Polish Special Forces
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2022) |
| Special Troops Command | |
|---|---|
| Wojska Specjalne | |
 | |
| Founded | 2007 |
| Country | |
| Type | Special forces command |
| Size | 3 841 soldiers (2023)[1] |
| Part of | Polish Armed Forces |
| Garrison/HQ | Kraków |
| Engagements | Operation Uphold Democracy War in Afghanistan Iraq War Syrian civil war • Personnel recovery • Emergency evacuation |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the General Staff | Gen. broni Rajmund Andrzejczak |
| General Commander | Gen. broni Jarosław Mika |
| Special Operations Component Commander | Gen. bryg. Sławomir Drumowicz |
| Insignia | |
| Flag[2] |  |
The Special Troops Command (Polish: Wojska Specjalne) is the special forces command of the Polish Armed Forces (SZ RP). The command was formed in 2007 and is the fourth military branch of the SZ RP.
Composition
[edit]The Special Troops Command (Dowództwo Wojsk Specjalnych) is based in Kraków and comprises:
- Jednostka Wojskowa GROM, or GROM, based in Warsaw and Gdańsk
- Jednostka Wojskowa Komandosów, or JWK, based in Lubliniec
- Jednostka Wojskowa Formoza, or JW FORMOZA, is based in Gdynia
- Jednostka Wojskowa Agat, or AGAT, based in Gliwice
- Jednostka Wojskowa NIL, or NIL, is based in Kraków
- Special Operations Aviation Unit based in Powidz; only operational command it is part of the Air Force.
Structure
[edit]
GROM - Operational-Maneuver Response Group "Cichociemni" (Silent Unseen)
- Command and Support Staff – in Warsaw
- A Squadron (ZB A) – Land Element located in Warsaw
- B Squadron (ZB B) – Maritime Element located in Gdańsk
- C Squadron (ZB C) – Specialty unknown located in Warsaw
- Logistic and Security Unit - located in Warsaw
JW Komandosów - Army Commandos
- Command and Security – insignia of the Batalion Zośka from the Polish Home Army
- A Squadron (ZB A) – insignia of the Batalion Miotła from the Polish Home Army and insignia of PSBS
- B Squadron (ZB B) – Combined Operations insignia of the No. 10 (Inter-Allied) Commando unit and its No. 6 Troop (Polish)
- C Squadron (ZB C) – insignia of the Batalion Parasol from the Polish Home Army
- D Squadron (ZB D) – set up in 2016
- Information Support Group
- Special Forces Training Center
JW Formoza – name comes from the colloquial name of the units base, the post-German torpedo house in Gdynia, called "Formoza".[3]
- Special Operations Squadron - at least six special operations sections and a base unit

JW AGAT – formed on the basis of the Special Branch of the Military Police in Gliwice.[4] Named after "Agat" (abbreviation of anty-gestapo) special unit of the Polish Home Army
- HQ Staff and Command Group
- "A" Company
- "B" Company
- "C" Company
- Combat Support Team
- Logistics Security Team
- Medical Security Group
JW NIL – Support Unit of Command and Security of Special Forces[5]
- HQ Staff
- Command Team
- Logistics Security Team
- Information Support Team
- Medical Security Group
Special Operations Aviation Unit – based in Powidz
- HQ staff
- Aerospace Group - equipped with 8 Mi-17, including 4 Mi-17-1W and 4 Sikorsky S-70i[6][7] all helicopters are to be equipped with M134Gs[8]
- Maintenance Group
Gallery
[edit]-
GROM operator conducting a port security exercise
-
Polish GROM and US Navy SEALs conducting joint field exercises
-
GROM unit conducting ship seizure training
-
GROM operator conducting a pistol training exercise
Equipment
[edit]Weaponry
[edit]| Name | Type | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard firearms of the Polish Armed Forces | |||
| Kbs wz. 1996 Beryl | Assault rifle | 
|
Most commonly used weapon |
| Pallad grenade launcher | Grenade launcher | Polish made grenade launcher, used from its introduction to the army | |
| SWD | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Sako TRG | Sniper Rifle | ||
| PKM | General purpose machine gun | ||
| UKM-2000 | General purpose machine gun |  |
|
| Standard firearms of the Polish Special Forces | |||
| Heckler & Koch USP | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW GROM, JW NIL and JW komandosów |
| Glock 17 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW Komandosów, JW AGAT and JW NIL |
| SIG P226 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol in JW Formoza (Navy Unit) |
| FN Five-seven | Semi-auto pistol |  |
Standard pistol for close protection in JW Grom |
| CZ Scorpion Evo 3 | Submachine gun | New addition SMG for direct force operations in JW Grom | |
| Heckler & Koch MP5 | Submachine gun |  |
Standard SMG for direct force operations in JW GROM, JW komandosów, JW Formoza and JW AGAT |
| FN P90 | Submachine gun |  |
Standard SMG for close protection in JW Grom |
| Colt M4A1 | Assault rifle |  |
Mostly supplanted the Beryl in JW GROM and JW NIL (M4A3) |
| Heckler & Koch HK416 | Assault rifle |  |
Assault rifle used by the Polish SOF, JW Grom, JW Komandosów, JW NIL and JW Agat. Various barrel options used (10, 14.5 and 16.5 inch). Most commonly used assault rifle of the Special Forces |
| Heckler & Koch AG-C/GLM | Grenade launcher |  |
Standard under-barrel grenade launcher used with the HK416 |
| Heckler & Koch G36 | Assault rifle | Used in JW Formoza and JW GROM | |
| Heckler & Koch AG36 | Grenade launcher | Standard grenade launcher used with the G36 | |
| FN Minimi | Light machine gun |  |
Most common light machine gun in the Polish SOF |
| Carl Gustav | Recoilless rifle |  |
|
| Other firearms | |||
| Beretta 92 | Semi-auto pistol |  |
|
| M4 Carbine | Assault rifle |  |
Clones made by KAC and Bushmaster |
| F2000 | Assault rifle |  |
|
| M14 rifle | Battle rifle |  |
Upgraded to EBR standard |
| M203 | Grenade launcher |  |
|
| H&K MZP-1 | Grenade launcher | ||
| Remington 870 | Shotgun | ||
| Heckler & Koch PSG-1 | Sniper rifle | ||
| Remington 700 | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Mauser SP66 | Sniper rifle |  |
|
| Mauser 86 | Sniper rifle | ||
| Barrett M82 | Anti-material rifle | ||
Vehicles
[edit]| Name | Type | Variant | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMMWV | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | M1151A1
M1165A1 |
42
? |
In 2009, JW AGAT and JW Komandosów each received 15 M1151A1 vehicles. The remaining 12 vehicles, probably without Frag Kit armor but equipped with an advanced communication system, were delivered to JW GROM. Additionally, later the Special Forces Command decided to purchase an unspecified number of M1165A1 Special Ops, the so-called Ground Mobility Vehicle, i.e. a vehicle configured exclusively for the needs of special forces[9] |
| Oshkosh M-ATV | MRAP | M1240A1 | 45[10] | Donated by the United States.[11] |
| Toyota | Four-wheel drive vehicle | Land Cruiser Hilux[12] |
Used by GROM and 1 Pułk Specjalny Komandosów (1st Special Commando's Regiment) | |
| Land Rover Defender | Four-wheel drive vehicle | 90 110 |
4[13] 6 |
Used by JW GROM and JW Formoza |
| Mercedes-Benz | Four-wheel drive vehicle Truck |
G-class Atego 1323AK |
6 10[14] |
The Polish Armed forces currently operate a total of 140 G-class vehicles.[15] The Land forces operate 121 GD 290s and MB290GD WDs.[14] The military police uses 13 GD 290s.[14] |
| Tarpan Honker | 4x4 | Honker Skorpion 3 special version | Used by JW komandosów | Polish made off-road vehicles, best variants are powered with Polish Andoria engines |
| Defenture VECTOR | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | Defenture GRF 4x4 | 2 option of ordering additional units[16] | Purchased by Grom. Defenture GRF vehicles will join the fleet of the Polish Tier 1 unit.[17] |
| Star | Truck | Star 1444 (MAN TGM 18.280 BB) | 1[14] | Polish made trucks, now modernised to adjust to new weaponry and specifications |
| Volvo | Truck | Volvo FM 8x4 Volvo FM 6x6 Volvo FM 4x4 |
10[14] 11[14] 2[14] |
|
| Yamaha | Motorbike | Yamaha XT660 | unknown | Used in JW NIL |
| Polaris | Quad | Polaris Sportsman 500 EFI | unknown | Used in all Polish SOF units |
| Range Rover | SUV | Range Rover Armoured | unknown | Used in Polish SOF Command |
Aircraft
[edit]
| Name | Type | Variant | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-70i Black Hawk | Medium-lift transport/utility helicopter | S-70i | 4/8 | 4 on order, 2 scheduled for delivery in 2023, remaining in 2024.[18] In 2019 7 S-70i Black Hawks were ordered and received. 4 to Special Forces and 3 to the Police.[18] |
Unmanned aerial vehicle
[edit]| Name | Image | Type | In service | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FlyEye | 
|
Small UAV | 44 | |
| RQ-21 Blackjack | 
|
Small UAV | 10[19] | |
| ScanEagle | 
|
Small UAV | 10 | As a result of the contract concluded in 2010 by the United States Department of Defense with Insitu, the Polish Army received one ScanEagle Block D UAV set free of charge, containing a ground system and 10 air platforms. Its user is the Jednostka Wojskowa NIL |
| Aeronautics Orbiter | 
|
Mini UAV | 13[20] | The first set of mini Aeronautics Orbiter class UAVs (4 flying devices) was purchased in October 2005 for the Jednostka Wojskowa GROM, the next three sets (3 flying devices each) were purchased in February 2007 |
| Mayfly | Mikro UAV | 24[21] | ||
| Black Hornet 3 | 
|
Nano UAV | 40 sets[22] |
Rank insignia
[edit]- Officers
| NATO Code | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Special Forces |

|

|

|

|

|

|
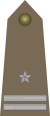
|

|

|

|
| Polish name | Generał1 | Generał broni |
Generał dywizji |
Generał brygady |
Pułkownik | Podpułkownik | Major | Kapitan | Porucznik | Podporucznik |
| Abbreviation | gen. | gen. broni | gen. dyw. | gen. bryg. | płk | ppłk | mjr | kpt. | por. | ppor. |
|
1 Until 2004 Generał armii | ||||||||||
- Enlisted
| NATO Code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Special Forces |

|

|

|

|

|

|
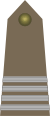
|

|

|

|

|
| Polish name | Starszy chorąży sztabowy |
Starszy chorąży |
Chorąży | Młodszy chorąży |
Starszy sierżant |
Sierżant | Plutonowy | Starszy kapral |
Kapral | Starszy szeregowy |
Szeregowy |
| Abbreviation | st. chor. szt. | st. chor. | chor. | mł. chor. | st. sierż. | sierż. | plut. | st. kpr. | kpr. | st. szer. | szer. |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "2021 Budżet MON - Decyzja budżetowa MON załącznik do decyzji" [Annex to 2023 Budget decision of the Ministry of National Defense] (PDF). Republic of Poland website (in Polish). Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ "Ustawa z dnia 19 lutego 1993 r. o znakach Sił Zbrojnych Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej" [Act of February 19, 1993 on the symbols of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland] (PDF). isap.sejm.gov.pl (in Polish). Internet System of Legal Acts. pp. 24–28. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ "JW FORMOZA - USSE". usse.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Jednostka Wojskowa "Agat"". www.jednostki-wojskowe.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Jednostka Wojskowa "Nil"". www.jednostki-wojskowe.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Siminski, Jacek (2019-12-23). "Polish Special Ops Component Receives S-70i Black Hawk Helicopters". The Aviationist. Retrieved 2020-04-21.
- ^ "Mil Mi-17-1V Hip, lokalizacja: Powidz - (EPPW), autor: Marek Purat". Galeria Aviateam.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Miniguny w końcu kupione". www.altair.com.pl. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "HMMWV w Wojsku Polskim".
- ^ "Kolejna dostawa sprzętu z USA dla Wojska Polskiego". defence24.pl (in Polish). 2024-01-08. Retrieved 2024-01-08.
- ^ "Polskie Wojska Specjalne otrzymały od Amerykanów 45 pojazdów opancerzonych M-ATV". technologie.onet.pl. 26 February 2015. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09
- ^ "Nadjeżdża Huzar". 4 January 2005.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Zakupy pojazdów dla Wojska Polskiego". Gdzie zaczyna się wojsko... 3 January 2011.
- ^ Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09 96
- ^ "GROM kupuje holenderskie wszędołazy [ANALIZA]" (in Polish). 24 July 2024. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- ^ "GROM kupuje holenderskie wszędołazy [ANALIZA]" (in Polish). 24 July 2024. Retrieved 2024-08-12.
- ^ a b "Poland Purchases Four New S-70i Black Hawk Helicopters". 17 December 2021.
- ^ "RQ-21A BlackJack na MSPO". polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 2023-12-24.
- ^ ZBIAM (2022-05-19). "Bezzałogowe statki powietrzne w Wojsku Polskim - raport specjalny [DO POBRANIA]". Wydawnictwo militarne ZBIAM (in Polish). Retrieved 2023-12-24.
- ^ "Polska Zbrojna". polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 2023-12-24.
- ^ "Nano bezzałogowce dla wojska. Black Hornet w Lublińcu". defence24.pl (in Polish). 2019-06-15. Retrieved 2023-12-24.




