Mind, Self and Society
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2016) |
 | |
| Author | George Herbert Mead |
|---|---|
| Translator | Charles W. Morris |
| Language | English |
| Subject | Sociology |
| Publisher | University of Chicago Press |
Publication date | 1 December 1934 |
| Publication place | United States |
| Media type | |
| Pages | 439 pages |
| ISBN | 9780226112732 |
Mind, Self, and Society is a book based on the teaching of American sociologist George Herbert Mead's, published posthumously in 1934 by his students. It is credited as the basis for the theory of symbolic interactionism. Charles W. Morris edition of Mind, Self, and Society initiated controversies about authorship because the book was based on oral discourse and Mead's students notes.[1] Nevertheless, the compilation of his students represents Mead’s most important work in the social sciences. Among them, Mead published a conceptual view of human behaviour, interaction and organization, including various schools of thought such as role theory, folklore methodology, symbolic interactionism, cognitive sociology, action theory, and phenomenology.[2]
George H. Mead shows a psychological analysis through behavior and interaction of an individual's self with reality.[3] The behavior is mostly developed through sociological experiences and encounters. These experiences lead to individual behaviors that make up the social factors that create the communications in society.[4] Communication can be described as the comprehension of another individual's gestures. Mead explains that communication is a social act because it requires two or more people to interact.[5] He also explains that the self is a social process with communication between the "I", the pure form of self, and the "Me", the social form of self. "I" becomes a response to the "Me" and vice versa. That same "I" deals with the response of an individual and the "Me" is considered the attitudes you take on, both being related to social selves.[6]
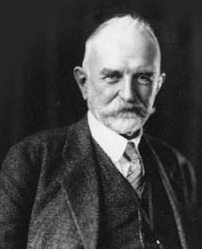
Biography
[edit]George Herbert Mead was an American philosopher. He was born on February 27, 1863, in South Hadley, Massachusetts.[7] He died on April 26, 1931, in Chicago, Illinois. George H. Mead studied at Oberlin College and Harvard University.[7] Mead was an instructor in philosophy and psychology at the University of Michigan from 1891 - 1894.[7] In 1894, Mead attended the University of Chicago as an instructor and remained there until his death. Mead was known for his work in Social Psychology and Pragmatism.[7]
George Mead's contribution to Social Psychology showed how the human self-arises in the process of social interactions.[5] Mead was a major thinker among American Pragmatists he was heavily influenced, as were most academics of the time, by the theory of relativity and the doctrine of emergence.[5] Objective relativism is the center of Mead philosophical work. Great minds such as Mead was exploited to other great philosophers such as John Dewey and Josiah Royce.[5]
Mead never published any of his work. His students edited his lectures and notes from stenographic recordings and unpublished papers and published his work after his death.[5]
Mead Work on the concept of the "I" and the "Me"
[edit]The main concept of the irony between the "I" and the "Me" is that the self is a social process.[3] It states that man or the individual is a social process, meaning that we are unfinished. This is a big question that many Sociologists today are studying. How can the self be social and yet unfinished? The book looks at this concept in the point of view of conduct and social attitudes on how the "I" and the "Me" are parts of the same whole which constitutes the self.
The "I" is the "I" and the "Me" is the "Me" they cannot be one or the other, or top each other in any way because although they are separate, and occur at different times, they work together hand-in-hand; to help individual navigate society in different circumstances we might present ourselves with.[6]
The state of the "I", the individual feels they have a position in society, that they have a certain function or privilege, yet they are not fully aware of it as in the state of the "Me" the individual is calling for a response and can organize a community in their own attitude because the "Me" is a social, reliable, and predictable self - that is conscious and has an understanding of the social norms of society. Whereas the "I" is a small pure form of the self where our existence gets to act, make a decision in a split second, and has no self - also conscious, unpredictable immediate response of the "I" is not available until after. According to the book, remembering "what you were" a minute ago, a day ago, or a year ago.
According to the book, taking in the attitude introduces the "Me" and then reacts to it as an "I". Meaning the individual is the "I" and in the split second when the decision was made the "I" becomes the "Me" and then back to the "I". It is an ironic continuous circle because the question of which one comes before the other is the same analogy as; what comes first? The chicken or the egg. Usually, the "I" is historical and comes into effect much later, the "Me" is more present and fast acting in situations. "The "I" is in a certain sense that with which we do identify ourselves.
The "I" is a response to other's attitudes while the "me" is attitudes an individual shares with other subjects. That is, the "me" is the shared beliefs and the "I" is a reaction to the beliefs of others.[8]
Construction of the book
[edit]"Mind, self, and Society" was not created by an "individual self wish without considering other social actors, available documents, and practical constraints".[9] During the construction of the book there were "several projects in place to bring Mead to greater attention".[9] According to Smith and Wright, the books were decided upon as "one Festschrift for Mead —along with the work of James H. Tufts, Addison W. Moore, and Edwards S. Ames— which had already come out in print"[9]
The book is divided among four major parts, taking the point of view of social behavior
- The Mind
- The Self
- The Society
- The Culture
See also
[edit]Articles about Mead:
- Blumer, Herbert. "Sociological Implications of the Thought of G.H. Mead," American Journal of Sociology, 71 (1966): 535-44
- Batiuk, Mary-Ellen. "Misreading Mead: Then and Now," Contemporary Sociology, 11 (1982): 138–40.
Writings by Mead:
- 1900 – "Suggestions Towards a Theory of the Philosophical Disciplines"
- 1910 – "Social Consciousness and the Consciousness of Meaning" and "The Mechanism of Social Consciousness"
- 1913 – "The Social Self"
- 1926 – "The objective Reality of Perspectives"
References
[edit]- ^ Côté, Jean-François. "Becoming Mead: The Social Process of Academic Knowledge/Mind, Self & Society: The Definitive Edition." Canadian Journal of Sociology 41, no. 1 (September 2016): 75-80.
- ^ Mead, George Herbert (12 May 2015). Mind, self & society. ISBN 978-0-226-11273-2. OCLC 1013345971.
- ^ a b Mead, George. H. (1934). Mind, Self, and Society: From the Standpoint of a Social Behaviorist. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 178.
- ^ "George Herbert Mead: Mind Self and Society: Section 1: Social Psychology and Behaviorism". www.brocku.ca. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
- ^ a b c d e "Mead, George Herbert | Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy". www.iep.utm.edu. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
- ^ a b Mead, George (1934). Mind, Self, and Society. United States of America: The University of Chicago Press. pp. 173–178. ISBN 978-0-226-51668-4.
- ^ a b c d "George Herbert Mead | American philosopher". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2016-11-02.
- ^ Mead, George H. (1934). Mind, Self, and Society. The University Of Chicago Press. p. 175.
- ^ a b c Huebner, Daniel (2014). Becoming Mead. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. pp. 115–116. ISBN 978-0-226-17140-1.
