Portal:Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands Portal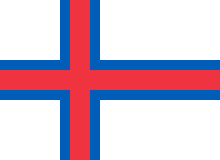 The Faroe or Faeroe Islands (/ˈfɛəroʊ/ FAIR-oh), or simply the Faroes (Faroese: Føroyar, pronounced [ˈfœɹjaɹ] ; Danish: Færøerne [ˈfeɐ̯ˌøˀɐnə]), are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. The official language of the country is Faroese, which is closely related to and partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic. Located a similar distance from Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a total area of about 1,400 square kilometres (540 sq mi) with a population of 54,676 as of August 2023. The terrain is rugged, and the subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc), is windy, wet, cloudy, and cool. Despite the northerly climate, the temperatures are moderated by the Gulf Stream and average above freezing throughout the year, hovering around 12 °C (54 °F) in summer and 5 °C (41 °F) in winter. As a result of its northerly latitude and proximity to the Arctic Circle, the islands experience perpetual civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days. The capital and largest city, Tórshavn, receives the fewest recorded hours of sunshine of any city in the world at only 840 per year. While archaeological evidence places the first known habitation as early as the 4th century, Færeyinga Saga and the writings of Dicuil place initial Norse settlement in the early 9th century. As with the subsequent Settlement of Iceland, the islands were mainly settled by Norwegians and Norse-Gaels, who additionally brought thralls (i.e. slaves or serfs) of Gaelic origin. Following the introduction of Christianity by Sigmundur Brestisson, the islands came under Norwegian rule in the early 11th century. The Faroe Islands followed Norway's integration into the Kalmar Union in 1397, and came under de facto Danish rule following that union's dissolution in 1523. Following the introduction of Lutheranism in 1538, the usage of Faroese was banned in churches, schools and state institutions, and disappeared from writing for more than three centuries. The islands were formally ceded to Denmark in 1814 by the Treaty of Kiel along with Greenland and Iceland, and the Løgting was subsequently replaced by a Danish judiciary. Following the re-establishment of the Løgting and an official Faroese orthography, the Faroese language conflict saw Danish being gradually displaced by Faroese as the language of the church, public education and law in the first half of the 20th century. The islands were occupied by the British during the Second World War, who refrained from governing Faroese internal affairs: inspired by this period of relative self-government and the declaration of Iceland as a republic in 1944, the islands held a referendum in 1946 that resulted in a narrow majority for independence. The results were annulled by Christian X, and subsequent negotiations led to the Faroe Islands being granted home rule in 1948. While remaining part of the Kingdom of Denmark to this day, the Faroe Islands have extensive autonomy and control most areas apart from military defence, policing, justice and currency, with partial control over its foreign affairs. Because the Faroe Islands are not part of the same customs area as Denmark, they have an independent trade policy and are able to establish their own trade agreements with other states. The islands have an extensive bilateral free trade agreement with Iceland, known as the Hoyvík Agreement. In the Nordic Council, they are represented as part of the Danish delegation. In certain sports, the Faroe Islands field their own national teams. They did not become a part of the European Economic Community in 1973, instead keeping autonomy over their own fishing waters; as a result, the Faroe Islands are not a part of the European Union today. The Løgting, albeit suspended between 1816 and 1852, holds a claim as one of the oldest continuously running parliaments in the world. (Full article...) Selected article -The Faroe Islands sent a delegation to compete at the 2016 Summer Paralympics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from 7–18 September 2016. They sent one participant, Krista Mørkøre, who participated in three events in swimming. Her top finish was 10th in women's 400 m freestyle S10, and she did not qualify for the finals of any of her three events. (Full article...) Selected picture -Things you can do
Geography stubs · People stubs · Sports clubs stubs · Faroese stubs in general
Help us categorize Faroe Islands-related articles
Have a look at WikiProject Faroe Islands, WikiProject Denmark, WikiProject Greenland and WikiProject Norse history and culture Related portalsGeneral imagesThe following are images from various Faroe Islands-related articles on Wikipedia.
SubcategoriesDid you know...
Wikipedia in Faroese
Faroe Islands topicsAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |