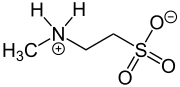
N-Methyltaurine
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.192 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 139.17 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H315, H319 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Methyltaurine (2-methylaminoethanesulfonic acid) is an aminosulfonic acid which is present as a zwitterion in the crystalline state and in polar solvents (just like amino acids).[1] In contrast to the widespread taurine, N-methyltaurine has been found in nature only in red algae,[2] where it is formed by methylation of taurine. It is suitable for esterification (actually amide formation) with long-chain carboxylic acids to taurides (acylaminoethansulfonaten) because of its high polarity and the relatively good solubility of its alkaline earth metal salts, which are also used as mild anionic surfactants.[3]
Preparation
[edit]The synthesis of N-methyltaurine was reported as early as 1878,[4] with methylamine being reacted with the silver salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid. An obvious modification for this reaction is the replacement of the silver salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid by the sodium salt of 2-chloroethanesulfonic acid.[5] The addition of methylamine to sodium vinylsulfonate in aqueous solution gives N-methyltaurine in 85% yield after acidification with acetic acid.[6] The purification of the crude product and preparation of the N-methyltaurine can also be accomplished by passage of the sodium salt solution through a cation exchange resin in its H form and then through an anion exchange resin in its OH form.[7] The reaction of sodium isethionate with methylamine in water at high temperature and pressure yields the sodium salt of N-methyltaurine[8]
which yields pure N-methyltaurine upon saturation with CO2 and removal of the precipitated sodium bicarbonate.[9]
Properties
[edit]N-Methyltaurine is a white powdery solid which is readily soluble in water.
Use
[edit]N-Methyltaurine (or its sodium salt) is used as a polar head group in surfactants from the class of taurides (acylaminoethanesulfonates), sometimes also called methyltaurates. The Taurides are characterized by excellent foaming - even in the presence of oil and skin fats - and foam stability, with good skin compatibility and broad pH stability.[10] The market breakthrough for N-methyltaurine as a hair restorer is still pending.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Kalaitzis, John A; Almeida Leone, Priscila de; Quinn, Ronald J; Healy, Peter C (2003). "Zwitterionic 2-(methylamino)ethanesulfonic acid". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 59 (5): o726. doi:10.1107/S160053680300895X. hdl:10072/6334.
- ^ B. Lindberg, Methylated Taurines and Choline Sulfate in Red Algae, Acta Chem. Scand., 9, 1955, pp 1323 – 1326.
- ^ E.W. Flick, Cosmetic Additives: An Industrial Guide, Noyes Publication, Park Ridge, New Jersey, 1991, ISBN 0-8155-1255-4, S. 352.
- ^ Dittrich, Eugen (1878). "Ueber Methyltaurin und die Bildung von Methyltaurocyamin und Taurocyamin". Journal für Praktische Chemie. 18: 63–78. doi:10.1002/prac.18780180102..
- ^ Schick, John W; Degering, Ed. F (1947). "Synthesis of Taurine and N-Methyltaurine". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 39 (7): 906. doi:10.1021/ie50451a024..
- ^ US 7049464, Kimura, Takuhiro; Tani, Tsutomu & Miyahara, Reiji, "Process for producing of an aminoalkylsulfonic acid and a method of salt exchange for a salt thereof", published 2006-05-23, assigned to Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.
- ^ US 2693488, Sexton, Arthur R., "Purification of amino alkane sulfonic acids by ion exchange", published 1954-11-02, assigned to The Dow Chemical Co.
- ^ US 1932907, Nicodemus, Otto & Schmidt, Walter, "Process of preparing aminoalkylsulphonic acids", published 1933-10-31, assigned to I.G. Farbenindustrie AG
- ^ DE 1122540, Elbel, Eberhard; Kaltenhaeuser, Herbert & Beck, Herwig, "Verfahren zur Herstellung von reinem N-Methyltaurin [Process for the production of pure N-methyltaurine]", published 1962-01-25, assigned to Farbwerke Hoechst AG
- ^ Clariant-Broschüre: Mild Surfactants, (pdf; 801 kB)

