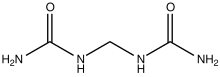
Methylene diurea
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′′-Methylenediurea | |
| Other names
methylenebis(urea), (carbamoylamino)methylurea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1812254 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.547 |
| EC Number |
|
| 694187 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H8N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 132.123 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 203 °C (397 °F; 476 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methylene diurea (MDU) is the organic compound with the formula CH2(NHC(O)NH2)2. It is a white water-soluble solid. The compound is formed by the condensation of formaldehyde with urea. Methylene diurea is the substrate for the enzyme methylenediurea deaminase.
Applications
[edit]MDU is an intermediate in the production of urea-formaldehyde resins.[1]
Together with dimethylene triurea, MDU is a component of some controlled-release fertilizers.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Steinhof, Oliver; Kibrik, Éléonore J.; Scherr, Günter; Hasse, Hans (2014). "Quantitative and qualitative1H, 13C, and15N NMR spectroscopic investigation of the urea-formaldehyde resin synthesis". Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry. 52 (4): 138–162. doi:10.1002/mrc.4044. PMID 24496721. S2CID 1457586.
- ^ Dittmar, Heinrich; Drach, Manfred; Vosskamp, Ralf; Trenkel, Martin E.; Gutser, Reinhold; Steffens, Günter (2009). "Fertilizers, 2. Types". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.n10_n01. ISBN 978-3527306732.
