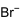Methylammonium bromide
Appearance
| |||
 Methylammonium bromide crystals
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methylazanium bromide
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methanaminium bromide | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.255 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH3NH3Br | |||
| Molar mass | 111.96904 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | White crystals [1] | ||
| Melting point | 296[2] °C (565 °F; 569 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
irritant | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Methylammonium bromide in an organic halide with the formula of CH3NH3Br. It is the salt of methylammonium and bromide. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid.
The methylammonium halides are precursors to perovskite solar cells, which are being evaluated.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ "Methylammonium bromide". Greatcell Solar Materials. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ "Sigma-Aldrich". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 5 February 2017.
- ^ Li, Hangqian. (2016). "A modified sequential deposition method for fabrication of perovskite solar cells". Solar Energy. 126: 243–251. Bibcode:2016SoEn..126..243L. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2015.12.045.