Portal:Chess
Introduction
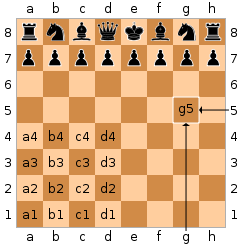
Chess is a board game for two players. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess).
Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no elements of chance. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, generically referred to as "White" and "Black", each control sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, two bishops, two knights, and eight pawns. White moves first, followed by Black; they then alternate moves. Each player’s ultimate goal is to checkmate (threaten with inescapable capture) the opposing king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw.
The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. After its introduction in Persia, it spread to the Arab world and then to Europe. The rules of chess as they are known today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games and is played by millions of people worldwide. (Full article...)
Selected article -
In chess, a relative value (or point value) is a standard value conventionally assigned to each piece. Piece valuations have no role in the rules of chess but are useful as an aid to assessing a position.
The best known system assigns 1 point to a pawn, 3 points to a knight or bishop, 5 points to a rook and 9 points to a queen. However, valuation systems provide only a rough guide and the true value of a piece is very position dependent.
(Full article...)General images
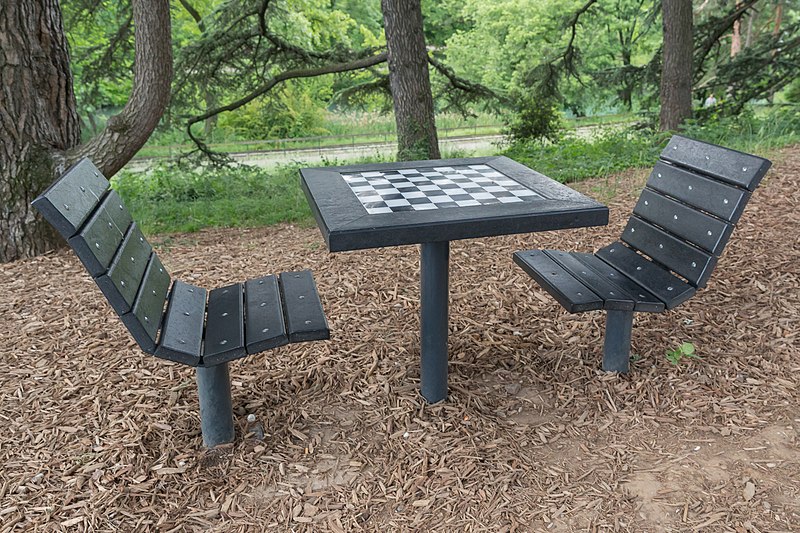
Selected image
FIDE world ranking
| Rank | Player | Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2831 | |
| 2 | 2805 | |
| 3 | 2802 | |
| 4 | 2799 | |
| 5 | 2783 | |
| 6 | 2777 | |
| 7 | 2763 | |
| 8 | 2755 | |
| 9 | 2753 | |
| 10 | 2750 | |
| 11 | 2747 | |
| 12 | 2741 | |
| 13 | 2740 | |
| 14 | 2739 | |
| 15 | 2739 | |
| 16 | 2739 | |
| 17 | 2738 | |
| 18 | 2737 | |
| 19 | 2737 | |
| 20 | 2734 |
Top 10 WikiProject Chess Popular articles of the month
Did you know...
- ... that Magnus Carlsen, the current World Chess Champion, resigned a recent tournament game after only one move?
Reviewed articles
Chess from A to Z
| Index: | A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z (0–9) |
| Glossary: | A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
Topics
Subcategories
Related portals
Related WikiProjects
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus