Sympathetic ganglia
| Sympathetic ganglia | |
|---|---|
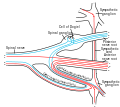
 Autonomic nervous system innervation, showing the sympathetic (thoracolumbar) and parasympathetic (craniosacral) systems, in red and blue, respectively | |
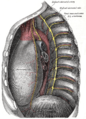
 Diagram of the course and branches of a typical intercostal nerve. (Sympathetic ganglion visible at center top.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglia sympathicum |
| MeSH | D005728 |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.011 |
| TA2 | 6169 |
| FMA | 5890 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. The cell bodies create long sympathetic chains that are on either side of the spinal cord. They also form para- or pre-vertebral ganglia of gross anatomy.
The efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain to the body regarding perceptions of danger. This perception of danger can instigate the fight-or-flight response associated with the sympathetic nervous system.[1] The fight-or-flight response is adaptive when there is a real and present danger which can be avoided or diminished through increased sympathetic activity. Sympathetic activity could be increased heart rate, dilated pupils, or sweaty palms, for example. The fight-or-flight response is maladaptive when the danger is imagined, prolonged, or when it lasts after the threat is over. When the intensity or duration of the response is excessive, the individual may meet criteria for a variety of psychological disorders.[2] Neuroblastoma tumors can arise from the sympathetic ganglia tissue.[3]
Structure
[edit]Sympathetic chain ganglia
[edit]The bilaterally symmetric sympathetic chain ganglia, also called the paravertebral ganglia, are located just ventral and lateral to the spinal cord.[3] The chain extends from the upper neck down to the coccyx, forming the unpaired ganglion impar. Ganglia within this chain are either cervical, thoracic, lumbar, or sacral. Preganglionic nerves from the spinal cord synapse at one of the chain ganglia, and the postganglionic fiber extends to an effector, a visceral organ in the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, or pelvic cavity.
There are usually 22–23 pairs of these ganglia: three cervical ganglia, 12 thoracic ganglia (the stellate ganglion (cervicothoracic) is formed from the fusion of the first thoracic ganglion with the inferior cervical ganglion), four lumbar ganglia, and four or five sacral ganglia. In the area of the coccyx there is a small ganglion impar. The stellate ganglion is so named due to its radiating pattern similar in appearance to a star.
The general rule of interaction of the nerve fibers in the sympathetic nervous system begins at the spinal cord. Here they arise from the thoracolumbar (T1–L2) regions' lateral horn of grey and emerge via the ventral root. They enter their respective spinal nerve (e.g. T5), and thus enter the white ramus communicans. This myelinated division can then enter the sympathetic chain.
Here four options are available to the fibers: (1) they can run up the chain and synapse, (2) they can synapse at the level of entry, (3) they can pass straight through and synapse elsewhere – such as in the case of T5–12 (the splanchnic nerves), or (4) they can enter the chain and descend to synapse. It is this ability to move superiorly and inferiorly along the chain that results in the mass response to the sympathetic nervous system. A preganglionic fibre may synapse to 15–20 postganglionic fibres. The postganglionic neurons extend across most of the body.[4]
Upon exiting the sympathetic chain, the fibres enter a less-myelinated gray ramus communicans. There is still a myelin sheath present – but in far lower amounts compared to the white ramus communicans. This ramus then enters the spinal nerve and is either sent to its synapsing target, or becomes a visceral branch to enter a plexus such as the superficial or deep cardiac plexuses.
Prevertebral ganglia
[edit]Neurons of the prevertebral ganglia, also called collateral ganglia, receive input from the splanchnic nerves and innervate organs of the abdomen and pelvis. These include the celiac ganglia, superior mesenteric ganglia, and inferior mesenteric ganglia.
Additional images
[edit]-
Schematic Illustration of Sympathetic Innervation
-
The thoracic aorta, viewed from the left side.
-
Scheme showing structure of a typical spinal nerve.
-
Transverse section of human embryo eight and a half to nine weeks old.
References
[edit]- ^ Life, the science of biology. Sadava, David E. (8th ed.). Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates. 2008. ISBN 9780716776710. OCLC 71632224.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ American Psychiatric Association (2013-05-22). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association. doi:10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596. hdl:2027.42/138395. ISBN 978-0890425558.
- ^ a b "Structure of the Autonomic Nervous System | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology". courses.lumenlearning.com. Retrieved 2019-10-28.
- ^ Drake, Richard L. (Richard Lee), 1950– (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Vogl, Wayne., Mitchell, Adam W. M., Gray, Henry, 1825–1861. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0443066124. OCLC 55139039.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
See also
[edit]- Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- Adrenaline
- Noradrenaline
- Sympathetic nervous system
- Ganglion
- Autonomic ganglia
- Parasympathetic ganglia
External links
[edit]- thoraxlesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (paravertebralregion)