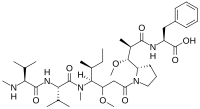
Monomethyl auristatin F
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(S)-2-((2R,3R)-3-((S)-1-((3R,4S,5S)-4-((S)-N,3-dimethyl-2-((S)-3-methyl-2-(methylamino)butanamido)butanamido)-3-methoxy-5-methylheptanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl)-3-methoxy-2-methylpropanamido)-3-phenylpropanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | MMAF |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H65N5O8 | |
| Molar mass | 731.976 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF) is a synthetic antineoplastic agent.[1] It is part of the approved drug belantamab mafodotin in multiple myeloma and some experimental anti-cancer antibody-drug conjugates such as vorsetuzumab mafodotin and SGN-CD19A. In International Nonproprietary Names for MMAF-antibody-conjugates, the name mafodotin refers to MMAF plus its attachment structure to the antibody.[2]
Mechanism of action
[edit]Monomethyl auristatin F is an antimitotic agent which inhibits cell division by blocking the polymerisation of tubulin. It is linked to an antibody with high affinity to structures on cancer cells, causing MMAF to accumulate in such cells.[3]
Chemistry
[edit]MMAF is actually desmethyl-auristatin F; that is, the N-terminal amino group has only one methyl substituent instead of two as in auristatin F itself.[3]

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Tai, Y. T.; Mayes, P. A.; Acharya, C; Zhong, M. Y.; Cea, M; Cagnetta, A; Craigen, J; Yates, J; Gliddon, L; Fieles, W; Hoang, B; Tunstead, J; Christie, A. L.; Kung, A. L.; Richardson, P; Munshi, N. C.; Anderson, K. C. (2014). "Novel afucosylated anti-B cell maturation antigen-monomethyl auristatin F antibody-drug conjugate (GSK2857916) induces potent and selective anti-multiple myeloma activity". Blood. 123 (20): 3128–38. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-10-535088. PMC 4023420. PMID 24569262.
- ^ Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN Council: Mafodotin
- ^ a b c Dosio, F.; Brusa, P.; Cattel, L. (2011). "Immunotoxins and Anticancer Drug Conjugate Assemblies: The Role of the Linkage between Components". Toxins. 3 (12): 848–883. doi:10.3390/toxins3070848. PMC 3202854. PMID 22069744.
