Portal:Geography/Featured article/8
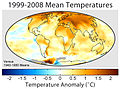
Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's atmosphere and oceans that has been observed in recent decades. The scientific opinion on climate change is that much of the recent change may be attributed to human activities. Carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases released by the burning of fossil fuels, land clearing, agriculture, among other human activities, are the primary sources of the human-induced component of warming. Observational sensitivity studies and climate models referenced by the IPCC predict that global temperatures may increase by between 1.4 and 5.8 °C between 1990 and 2100. An increase in global temperatures can in turn cause other changes, including rises in sea level and changes in the amount and pattern of precipitation. These changes may increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as tropical cyclones or floods. There are a few scientists who contest the view about attribution of recent warming to human activity. Uncertainties exist regarding how much climate change should be expected in the future, and there is a hotly contested political and public debate over attempts to reduce or reverse future warming, and how to cope with possible consequences.