Nanticoke River
| Nanticoke River | |
|---|---|
 The Nanticoke at Vienna, Maryland | |
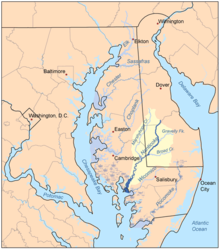 Map of the rivers of the Eastern Shore of Maryland with the Nanticoke and its watershed highlighted. | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| States | Maryland Delaware |
| Region | South Atlantic States |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Middleford, Delaware |
| • coordinates | 38°52′55″N 075°33′36″W / 38.88194°N 75.56000°W[1] |
| • elevation | about 60 feet |
| Mouth | Chesapeake Bay |
• location | Waterview, Maryland |
• coordinates | 38°14′00″N 075°55′29″W / 38.23333°N 75.92472°W[1] |
• elevation | sea level (0 ft.) |
| Length | about 63 miles[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Chesapeake Bay → Atlantic Ocean |
| River system | Chesapeake Bay |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Kent-Sussex Line Branch, Glade Branch, Gum Branch, Gravelly Branch, Hurley Drain, Deep Creek, Morgan Branch, Gum Branch, Broad Creek, Beaverdam Branch, Cod Creek, Plum Creek, Reconow Creek, Owens Creek, Grimes Creek, Barren Creek, Ingem Gut, Den Creek, Rewastico Creek, Quantico Creek, Wetipquin Creek, Dunn Creek, Windsor Creek |
| • right | White Marsh Branch, Cart Branch, Polk Branch, Birdgeville Branch, Turkey Branch, Ake Ditch, Clear Brook, Chapel Branch, Turtle Branch, Wright Creek, Gales Creek, Dennis Creek, Mill Creek, Molly Horn Creek, Marshyhope Creek, Chicone Creek, Redfin Creek, Mill Creek, Peach Orchard Creek, Wapremander Creek, Jacks Creek, Langrells Creek, Cow Creek |
The Nanticoke River is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay on the Delmarva Peninsula. It rises in southern Kent County, Delaware, flows through Sussex County, Delaware, and forms the boundary between Dorchester County, Maryland and Wicomico County, Maryland. The tidal river course proceeds southwest into the Tangier Sound, Chesapeake Bay. The river is 64.3 miles (103.5 km) long.[2] A 26-mile ecotourism water trail running along the River was set aside in July 2011 by Delaware state and federal officials, contiguous with a 37-mile water-trail extending through Maryland to the Chesapeake Bay.[3]
Some of the main tributaries that feed the Nanticoke on the west-side include: Cow Creek; Jack Creek; Wapremander Creek; Marshyhope Creek; and the east side: Gravelly Fork, Gum Branch, and Broad Creek. Notable towns and communities situated along the river include Nanticoke, Bivalve, Vienna, and Sharptown in Maryland; and further north the city of Seaford, Delaware.
According to a study paid for by the town of Vienna, the English explorer John Smith travelled up the Nanticoke River and mapped it, and visited with Native Americans in their settlement, now believed to be Vienna.[4]
The river was dredged in 1990 and 2013[5] to facilitate shipping travel along the course.[6]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c "GNIS Detail - Nanticoke River". geonames.usgs.gov. US Geological Survey. Retrieved 24 May 2019.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map, accessed April 1, 2011
- ^ Montgomery, Jeff (10 July 2011), "Officials dedicate trail along Nanticoke", The News Journal, archived from the original on July 10, 2011, retrieved 10 July 2011 Alt URL
- ^ Stump, Brice (2005-02-06). "He's Put Us on the Map". Daily Times. Salisbury, MD.
- ^ "Nanticoke River Dredging Begins (USA)". 28 January 2013. Retrieved 2019-06-12.
- ^ Shortridge, Dan (16 Jan 2012), "Funding holds up Nanticoke River dredging", The News Journal, retrieved 16 Jan 2012
References
[edit]
38°14′0″N 75°55′29″W / 38.23333°N 75.92472°W
- Nanticoke River
- Tributaries of the Chesapeake Bay
- Rivers of Delaware
- Rivers of Maryland
- Rivers of Caroline County, Maryland
- Rivers of Kent County, Delaware
- Rivers of Sussex County, Delaware
- Water trails
- Southern United States river stubs
- Delaware geography stubs
- Eastern Shore, Maryland, geography stubs
- Maryland river stubs
