickett County (5,128) and the smallest in area was Trousdale County, covering 114 sq mi (295 km2). As of the same year, Davidson County, in which the capital Nashville is located, covers 502 sq mi (1,300 km2) with a population of 712,334. The population of the state of Tennessee as of the 2023 census estimate was 7,126,489 in an area of 42,169 sq mi (109,217 km2). The oldest county is Washington County, founded in 1777. The most recently formed county is Chester County (1879).
According to the 2020 census, the center of population for Tennessee was located at , 3.5 mi (5.6 km) southeast of Murfreesboro in Rutherford County. The center of population pinpoints the location at which the population of the state, as placed on a map of the state where they reside, would balance out the map. The geographic center, the point where the map of Tennessee would balance without the population, is located 5 mi (8 km) northeast of Murfreesboro. In 1976, the Rutherford County Historical Society marked the geographic center of Tennessee with an obelisk. (Full article...)
The Roman emperor was the ruler and monarchical head of state of the Roman Empire, starting with the granting of the title augustus to Octavian in 27 BC. The term emperor is a modern convention, and did not exist as such during the Empire. When a given Roman is described as becoming emperor in English, it generally reflects his accession as augustus, and later as basileus. Another title used was imperator, originally a military honorific, and caesar, originally a cognomen. Early emperors also used the title princeps ('first one') alongside other Republican titles, notably consul and pontifex maximus.
The legitimacy of an emperor's rule depended on his control of the Roman army and recognition by the Senate; an emperor would normally be proclaimed by his troops, or by the Senate, or both. The first emperors reigned alone; later emperors would sometimes rule with co-emperors to secure the succession or to divide the administration of the empire between them. The office of emperor was thought to be distinct from that of a rex ('king'). Augustus, the first emperor, resolutely refused recognition as a monarch. For the first three hundred years of Roman emperors, efforts were made to portray the emperors as leaders of the Republic, fearing any association with the kings who ruled Rome prior to the Republic. (Full article...)

The Minister of Transport (Norwegian: Samferdelsministeren) is a Councillor of State and Chief of the Norwegian Ministry of Transport. The post has been held by Jon-Ivar Nygård of the Labour Party since 2021. The ministry is responsible for policy and public operations within postal services, telecommunications, civil aviation, public roads, rail transport and public transport, including ferry services that are part of national roads and coastal transport infrastructure. The ministry has seven agencies and four limited companies, including the airport operator Avinor, railway operator Vy, the Norwegian National Rail Administration, the Norwegian Public Roads Administration and Norway Post. There are also inspectorates and authorities related to accident investigation, civil aviation, and railways.
The position was created with the ministry on 22 February 1946, when Nils Langhelle (Labour) was appointed. The ministry and minister position were split out from the Ministry of Labour. Twenty-eight people have held the position, representing six parties. Sixteen people have represented the Labour Party, five the Centre Party, two each the Christian Democratic Party, the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party and one for the Progress Party. The longest-sitting minister is Kjell Opseth (Labour) who sat a week short of six years. Lars Leiro (Centre) sat for only four weeks, giving him the shortest tenure. He both succeeded and preceded Trygve Bratteli, the only person to have held the position twice and the only officeholder to later become Prime Minister. (Full article...)

The Ambassador Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary of the Russian Federation to the Republic of Austria is the official representative of the President and the Government of the Russian Federation to the President and the Government of the Republic of Austria.
The ambassador and his staff work at large in the Embassy of Russia in Vienna. The post of Russian Ambassador to Austria is currently held by Dmitry Lyubinsky, incumbent since 10 August 2015. (Full article...)

Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Australia-based NGO Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) which measures the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. The GPI ranks 163 independent states and territories (collectively accounting for 99.7 per cent of the world's population) according to their levels of peacefulness. In the past decade, the GPI has presented trends of increased global violence and less peacefulness.
The GPI (Global Peace Index) is developed in consultation with an international panel of peace experts from peace institutes and think tanks with data collected by the Economist Intelligence Unit. The Index was first launched in 2007, with subsequent reports being released annually. In 2015 it ranked 165 countries, up from 121 in 2007. The study was conceived by Australian technology entrepreneur Steve Killelea, and is endorsed by individuals such as former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan, the Dalai Lama, and 2008 Nobel Peace Prize laureate Martti Ahtisaari. The updated index is released each year at events in London, Washington, D.C., and at the United Nations Secretariat in New York City. (Full article...)
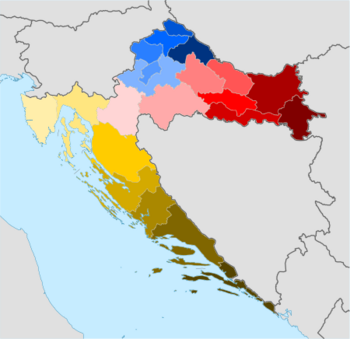
The counties of Croatia (Croatian: hrvatske županije) are the first-level administrative subdivisions of the Republic of Croatia. Since they were re-established in 1992, Croatia has been divided into 20 counties and the capital city of Zagreb, which has the authority and legal status of both a county and a city (separate from the surrounding Zagreb County). As of 2015, the counties are subdivided into 128 cities and 428 (mostly rural) municipalities. The divisions have changed over time since the medieval Croatian state. They reflected territorial losses and expansions; changes in the political status of Dalmatia, Dubrovnik and Istria; and political circumstances, including the personal union and subsequent development of relations between the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia and the Kingdom of Hungary. (Full article...)
Two counties were renamed after their creation. Carter County was renamed Sweetwater County on December 1, 1869. Pease County, formed in 1875, was renamed Johnson County in 1879. (Full article...)

The papal conclave of 2013 was convened to elect a pope, the leader of the Catholic Church, to succeed Benedict XVI following his resignation on 28 February 2013. In accordance with the apostolic constitution Universi Dominici gregis, which governed the vacancy of the Holy See, only cardinals who had not passed their 80th birthday on the day on which the Holy See became vacant (in this case, those who were born on or after 28 February 1933) were eligible to participate in the conclave. Although not a formal requirement, the cardinal electors invariably elect the pope from among their number. The election was carried out by secret ballot (Latin: per scrutinium).
Of the 207 members of the College of Cardinals at the time of Benedict XVI's resignation, there were 117 cardinal electors who were eligible to participate in the subsequent conclave. Two cardinal electors did not participate, decreasing the number in attendance to 115. The number of votes required to be elected pope with a two-thirds supermajority was 77. (Full article...)

Districts (Sinhala: දිස්ත්රික්ක, romanized: Distrikka, Tamil: மாவட்டம், romanized: Māvaṭṭam) are the second level administrative divisions of Sri Lanka, preceded by provinces. Sri Lanka has 25 districts organized into 9 provinces. Districts are further divided into a number of divisional secretariats (commonly known as D.S. divisions), which are in turn subdivided into 14,022 grama niladhari divisions. There are 331 DS divisions in Sri Lanka.
Each district is administered under a district secretary, who is appointed by the central government. The main tasks of the district secretariat involve coordinating communications and activities of the central government and divisional secretariats. The district secretariat is also responsible for implementing and monitoring development projects at the district level and assisting lower-level subdivisions in their activities, as well as revenue collection and coordination of elections in the district. (Full article...)

The prime minister of Pakistan (Urdu: وزير اعظم, romanized: Wazīr ē Aʿẓam, lit. 'Grand Vizier', Urdu pronunciation: [ʋəˈziːɾˌeː ˈɑː.zəm]) is the popularly elected politician who is the chief executive of the Government of Pakistan. The prime minister is vested with the responsibility of running the administration through his appointed federal cabinet, formulating national and foreign policies to ensure the safeguard of the interests of the nation and its people through the Council of Common Interests as well as making the decision to call nationwide general elections for the bicameral Parliament of Pakistan.
Since 1947, Pakistan has had 20 prime ministers, aside from the appointed caretaker prime ministers who were only mandated to oversee the system until the election process was finished. In Pakistan's parliamentary system, the prime minister is sworn in by the president and usually is the chairman or the president of the party or coalition that has a majority in the National Assembly– the lower house of Pakistan Parliament. (Full article...)
The governor of New Jersey is the head of government of New Jersey and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws and the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the New Jersey Legislature, to convene the legislature, and to grant pardons, except in cases of treason or impeachment.
The first New Jersey State Constitution, ratified in 1776, provided that a governor be elected annually by the state legislature, the members of which were selected by the several counties. Under this constitution, the governor was president of the upper house of the legislature, then called the Legislative Council. The 1844 constitution provided for a popular vote to elect the governor, who no longer presided over the upper house of the legislature, now called the Senate. The 1844 constitution also lengthened the governor's term to three years, set to start on the third Tuesday in January following an election, and barred governors from succeeding themselves. The 1947 constitution extended terms to four years, and limits governors from being elected to more than two consecutive terms, though they can run again after a third term has passed. Joseph Bloomfield, Peter Dumont Vroom, Daniel Haines, Joel Parker, Leon Abbett, and Walter Evans Edge each served two non-consecutive stints as governor while A. Harry Moore served three non-consecutive stints. Foster McGowan Voorhees, James Fairman Fielder, and Richard Codey each served two non-consecutive stints, one as acting governor and one as official governor. (Full article...)
Selected quote
Selected biography
Gregory Richard Gianforte (/ˌdʒiːənˈfɔːrteɪ/ JEE-ən-FOR-tay; born April 17, 1961) is an American businessman, politician, and software engineer serving as the 25th governor of Montana since 2021. A member of the Republican Party, Gianforte served as the U.S. representative for Montana's at-large congressional district from 2017 to 2021.
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that even though the Legislative Assembly of Quebec ordered a monument of Maurice Duplessis in front of its building, later premiers hid it for 16 years to avoid political tensions?
- ... that Nobel laureate Thomas Mann reportedly did not want his Reflections of a Nonpolitical Man to be translated into English during his lifetime due to its chauvinistic content?
- ... that political philosophy professor Werner J. Dannhauser was the basis for a character in a Saul Bellow novel?
- ... that Patricia Grace did not intend for her novel Potiki, about the impact of land development on an indigenous community, to be seen as political?
- ... that the Chinese government began compiling an official history of the Qing dynasty in 2002, but as of 2023 a protracted political review is forestalling its publication?
- ... that Ken Russell went on international yo-yo tours before turning to politics?
More did you know...
- ...that the Communist League of America was formed after some members of the Communist Party USA were expelled for Trotskyism?
- ...that, at a congress in May 1921, all Socialist Party of Romania delegates who supported Bolshevik guidelines were arrested 24 hours after a vote on affiliation to the Comintern?
- ...that Ngo Dinh Diem became president of South Vietnam after a fraudulent 1955 election run by his brother Ngo Dinh Nhu, polling 133% of registered voters in Saigon?
- ...that the Brothers Grimm were amongst the Göttingen Seven, university teachers who protested changes to the constitution of the Kingdom of Hanover in 1837?
- ...that the UK's Workers Socialist Federation began as a suffragette group?
- ...that the controversial Iraq De-Ba'athification policy banned anyone affiliated with the Ba'ath Party from working in the public sector?
In this month
- November 4, 1980 – Ronald Reagan defeats Jimmy Carter in the presidential election and becomes the 40th President of the United States.
- November 4, 2008 – Barack Obama was elected as the 44th President of the United States, becoming the first African American elected to the office. Congressional elections for the House of Representatives and one third of the Senators (second class) were also held.
- November 7, 2000 – Hillary Rodham Clinton is elected to the United States Senate, becoming the first First Lady of the United States to win public office.
- November 7, 1917 – The workers of the Petrograd Soviet in Russia, led by the Bolshevik Party and leader Vladimir Lenin, storm the Winter Palace and successfully destroy the Kerensky Provisional Government, resulting in the first overthrow of capitalism in history.
- November 11, 2004 – Former Palestinian President Yasser Arafat dies from a mysterious illness, aged 75.
- November 21, 2004 – Ukrainian presidential election, 2004: Viktor Yanukovych is declared the winner in the final round. International election observers express severe criticism, and large crowds gather in a protest rally in Kiev; 12 days later, the Supreme Court annuls the result, and a new poll is scheduled.
- November 22, – In Dallas, Texas, United States President John F. Kennedy is assassinated, Texas Governor John B. Connally is seriously wounded, and Vice President Lyndon Baines Johnson becomes the 36th President. All television coverage for the next four days is devoted to the assassination, its aftermath, the procession of the horsedrawn casket to the Capitol Rotunda, and the funeral of President Kennedy. Stores and businesses shut down for the entire weekend and Monday, in tribute.
News and Current events
- August 11: 4 local government areas in New South Wales, Australia locked down after COVID-19 case
- August 11: Australia: AstraZeneca vaccine access expanded by Victorian government
- August 1: Australia: Victorian lockdown lifted
- July 29: Tunisia's president dismisses prime minister, suspends parliament
- July 25: Australia: Wikinews interviews Reg Kidd, mayor of the City of Orange, about COVID-19 lockdown and local government
- July 23: South Australia enters week-long lockdown to contain COVID-19 Delta variant spread
- July 21: Technological University Dublin senior lecturer Dr Lorcan Sirr speaks to Wikinews on housing market in Ireland
- July 21: Three rural councils in New South Wales, Australia enter 7-day lockdown
- July 21: Australia: Victoria lockdown extended by a week with 85 active cases recorded
- July 15: California governor signs new state budget, eligible Californians to get stimulus payments
Topics and categories
General images
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus