Petasin
Appearance
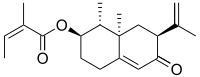
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
8-Oxo-7α-eremophila-9,11-dien-3α-yl (2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,2R,7S,8aR)-1,8a-Dimethyl-6-oxo-7-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,6,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-2-yl (2Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Petasol butenoate; O-Angeloylsencathenone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H28O3 | |
| Molar mass | 316.441 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Petasin is a natural chemical compound found in plants of the genus Petasites. Chemically, it is classified as a sesquiterpene and is the ester of petasol and angelic acid.
Petasin is believed to be responsible, at least in part, for the anti-inflammatory effects of common butterbur (Petasites hybridus) extracts.[1]
A 2021 study reported that petasin can inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in an animal model of cancer.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Thomet, O; Wiesmann, UN; Schapowal, A; Bizer, C; Simon, HU (2001). "Role of petasin in the potential anti-inflammatory activity of a plant extract of petasites hybridus". Biochemical Pharmacology. 61 (8): 1041–7. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(01)00552-4. PMID 11286996.
- ^ Heishima, Kazuki; Sugito, Nobuhiko; Soga, Tomoyoshi; Nishikawa, Masashi; Ito, Yuko (2021). "Petasin potently inhibits mitochondrial complex I–based metabolism that supports tumor growth and metastasis". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 131 (17): e139933. doi:10.1172/JCI139933. PMC 8409585.
